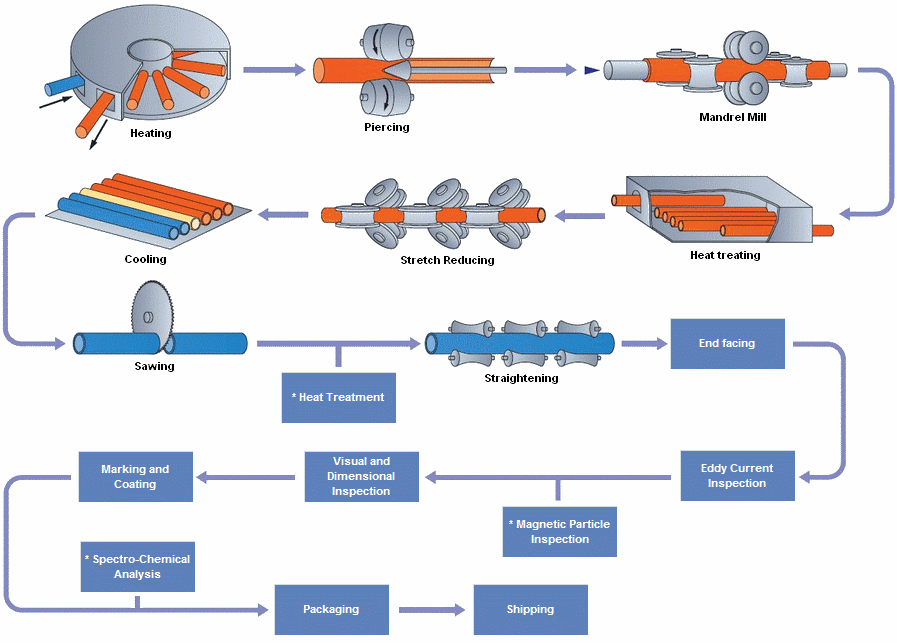
What is the difference between coating pipe and lining pipe ?
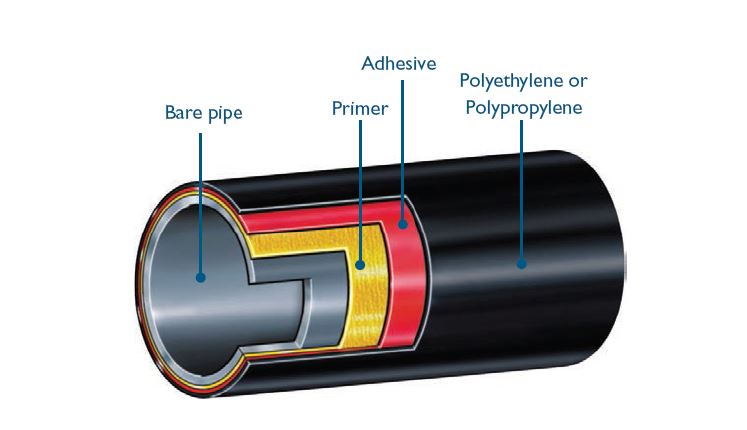
The distinction between coating and lining pipes is a significant one in the field of pipeline engineering and construction. Both processes are essential for enhancing the durability and functionality of pipes, but they serve different purposes and are applied in different contexts. In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the differences between coating and lining pipes, their applications, materials used, benefits, and the technological advancements shaping their future.
Understanding Pipe Coating and Lining
Pipe Coating and Pipe Lining are methods used to protect pipes from corrosion, abrasion, and other forms of wear and tear. They are critical in extending the lifespan of pipes and ensuring the safe and efficient transport of fluids and gases.
Pipe Coating
Pipe Coating refers to the application of a protective layer on the exterior surface of a pipe. This process is primarily aimed at protecting the pipe from external environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, and physical damage.
- Purpose: The main goal of coating is to prevent corrosion and physical damage to the pipe’s outer surface, thereby extending its service life.
- Materials Used: Common materials for pipe coating include epoxy, polyurethane, polyethylene, and fusion-bonded epoxy (FBE). Each material offers different levels of protection and is chosen based on the specific environmental conditions the pipe will face.
- Application Methods: Coatings can be applied through various methods, including spray application, brush application, or dipping. The choice of method depends on the type of coating material and the size and shape of the pipe.
- Types of Coatings:
- Fusion-Bonded Epoxy (FBE): Known for its excellent adhesion and corrosion resistance, FBE is commonly used in the oil and gas industry.
- Polyethylene Coating: Offers good moisture resistance and is often used for buried pipelines.
- Coal Tar Enamel: Provides a thick, durable coating suitable for harsh environments.
Pipe Lining
Pipe Lining, on the other hand, involves applying a protective layer to the interior surface of a pipe. This process is designed to protect the pipe from the corrosive effects of the substances being transported.
- Purpose: The primary purpose of lining is to prevent internal corrosion, reduce friction, and improve flow characteristics within the pipe.
- Materials Used: Common lining materials include cement mortar, epoxy, polyurethane, and plastic liners. The choice of material depends on the type of fluid being transported and the operating conditions.
- Application Methods: Lining can be applied using methods such as centrifugal lining, spray lining, or slip lining. Each method has its own advantages and is selected based on the specific requirements of the project.
- Types of Linings:
- Cement Mortar Lining: Commonly used in water pipelines to prevent corrosion and improve water quality.
- Epoxy Lining: Offers excellent chemical resistance and is often used in pipelines carrying aggressive chemicals.
- Polyurethane Lining: Provides a smooth surface that reduces friction and enhances flow efficiency.
Applications of Coating and Lining
Both coating and lining are used across various industries to enhance the performance and longevity of pipelines. Here are some common applications:
Pipe Coating Applications
- Oil and Gas Industry:
- Coatings are essential for protecting pipelines that transport oil and gas from corrosive environments, such as offshore and underground locations.
- Water and Wastewater:
- Coatings prevent external corrosion of pipelines used in water distribution and wastewater management systems.
- Industrial Applications:
- In industries where pipes are exposed to harsh chemicals or abrasive materials, coatings provide essential protection.
Pipe Lining Applications
- Water Supply Systems:
- Linings are used to protect the interior of water pipes from corrosion and to ensure the quality of the water being transported.
- Chemical Processing:
- Lining materials resistant to chemical attack are used in pipelines transporting aggressive chemicals.
- Sewage and Wastewater:
- Linings prevent corrosion and buildup within sewage and wastewater pipes, ensuring efficient flow and reducing maintenance needs.
Benefits of Coating and Lining
Both coating and lining offer numerous benefits that contribute to the efficiency and longevity of pipeline systems:
Benefits of Pipe Coating
- Corrosion Protection:
- Coatings provide a barrier that prevents moisture and corrosive substances from reaching the pipe’s surface.
- Physical Protection:
- Coatings protect pipes from physical damage during handling, transportation, and installation.
- Extended Lifespan:
- By preventing corrosion and damage, coatings significantly extend the service life of pipelines.
- Cost Savings:
- Reduced maintenance and replacement costs result from the enhanced durability provided by coatings.
Benefits of Pipe Lining
- Internal Corrosion Resistance:
- Linings protect the interior surface of pipes from corrosive substances, ensuring long-term integrity.
- Improved Flow Efficiency:
- Smooth lining surfaces reduce friction, enhancing the flow efficiency of fluids through the pipe.
- Enhanced Safety:
- By preventing leaks and contamination, linings contribute to the safe transport of hazardous substances.
- Reduced Maintenance:
- Linings minimize the buildup of deposits and corrosion, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and cleaning.
Technological Advancements
The fields of pipe coating and lining have seen significant technological advancements, improving the effectiveness and efficiency of these protective measures:
- Advanced Materials:
- The development of new materials, such as high-performance polymers and nanocomposites, offers enhanced protection and durability.
- Innovative Application Techniques:
- Techniques such as robotic application and automated spray systems improve the precision and consistency of coating and lining applications.
- Smart Coatings and Linings:
- Research into smart materials that can self-heal or indicate damage is ongoing, offering the potential for even greater protection and longevity.
- Environmental Considerations:
- Advances in environmentally friendly materials and processes are reducing the environmental impact of coating and lining applications.