Difference Between High Nickel Steel Alloys Pipe

Difference Between Seamless High Nickel Steel Alloys Pipe and High Nickel Steel Welded Alloys Pipes
Introduction
High nickel alloy pipes are essential in industries that demand materials with exceptional corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, and durability. These pipes are widely used in applications such as chemical processing, aerospace, power generation, and oil and gas. When selecting high nickel alloy pipes, one of the most critical decisions is choosing between seamless and welded pipes.
In this article, we will explore the differences between seamless high nickel steel alloy pipes and welded high nickel steel alloy pipes, focusing on their manufacturing processes, properties, applications, and advantages. We will also discuss specific high nickel alloys such as X-750 Nickel Alloy Tubing, Nickel Alloy 600 Tubing, and Nickel Alloy 52 Tubing.

Normally, nickel content is limited to 8-11% in most 300 series stainless steels, but in the alloys below it represents a much larger percentage of the components in each respective alloy.
Each of the high nickel alloys described below has unique characteristics which should be considered prior to purchase.
abtersteel can form tubing in these alloys to sizes and tolerances within our manufacturable range.
All of our nickel alloy tubing is welded and drawn to size, custom manufactured to your specifications, and can be manufactured in tube lengths up to 30’. Gauge information regarding tubing sizes is available.
What Are High Nickel Alloys?
High nickel alloys are materials that contain a significant percentage of nickel along with other elements such as chromium, iron, molybdenum, and copper. These alloys are known for their excellent resistance to corrosion, oxidation, and high temperatures, making them ideal for use in harsh environments.
Some common high nickel alloys include:
- Inconel X-750: A nickel-chromium alloy known for its high strength and oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures.
- Nickel Alloy 600: A nickel-chromium alloy with excellent resistance to corrosion and heat, commonly used in chemical and nuclear industries.
- Nickel Alloy 52: A nickel-iron alloy with controlled thermal expansion properties, often used in electronic and aerospace applications.
These alloys are typically available in both seamless and welded pipe forms, each with distinct characteristics.
Seamless High Nickel Steel Alloy Pipes
Manufacturing Process
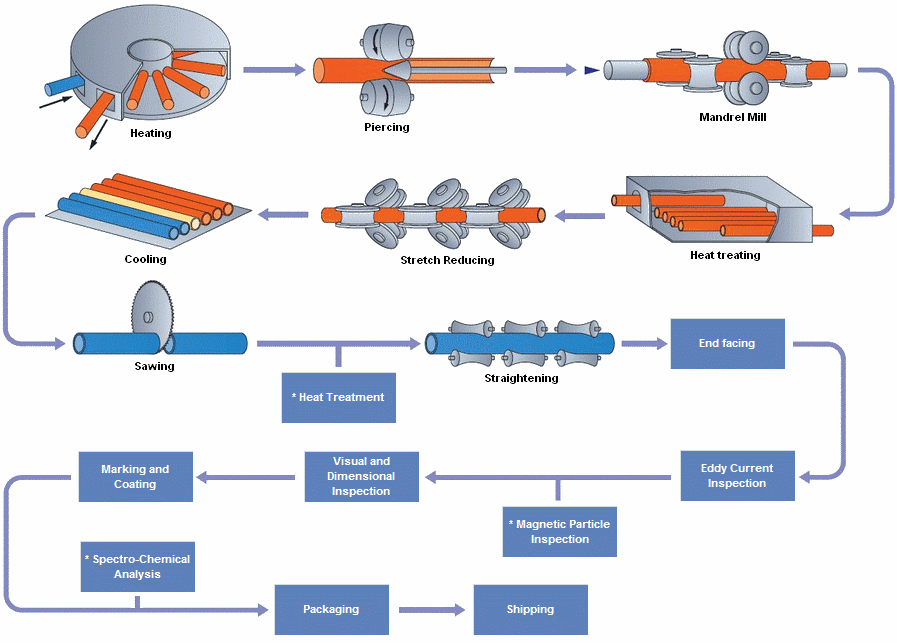
Seamless pipes are manufactured without any welding or joints. The process involves:
- Extrusion or Piercing: A solid billet of high nickel alloy is heated and pierced to create a hollow tube.
- Rolling: The hollow tube is then rolled and stretched to achieve the desired diameter and wall thickness.
- Finishing: The pipe is heat-treated, straightened, and cut to the required length.
Since there are no welds or seams in seamless pipes, they are considered to have a more uniform structure and higher strength.
Properties of Seamless High Nickel Steel Alloy Pipes
- Higher Strength: Seamless pipes generally have higher tensile strength and pressure ratings due to the absence of welded joints.
- Uniform Structure: The absence of welds ensures a uniform grain structure, enhancing mechanical properties.
- Better Resistance to Corrosion and Pressure: Seamless pipes are better suited for high-pressure and high-corrosion environments due to their uniformity and strength.
- Higher Cost: The manufacturing process for seamless pipes is more complex and costly, making them more expensive than welded pipes.
Applications of Seamless High Nickel Steel Alloy Pipes
Seamless high nickel alloy pipes are used in applications where strength, uniformity, and resistance to high pressure and temperature are critical. Common applications include:
- Aerospace: For high-temperature components such as exhaust systems and turbine blades.
- Chemical Processing: For handling corrosive chemicals and high-pressure fluids.
- Nuclear Power: For reactor components and heat exchangers.
- Oil and Gas: For high-pressure pipelines and offshore drilling equipment.
Advantages of Seamless High Nickel Steel Alloy Pipes
- No Welds or Seams: Seamless pipes are free from welding joints, eliminating weak points or defects at the weld.
- Higher Pressure Tolerance: Seamless pipes can withstand higher pressures, making them suitable for critical applications.
- Better Corrosion Resistance: The uniform structure of seamless pipes provides better resistance to corrosion, especially in aggressive environments.
- Longer Lifespan: Due to their strength and resistance to defects, seamless pipes tend to have a longer service life.
Welded High Nickel Steel Alloy Pipes
Manufacturing Process
Welded pipes are manufactured by forming a flat sheet or strip of high nickel alloy into a cylindrical shape and then welding the edges together. The process involves:
- Forming: A flat sheet or strip of high nickel alloy is bent into the shape of a pipe.
- Welding: The edges of the sheet are welded together using techniques such as electric resistance welding (ERW) or fusion welding.
- Finishing: The welded pipe is heat-treated, straightened, and cut to the required length. The weld seam is often tested and inspected to ensure it meets the required standards.
Properties of Welded High Nickel Steel Alloy Pipes
- Lower Cost: Welded pipes are generally less expensive than seamless pipes because the manufacturing process is simpler and less labor-intensive.
- Welded Joint: The presence of a weld seam can be a potential weak point, especially in high-pressure applications. However, modern welding techniques can produce high-quality welds with minimal defects.
- Good for Large Diameters: Welded pipes are more suitable for larger diameters, as it is easier to form and weld large sheets of material than to manufacture large seamless pipes.
- Slightly Lower Strength: Welded pipes may have slightly lower strength compared to seamless pipes, especially if the weld seam is not properly inspected or treated.
Applications of Welded High Nickel Steel Alloy Pipes
Welded high nickel alloy pipes are used in applications where cost is a concern, and the operating conditions do not require the high strength or pressure tolerance of seamless pipes. Common applications include:
- Low to Medium Pressure Systems: For transporting fluids and gases at lower pressures.
- Structural Applications: For use in construction and architectural projects where high strength is not critical.
- Heat Exchangers: For transferring heat in systems where the pressure is moderate.
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: For piping systems that handle corrosive fluids at moderate pressures.
Advantages of Welded High Nickel Steel Alloy Pipes
- Cost-Effective: Welded pipes are generally more affordable than seamless pipes due to the simpler manufacturing process.
- Availability in Larger Sizes: Welded pipes are more readily available in larger diameters, making them suitable for large-scale projects.
- Custom Lengths: Welded pipes can be produced in longer lengths, reducing the need for joints and fittings in long pipelines.
- Good for Non-Critical Applications: Welded pipes are suitable for applications where extreme pressure and temperature resistance are not required.
Key Differences Between Seamless and Welded High Nickel Steel Alloy Pipes
| Feature | Seamless Pipes | Welded Pipes |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Made from a solid billet, no welding involved | Made from flat sheets or strips, edges welded together |
| Strength | Higher strength due to the absence of welds | Slightly lower strength due to the presence of a weld seam |
| Pressure Tolerance | Better suited for high-pressure applications | Suitable for low to medium pressure applications |
| Corrosion Resistance | Uniform structure provides better corrosion resistance | Slightly lower resistance at the weld seam |
| Cost | More expensive due to complex manufacturing | More cost-effective due to simpler manufacturing |
| Size Availability | Limited to smaller diameters | Readily available in larger diameters |
| Applications | Critical applications (high pressure, high temperature) | Non-critical applications (moderate pressure, structural) |
| Lifespan | Longer lifespan due to higher strength and uniformity | Shorter lifespan in high-stress environments |
High Nickel Alloys: X-750, Nickel Alloy 600, and Nickel Alloy 52
1. X-750 Nickel Alloy Tubing
Inconel X-750 is a nickel-chromium alloy known for its excellent creep resistance, oxidation resistance, and high-temperature strength. It is commonly used in aerospace, gas turbines, and nuclear reactors.
- Seamless X-750 Tubing: Ideal for high-temperature applications where uniformity and strength are critical.
- Welded X-750 Tubing: Suitable for less critical applications where cost and size flexibility are more important.
2. Nickel Alloy 600 Tubing
Nickel Alloy 600 is a nickel-chromium alloy with excellent resistance to oxidation, corrosion, and high temperatures. It is widely used in chemical processing, nuclear reactors, and heat exchangers.
- Seamless Nickel Alloy 600 Tubing: Preferred for high-pressure, high-temperature environments such as reactors and heat exchangers.
- Welded Nickel Alloy 600 Tubing: Used in applications where moderate pressure and temperature resistance are sufficient.
3. Nickel Alloy 52 Tubing
Nickel Alloy 52 is a nickel-iron alloy with controlled thermal expansion properties, making it ideal for electronic and aerospace applications.
- Seamless Nickel Alloy 52 Tubing: Used in precision applications where thermal expansion control is critical.
- Welded Nickel Alloy 52 Tubing: Suitable for larger-scale applications where precision is less critical but cost is a concern.
Conclusion
Both seamless and welded high nickel steel alloy pipes have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of your application.
- Seamless pipes are ideal for applications that require high strength, pressure tolerance, and corrosion resistance, such as in the aerospace, chemical processing, and nuclear industries. However, they are more expensive and may be limited in size.
- Welded pipes, on the other hand, are more cost-effective and available in larger diameters, making them suitable for structural applications, low to medium pressure systems, and heat exchangers. While welded pipes may have slightly lower strength, modern welding techniques can produce high-quality pipes that meet the needs of many industrial applications.