PTFE Lined Pipe and Fitting
PTFE Lined Pipe and Fittings: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known by the brand name Teflon, is a high-performance plastic widely recognized for its exceptional chemical resistance and non-stick properties. When used to line pipes and fittings, PTFE provides a robust solution for industries dealing with highly corrosive or reactive fluids. This article delves into the characteristics, applications, benefits, and considerations of PTFE-lined pipes and fittings, providing a thorough understanding of their role in modern industrial processes.
Characteristics of PTFE
Chemical Resistance
PTFE is renowned for its unparalleled chemical resistance. It can withstand aggressive chemicals, including acids, bases, solvents, and oxidizers, making it suitable for handling a wide range of industrial fluids.
Thermal Stability
PTFE exhibits excellent thermal stability, maintaining its properties across a broad temperature range. It can withstand temperatures from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F), which is critical for applications involving extreme temperatures.
Low Friction and Non-Stick Properties
The low friction coefficient and non-stick nature of PTFE minimize the risk of material buildup and clogging inside pipes and fittings. This ensures smooth fluid flow and reduces maintenance requirements.
Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator, which can be advantageous in applications where electrical conductivity must be minimized or controlled.
Mechanical Strength
While PTFE itself is relatively soft and flexible, it can be reinforced with other materials to improve its mechanical strength. When used as a lining, it combines its chemical resistance with the structural integrity of the outer pipe material, such as steel.
Manufacturing of PTFE Lined Pipes and Fittings
Lining Process
The process of lining pipes and fittings with PTFE typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The inner surface of the pipe or fitting is cleaned and prepped to ensure proper adhesion of the PTFE liner.
- Liner Installation: PTFE liners can be installed using a variety of methods, including:
- Extrusion: PTFE is extruded into a tubular form and inserted into the pipe.
- Paste Extrusion: PTFE paste is extruded and then sintered inside the pipe.
- Isostatic Molding: PTFE powder is molded under high pressure and sintered to form a seamless liner.
- Sintering: The lined pipe is heated to sinter the PTFE, creating a uniform, non-porous lining.
- Quality Control: The final product undergoes rigorous testing to ensure the integrity and uniformity of the PTFE lining.
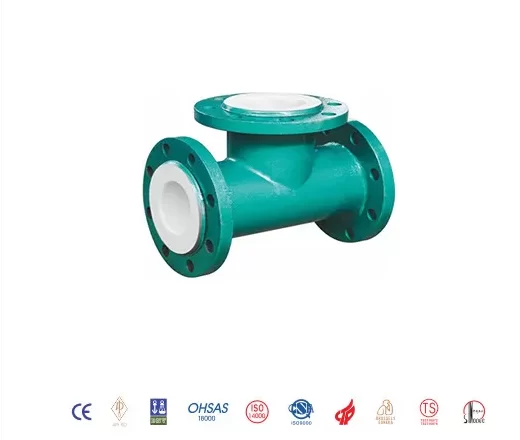
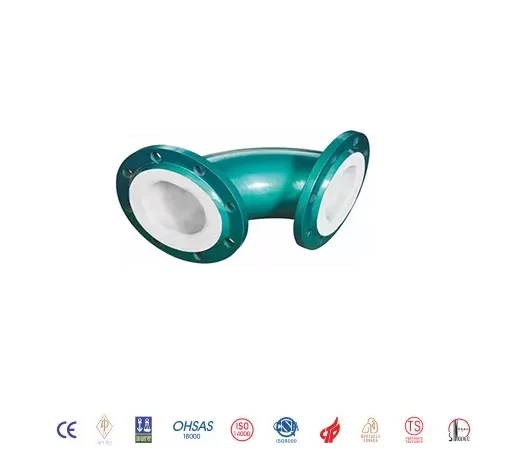
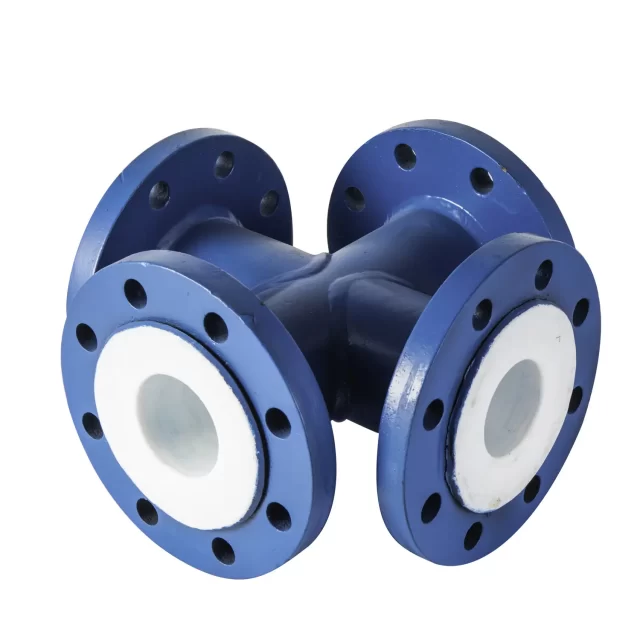
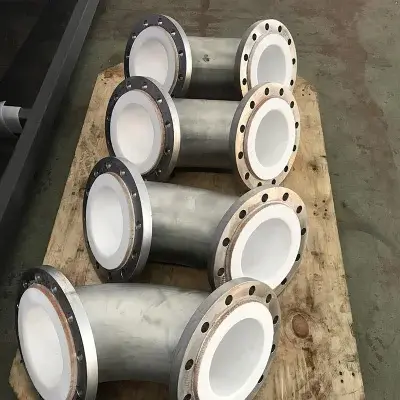
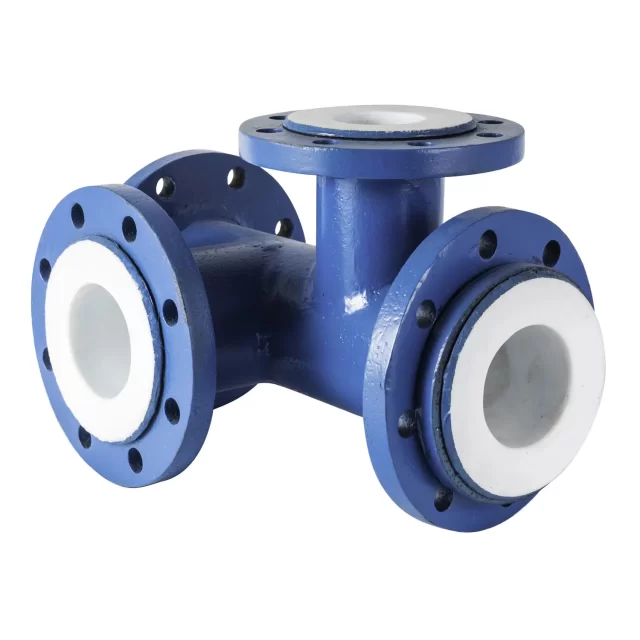
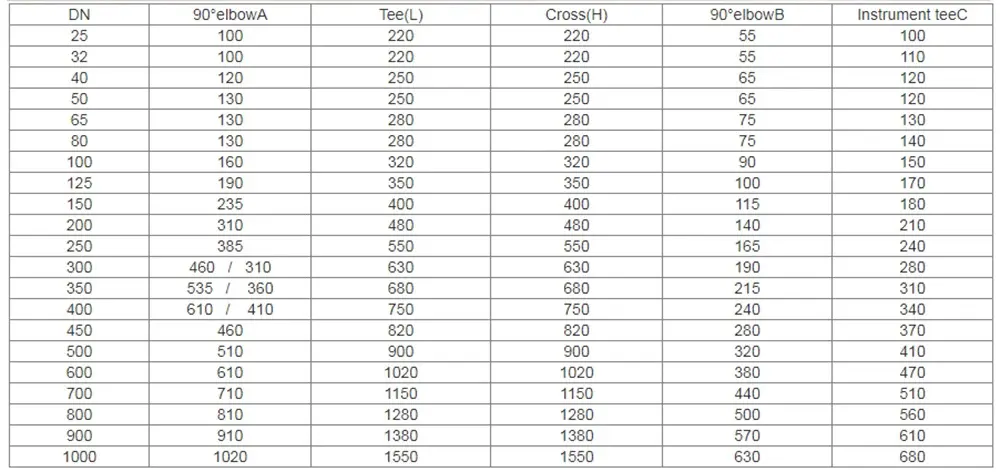
Types of PTFE Lined Fittings
PTFE lined fittings come in various types to cater to different piping configurations:
- Elbows: For changing the direction of the pipe run.
- Tees: For branching off the main pipeline.
- Reducers: For changing the pipe diameter.
- Flanges: For connecting pipes and ensuring a leak-proof seal.
- Valves: For controlling fluid flow within the system.
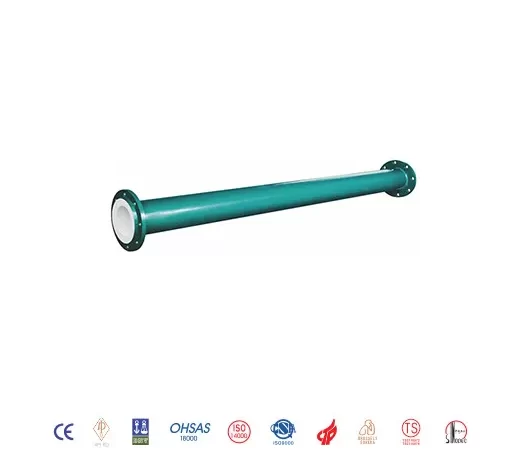
PTFE Lined Pipe Manufacturer
PTFE Lined Pipe by Ram Extrusion
PTFE lined pipes produced through ram extrusion can vary in length, with the shortest being around 100mm depending on the nominal bore, and the longest reaching up to 6 meters for diameters up to DN150. For diameters above DN150, the maximum length is typically 3 meters. These pipes are generally constructed from carbon steel, though stainless steel is also commonly used in hazardous areas where external corrosion is a concern.
Technical Specification
- Design and Manufacture Standard: ASTM F1545, HG/T 21562
- Flange Standard: ASME B16.5, HG/T 20592, DIN, JIS
- Inspection & Testing: ASTM F1545
Product Specification
- Body Material: A105, SS304, SS316, SS316L
- Lining Material: PTFE, PFA, PO
- Nominal Diameter: 1″
24″ (DN25DN600) - Pressure Range: Class 150, PN10, PN16
Product Description
Abtersteel manufactures lined pipes and fittings using various molding techniques, including compression molding, isostatic molding, injection molding, transfer molding, hot rotomolding, ram/paste extrusion, and 3D rotational molding. The key characteristics are as follows:
- Operating Temperature: The working temperature ranges from -29°C to 200°C. Apart from molten alkali metals, elemental fluorine, and aromatic hydrocarbons, these lined products can be used with any chemical medium.
- Vacuum Resistance: Suitable for vacuum conditions within the temperature range of -29°C to 150°C. This is particularly relevant in chemical production where vacuum conditions can occur due to cooling, longitudinal emissions, or medium backflow.
- High-Pressure Resistance: Can withstand working pressures of up to 3.0 MPa within the specified temperature range.
- Penetration Resistance: Utilizes high-quality PTFE to ensure high density and sufficient thickness, providing excellent anti-osmosis properties.
- Advanced Lining Process: The PTFE lining process involves synchronous hot expansion or cold shrinkage for steel components and fluorine plastic, enhancing the integrity of the lining.
- Standard Sizes: Abtersteel produces according to standards such as HG, GB, DIN, ANSI, and JIS, ensuring high interchangeability and ease of installation.
- Physical Properties:
- Specific Gravity: 2.14-2.19 g/cm³ (as per ASTM D792 test standard)
- Tensile Strength: Minimum of 20.7 MPa (as per ASTM D638 test standard)
- Elongation: Minimum of 250% (as per ASTM D638 test standard)
- Manufacture Standard: ASTM D4895. These pipes can operate under vacuum conditions up to 150°C.
PTFE lined pipes and fittings by Abtersteel offer robust solutions for handling aggressive chemicals and demanding operational environments, ensuring durability and reliability in diverse industrial applications.
Applications of PTFE Lined Pipes and Fittings
Chemical Processing
In the chemical industry, PTFE lined pipes and fittings are essential for handling corrosive substances such as acids, alkalis, and solvents. They ensure safe transport and containment of these aggressive chemicals, preventing leaks and contamination.
Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry requires materials that resist contamination and maintain purity. PTFE lined pipes and fittings are used to transport sensitive and reactive compounds, ensuring that product integrity is maintained.
Food and Beverage Industry
PTFE’s non-reactive nature makes it suitable for the food and beverage industry, where it is used in processes involving acidic or alkaline substances, as well as high-temperature applications such as steam cleaning.
Oil and Gas
The oil and gas industry uses PTFE lined pipes and fittings for transporting corrosive fluids and gases. These components are critical in offshore drilling, refining, and chemical injection processes.
Water Treatment
In water treatment facilities, PTFE lined pipes and fittings are employed to handle aggressive chemicals used in water purification and disinfection processes, including chlorine and other oxidizing agents.
Benefits of PTFE Lined Pipes and Fittings
Enhanced Corrosion Resistance
PTFE provides superior resistance to a wide variety of corrosive substances, extending the lifespan of pipes and fittings and reducing maintenance costs.
Improved Safety
By preventing leaks and contamination, PTFE lined pipes and fittings improve safety in industrial environments, protecting workers and the environment from hazardous substances.
Cost-Effectiveness
Although the initial cost of PTFE lined pipes and fittings may be higher than unlined alternatives, their durability and reduced maintenance needs result in lower total cost of ownership over time.
Versatility
PTFE lined pipes and fittings are versatile and can be used in a broad range of industries and applications, from chemical processing to food production.
Reduced Maintenance
The non-stick properties of PTFE minimize the accumulation of residues and scale within the pipes and fittings. This reduces the frequency of cleaning and maintenance, leading to lower operational costs and increased uptime for industrial processes.
Thermal and Chemical Stability
PTFE lined pipes and fittings maintain their integrity across a wide range of temperatures and chemical exposures. This stability ensures consistent performance and reliability, even in harsh operating conditions.
Considerations and Challenges
Cost
While PTFE lined pipes and fittings offer long-term benefits, the initial cost can be significantly higher compared to unlined alternatives. It’s important to weigh the upfront investment against the potential savings in maintenance and replacement costs over the lifecycle of the system.
Installation
Proper installation is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of PTFE linings. This often requires skilled labor and specialized equipment, which can add to the overall project cost. Ensuring that joints and connections are properly sealed is also essential to prevent leaks.
Mechanical Stress
PTFE, while chemically resistant, is relatively soft and can be susceptible to mechanical damage such as cuts, abrasions, and deformation under high pressure. Reinforcement and careful handling during installation and operation are necessary to maintain the integrity of the lining.
Compatibility
Not all fluids and operating conditions are compatible with PTFE. For example, PTFE can degrade when exposed to certain high-energy radiation environments or at temperatures exceeding its thermal limits. It’s essential to ensure that PTFE is suitable for the specific application in which it will be used.
Future Trends and Innovations
Advanced Composites
Research into advanced composite materials that combine PTFE with other polymers or reinforcements is ongoing. These composites aim to enhance the mechanical properties of PTFE while retaining its excellent chemical resistance, potentially expanding its range of applications.
Enhanced Installation Techniques
Innovations in installation methods, such as improved bonding techniques and automated installation processes, are being developed to reduce costs and improve the reliability of PTFE lined pipes and fittings.
Smart Monitoring
Integrating smart sensors and IoT technology into PTFE lined systems can provide real-time monitoring of conditions such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates. This data can help in predictive maintenance and early detection of potential issues, further enhancing the reliability and efficiency of industrial processes.
Sustainability
As environmental concerns grow, there is increasing interest in developing more sustainable production methods for PTFE and exploring recycling options for PTFE-lined components at the end of their service life.
Conclusion
PTFE lined pipes and fittings play a critical role in modern industrial applications, offering unmatched chemical resistance, thermal stability, and durability. Their benefits in reducing maintenance, enhancing safety, and ensuring reliable performance make them a valuable investment in sectors ranging from chemical processing to pharmaceuticals and beyond.
While the initial cost and installation challenges can be considerable, the long-term advantages often justify the investment. As technology advances, the development of new materials and installation techniques will likely further improve the performance and cost-effectiveness of PTFE lined systems.
By understanding the properties, applications, and considerations associated with PTFE lined pipes and fittings, industries can make informed decisions to enhance the efficiency, safety, and sustainability of their operations.
References
- DuPont. (2021). Teflon™ PTFE: Properties Handbook.
- American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). (2018). Standards for Piping Systems.
- International Journal of Polymer Science. (2020). Advances in PTFE Lining Technology.
- Chemical Engineering Journal. (2019). Application of PTFE Lined Pipes in Corrosive Environments.
- Society of Plastics Engineers (SPE). (2022). Innovations in Fluoropolymer Technologies.













