ERW Steel Pipe
ERW Steel Pipe
ERW (Electric Resistance Welded) steel pipes are a type of steel pipe that are manufactured through a welding process that employs electric resistance. ERW pipes are used in various applications due to their high quality, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here’s an overview of ERW steel pipes, their manufacturing process, applications, and benefits.
Manufacturing Process
- Raw Material:
- The manufacturing process begins with coils of steel, which are cut into strips of appropriate width.
- Forming:
- The steel strips are passed through a series of rollers to form them into a cylindrical shape.
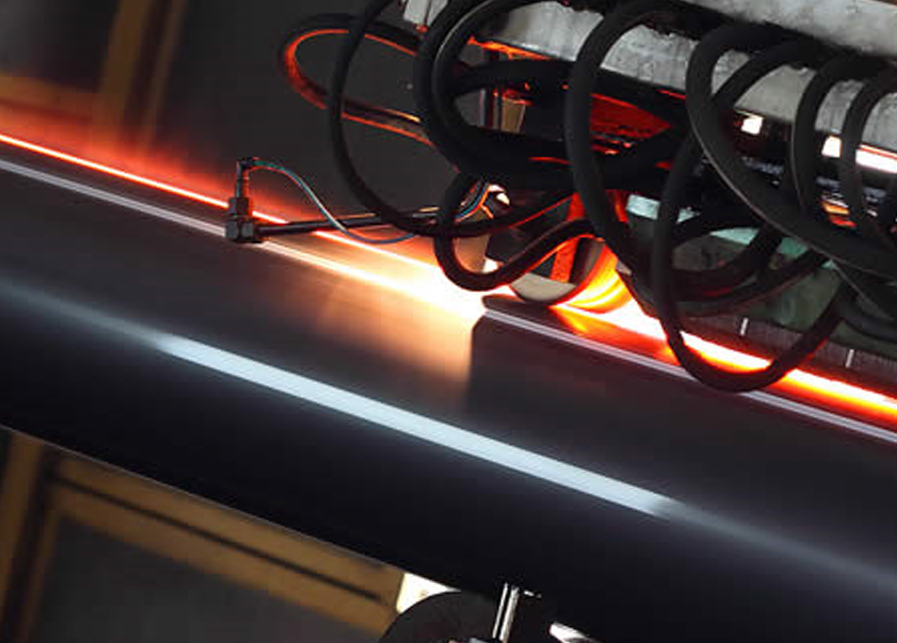
- Welding:
- The edges of the cylindrical steel strip are heated and pressed together using electric resistance welding, forming a continuous seam. Unlike other welding methods, no filler material is used.
- Finishing:
- The welded seam is then annealed (heat-treated) to remove any residual stresses from the welding process.
- The pipe is then cut to the desired length, and further finishing processes like straightening, end-facing, and coating may be applied.
- Quality Control:
- ERW pipes undergo various quality control tests, including ultrasonic testing, hydrostatic testing, and visual inspection to ensure they meet industry standards and specifications.
Outer Diameter
- Range: 1/2″ to 28″
Wall Thickness
- Range: 1.65 mm to 20 mm (All Schedules)
Length
- Range: 1 m to 12 m or as per customer requirements
Standards
- ASTM 5L
- ASTM A53
- ASTM A178
- ASTM A500/501
- ASTM A691
- ASTM A252
- ASTM A672
- EN 10217
Material Grades
- API 5L: PSL1/PSL2 Gr.A, Gr.B, X42, X46, X52, X56, X60, X65, X70
- ASTM A53: GR.A, GR.B
- EN: S275, S275JR, S355JRH, S355J2H
Pipe Ends
- Plain End
- Beveled End
- Threaded
Surface Treatment Options
- Bare
- Painted Black
- Varnished
- Galvanized
- Anti-corrosion coatings (3PE, PP/EP, FBE coating, etc.)
Manufacturing Process
- Cold Drawn
- Hot Rolled
Testing and Quality Assurance
- Chemical Component Analysis
- Mechanical Properties:
- Ultimate tensile strength
- Yield strength
- Elongation
- Technical Properties:
- Flattening Test
- Bending Test
- Hardness Test
- Impact Test
- Exterior Size Inspection
- Hydrostatic Test
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT):
- ET (Eddy Current Test)
- RT (Radiographic Test)
- UT (Ultrasonic Test)
Specification
Specification:
|
INCH
|
OD
(MM)
|
Strandard Wall Thickness
|
|||||||
|
SCH 10WT
(mm)
|
SCH 20WT
(mm)
|
SCH 40WT
(mm)
|
SCH 60WT
(mm)
|
SCH 80WT (mm) |
SCH 100WT (mm) |
SCH 160WT (mm) |
XXS (mm) |
||
|
1/4”
|
13.7
|
|
|
2.24
|
|
3.02
|
|
|
|
|
3/8”
|
17.1
|
|
|
2.31
|
|
3.2
|
|
|
|
|
1/2”
|
21.3
|
2.11
|
|
2.77
|
|
3.73
|
|
4.78
|
7.47
|
|
3/4″
|
26.7
|
2.11
|
|
2.87
|
|
3.91
|
|
5.56
|
7.82
|
|
1″
|
33.4
|
2.77
|
|
3.38
|
|
4.55
|
|
6.35
|
9.09
|
|
1-1/4″
|
42.2
|
2.77
|
|
3.56
|
|
4.85
|
|
6.35
|
9.7
|
|
1-1/2″
|
48.3
|
2.77
|
|
3.68
|
|
5.08
|
|
7.14
|
10.15
|
|
2″
|
60.3
|
2.77
|
|
3.91
|
|
5.54
|
|
8.74
|
11.07
|
|
2-1/2″
|
73
|
3.05
|
|
5.16
|
|
7.01
|
|
9.53
|
14.02
|
|
3″
|
88.9
|
3.05
|
|
5.49
|
|
7.62
|
|
11.13
|
15.24
|
|
3-1/2″
|
101.6
|
3.05
|
|
5.74
|
|
8.08
|
|
|
|
|
4″
|
114.3
|
3.05
|
4.5
|
6.02
|
|
8.56
|
|
13.49
|
17.12
|
|
5″
|
141.3
|
3.4
|
|
6.55
|
|
9.53
|
|
15.88
|
19.05
|
|
6″
|
168.3
|
3.4
|
|
7.11
|
|
10.97
|
|
18.26
|
21.95
|
|
8″
|
219.1
|
3.76
|
6.35
|
8.18
|
10.31
|
12.7
|
15.09
|
23.01
|
22.23
|
|
10″
|
273
|
4.19
|
6.35
|
9.27
|
12.7
|
15.09
|
18.26
|
28.58
|
25.4
|
|
12″
|
323.8
|
4.57
|
6.35
|
10.31
|
14.27
|
17.48
|
21.44
|
33.32
|
25.4
|
|
14″
|
355
|
6.35
|
7.92
|
11.13
|
15.09
|
19.05
|
23.83
|
36.71
|
|
|
16″
|
406
|
6.35
|
7.92
|
12.7
|
16.66
|
21.44
|
26.19
|
40.49
|
|
|
18″
|
457
|
6.35
|
7.92
|
14.27
|
19.05
|
23.83
|
29.36
|
46.24
|
|
|
20″
|
508
|
6.35
|
9.53
|
15.09
|
20.62
|
26.19
|
32.54
|
50.01
|
|
|
22″
|
559
|
6.35
|
9.53
|
|
22.23
|
28.58
|
34.93
|
54.98
|
|
|
24″
|
610
|
6.35
|
9.53
|
17.48
|
24.61
|
30.96
|
38.89
|
59.54
|
|
|
26″
|
660
|
7.92
|
12.7
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28″
|
711
|
7.92
|
12.7
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30″
|
762
|
7.92
|
12.7
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32″
|
813
|
7.92
|
12.7
|
17.48
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34″
|
863
|
7.92
|
12.7
|
17.48
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36″
|
914
|
7.92
|
12.7
|
19.05
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38″
|
965
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40″
|
1016
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
42″
|
1066
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44″
|
1117
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
46″
|
1168
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48″
|
1219
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Standard
Chemical Analysis and Mechanical Properties
| Standard | Class | Grade | Chemical Analysis(%) | Mechanical Properties(min)(Mpa) | ||||
| C | Mn | P | S | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength | |||
| API 5L | PSL1 | B | 0.26 | 1.20 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 414 | 241 |
| X42 | 0.26 | 1.30 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 414 | 290 | ||
| X46 | 0.26 | 1.40 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 434 | 317 | ||
| X52 | 0.26 | 1.40 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 455 | 359 | ||
| X56 | 0.26 | 1.40 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 490 | 386 | ||
| X60 | 0.26 | 1.40 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 517 | 414 | ||
| X65 | 0.26 | 1.45 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 531 | 448 | ||
| X70 | 0.26 | 1.65 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 565 | 483 | ||
| PSL2 | B | 0.22 | 1.20 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 414 | 241 | |
| X42 | 0.22 | 1.30 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 414 | 290 | ||
| X46 | 0.22 | 1.40 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 434 | 317 | ||
| X52 | 0.22 | 1.40 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 455 | 359 | ||
| X56 | 0.22 | 1.40 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 490 | 386 | ||
| X60 | 0.22 | 1.40 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 517 | 414 | ||
| X65 | 0.22 | 1.45 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 531 | 448 | ||
| X70 | 0.22 | 1.65 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 565 | 483 | ||
| X80 | 0.22 | 1.85 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 621 | 552 | ||
Process
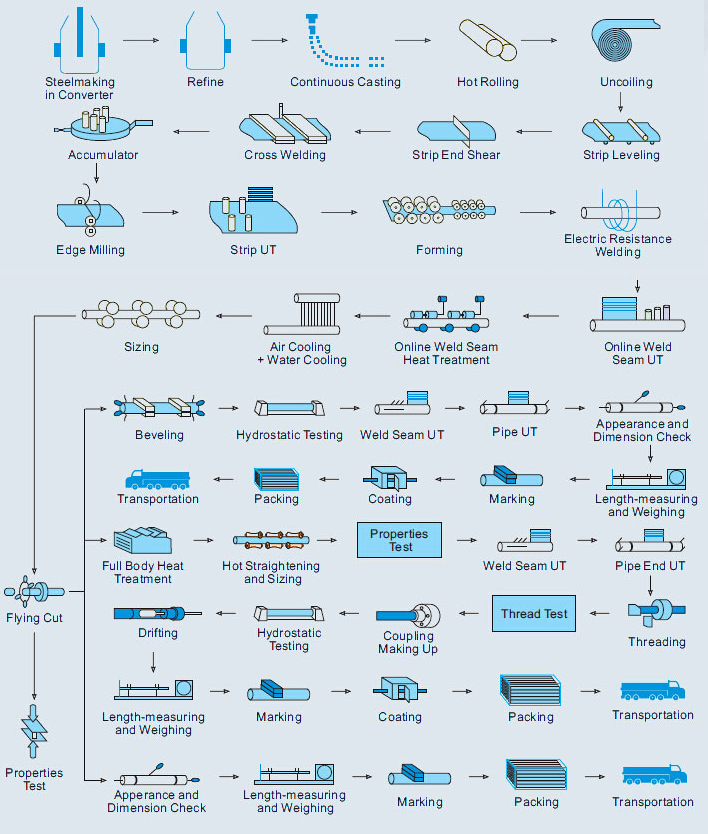
Applications
ERW steel pipes are used in a wide range of applications due to their versatility and cost-efficiency:
- Oil and Gas Industry: Transportation of oil, gas, and other fluids.
- Water Supply Systems: Pipes for potable water and sewage systems.
- Automotive Industry: Structural components, exhaust systems, and other automotive parts.
- Construction: Structural applications in buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
- Mechanical and General Engineering: Fabrication of mechanical parts and general engineering components.
Benefits
- Cost-Effective: ERW pipes are generally less expensive than seamless pipes.
- High Quality: The manufacturing process ensures a high degree of dimensional accuracy and uniformity.
- Strength and Durability: ERW pipes have good mechanical properties and are suitable for high-pressure applications.
- Versatility: Available in various sizes, thicknesses, and lengths, making them suitable for diverse applications.
- Efficiency: The ERW process is efficient, allowing for mass production with consistent quality.
Types of ERW Pipes
- Round ERW Pipes: Commonly used in fluid transportation.
- Square and Rectangular ERW Pipes: Often used in structural applications.
- Galvanized ERW Pipes: Coated with zinc to prevent corrosion, used in outdoor and harsh environments.
Standards and Specifications
ERW steel pipes are manufactured to meet various international standards and specifications, including:
- API 5L: Specification for line pipes.
- ASTM A53: Standard specification for pipe, steel, black and hot-dipped, zinc-coated, welded and seamless.
- ASTM A252: Standard specification for welded and seamless steel pipe piles.
- BS 1387: Specification for screwed and socketed steel tubes and tubulars and for plain end steel tubes suitable for welding or for screwing to BS 21 pipe threads.
Conclusion
ERW steel pipes are an essential component in various industries due to their reliability, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. Their manufacturing process ensures a high-quality product that meets stringent industry standards, making them a preferred choice for many applications.

















