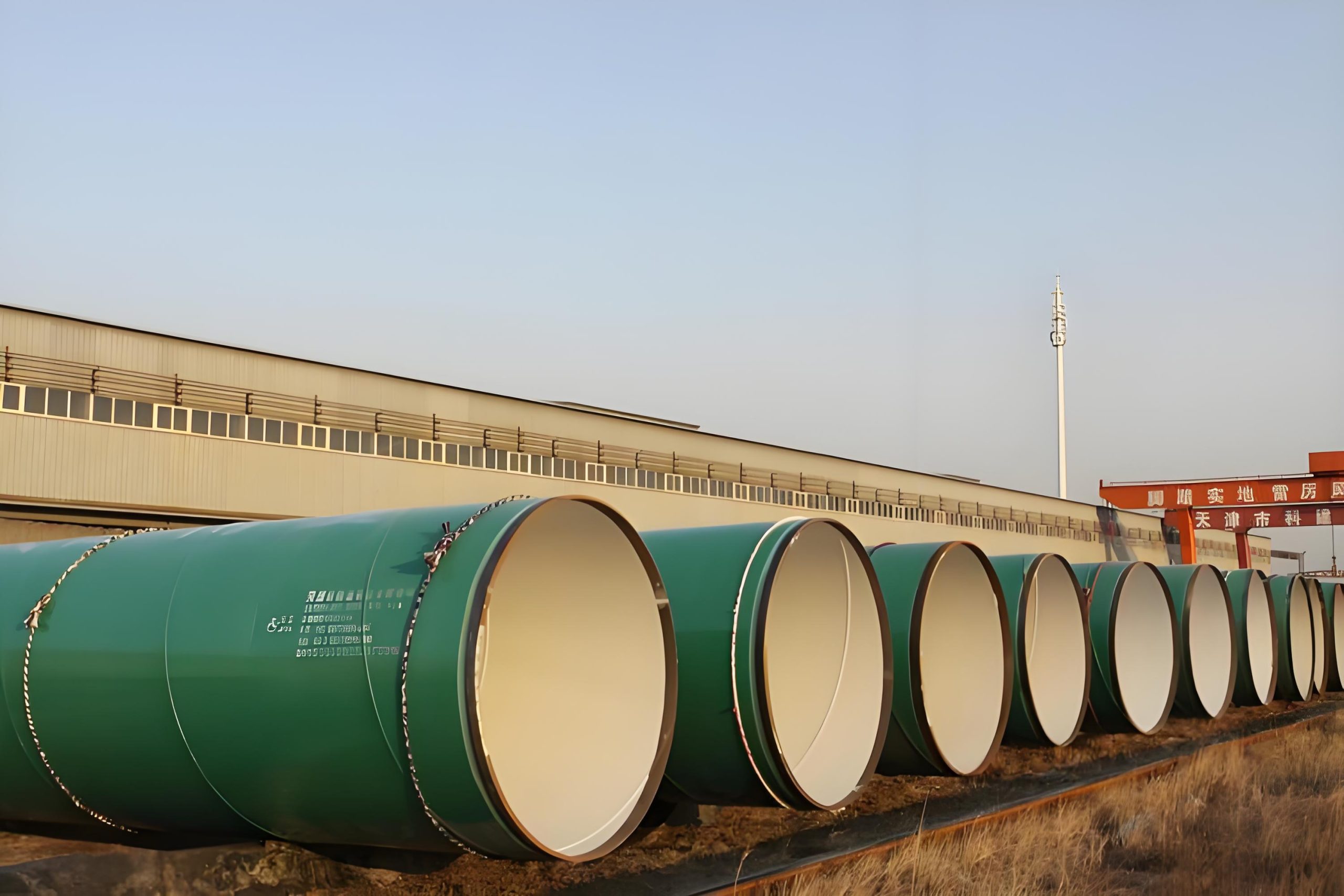
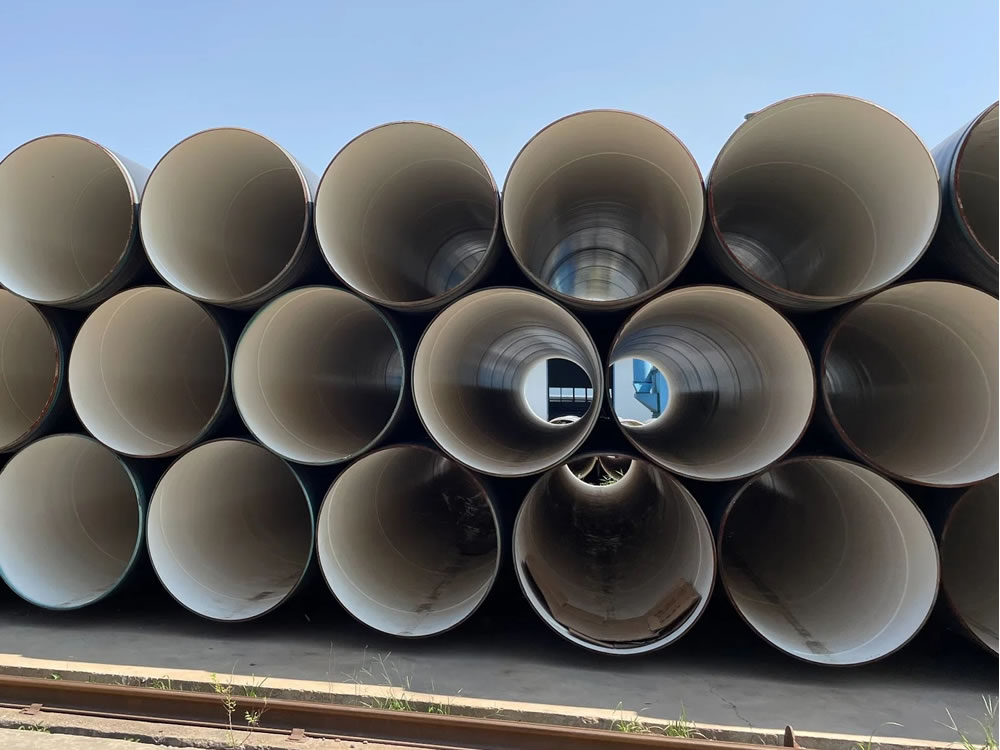
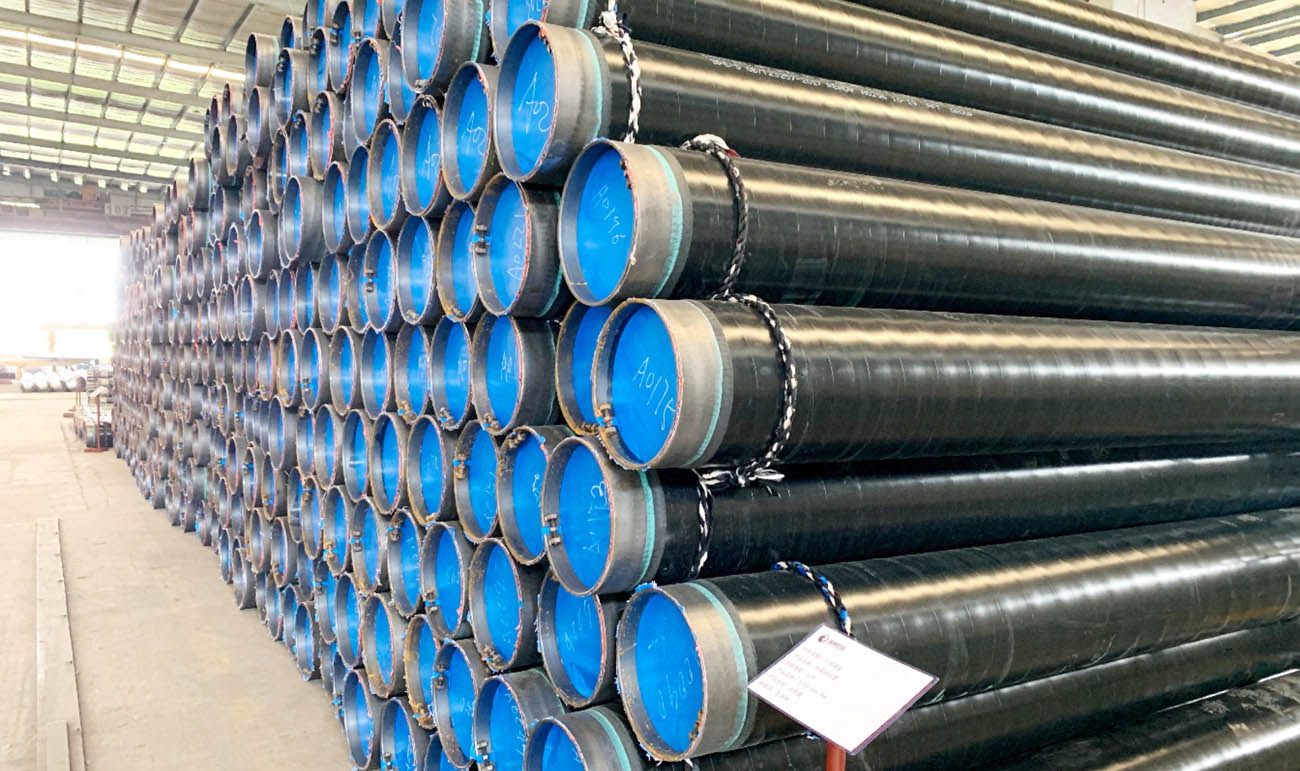
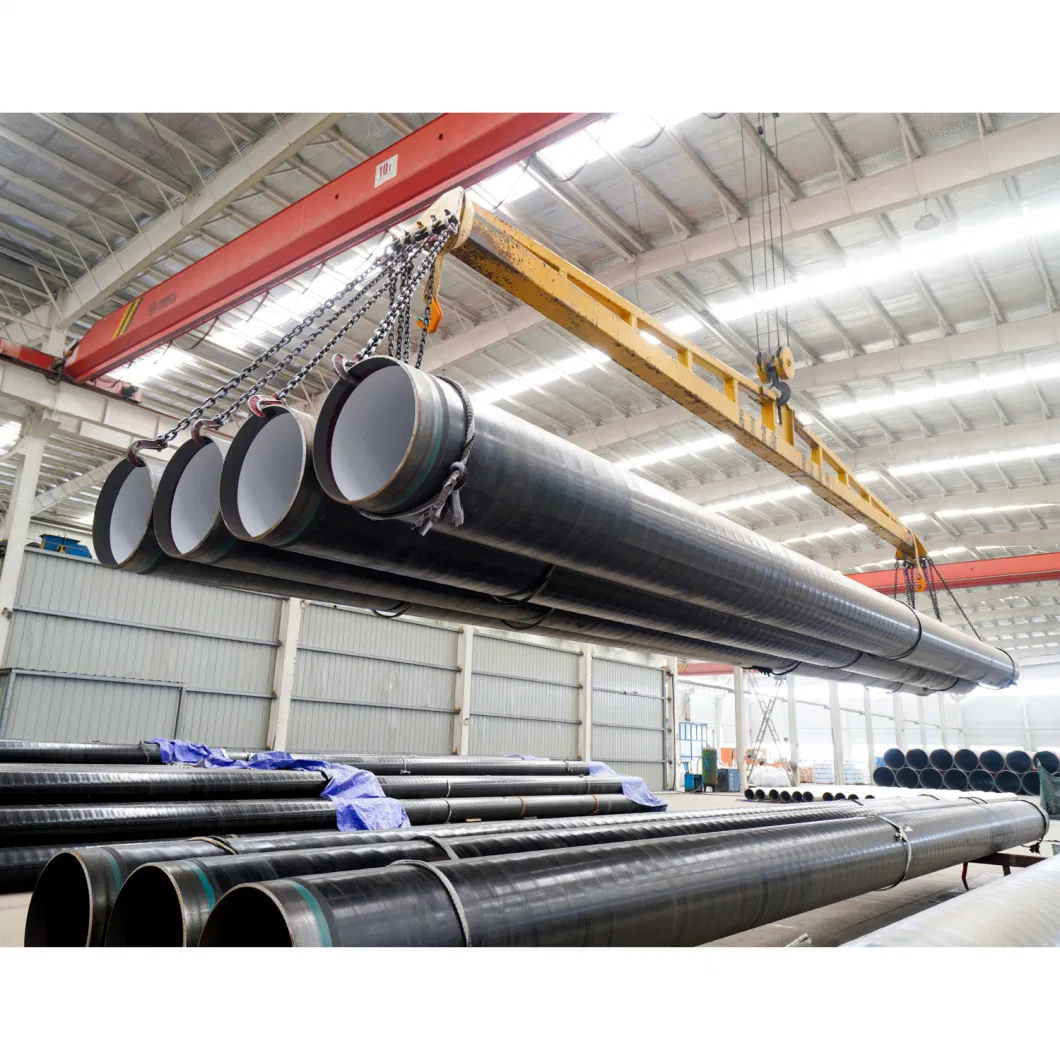
Epoxy Coating Lining Steel Pipe

Epoxy Coating Lining Steel Pipe
| Main Headings | Subheadings |
|---|---|
| H1: Introduction to Epoxy Coating Lining Steel Pipe | – Definition and Overview of Epoxy-Coated Pipes |
| – Importance of Epoxy Coating for Steel Pipes | |
| H2: Understanding Epoxy Coating and Lining | – What Is Epoxy Coating? |
| – Types of Epoxy Coatings: Fusion-Bonded and Liquid Epoxy | |
| – Difference Between External Coating and Internal Lining | |
| H2: Types of Steel Pipes for Epoxy Coating | – Spiral Submerged Arc Welded (SSAW/SAWH) Steel Pipes |
| – Key Features of SSAW Pipes | |
| – Other Pipe Types (ERW, LSAW, Seamless) | |
| H2: Key Standards for Epoxy-Coated Steel Pipes | – ANSI/AWWA C213: Fusion Bonded Epoxy for Water Pipes |
| – ISO 21809-2: Coatings for Buried or Submerged Pipelines | |
| – API RP 5L9: External Fusion-Bonded Coating Standards | |
| – API RP 5L2: Internal Coating for Non-Corrosive Gas | |
| – AS 3862: Australian Standards for Fusion-Bonded Epoxy | |
| H2: The Epoxy Coating Process | – Surface Preparation Techniques (Blasting and Cleaning) |
| – Fusion-Bonded Epoxy (FBE) Application | |
| – Curing and Inspection of Epoxy Coatings | |
| H2: Properties and Benefits of Epoxy Coatings | – Corrosion Resistance |
| – Chemical and Abrasion Resistance | |
| – Longevity and Low Maintenance | |
| – Improved Flow Efficiency | |
| H2: Applications of Epoxy-Coated Steel Pipes | – Dredging Pipe Systems |
| – Water Supply Systems | |
| – Drainage and Sewer Systems | |
| – Oil and Gas Pipelines | |
| H2: Epoxy Coating in Water Supply Systems | – Why Epoxy Coating Is Critical for Water Pipelines |
| – Ensuring Water Quality and Safety | |
| – Case Study: Epoxy-Coated Pipes in Municipal Water Systems | |
| H2: Challenges in Epoxy Coating Application | – Surface Preparation Issues |
| – Coating Defects and Remedies | |
| – Environmental and Temperature Constraints | |
| H2: Comparison of Epoxy Coating with Other Coating Methods | – Epoxy vs Polyurethane Coating |
| – Epoxy vs Galvanized Coating | |
| – Epoxy vs Cement Mortar Lining | |
| H2: Inspection and Quality Control | – Coating Thickness Measurement |
| – Adhesion and Bond Strength Testing | |
| – Holiday Testing for Coating Defects | |
| H2: Maintenance and Repair of Epoxy Coatings | – Routine Inspection of Coated Pipelines |
| – Common Damage and Repair Techniques | |
| – Preventive Maintenance Tips | |
| H2: Cost Factors for Epoxy-Coated Steel Pipes | – Material and Labor Costs |
| – Factors Affecting Coating Costs | |
| – Cost Efficiency Over the Pipe Lifecycle | |
| H2: Environmental Impact of Epoxy-Coated Pipes | – Sustainability and Reduced Leakage |
| – Compliance with Environmental Standards | |
| H2: Buying Guide for Epoxy-Coated Steel Pipes | – Choosing the Right Standard and Specification |
| – Selecting the Correct Pipe Type for Your Application | |
| – Evaluating Manufacturer Quality | |
| H2: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) | – What Is Fusion-Bonded Epoxy Coating? |
| – What Applications Require Epoxy-Coated Steel Pipes? | |
| – How Durable Is Epoxy Coating for Pipelines? | |
| – How Is Coating Thickness Tested? | |
| – What Are the Key Standards for Epoxy Coating? | |
| H2: Conclusion | – Summary of Epoxy-Coated Steel Pipe Benefits |
| – Final Thoughts on Epoxy Coating Technology |
Long-Form Article on Epoxy Coating Lining Steel Pipe
H1: Introduction to Epoxy Coating Lining Steel Pipe
Epoxy coating-lined steel pipes are widely used in industrial and municipal piping systems, particularly for water supply, drainage, and dredging operations. Epoxy coatings provide a protective layer that enhances the durability and longevity of steel pipes by offering resistance to corrosion, abrasion, and chemical damage.
In sectors such as water infrastructure, oil and gas pipelines, and sewer systems, epoxy-coated pipes are preferred for their superior performance under harsh environmental conditions. The combination of steel strength and epoxy protection ensures safe and efficient fluid transportation.
H2: Understanding Epoxy Coating and Lining
What Is Epoxy Coating?
Epoxy coating is a polymer-based material applied as a thin, protective layer on steel pipes. It creates a barrier between the steel surface and corrosive elements, preventing rust and extending the pipe’s life.
Types of Epoxy Coatings
- Fusion-Bonded Epoxy (FBE):
- Applied as a powder and fused to the steel surface using heat.
- Common for external coatings of buried and submerged pipelines.
- Liquid Epoxy Coating:
- Applied as a liquid for internal linings to provide corrosion resistance.
Difference Between External Coating and Internal Lining
- External Coating: Protects the pipeline from soil, water, and external abrasions.
- Internal Lining: Prevents corrosion caused by transported fluids (e.g., potable water, sewage).
H2: Types of Steel Pipes for Epoxy Coating
Spiral Submerged Arc Welded Steel Pipe (SSAW/SAWH)
SSAW pipes are made by spirally welding steel plates, offering a cost-effective solution for large-diameter pipelines.
Key Features of SSAW Pipes
- Ideal for transporting water, oil, and gas.
- High strength and flexibility for dredging and drainage pipelines.
- Cost-effective manufacturing for large-diameter applications.
Other Pipe Types
- ERW Pipes (Electric Resistance Welded)
- LSAW Pipes (Longitudinal Submerged Arc Welded)
- Seamless Pipes
H2: Key Standards for Epoxy-Coated Steel Pipes
Epoxy-coated pipes comply with the following international standards:
- ANSI/AWWA C213: Fusion Bonded Epoxy Coatings and Linings for Water Pipes.
- ISO 21809-2: External Coatings for Buried or Submerged Pipelines in Petroleum and Gas Systems.
- API RP 5L9: External Fusion Bonded Epoxy Coating of Line Pipes.
- API RP 5L2: Internal Coating for Non-Corrosive Gas Transmission.
- AS 3862: Australian Standard for External FBE Coating of Steel Pipes.
H2: The Epoxy Coating Process
- Surface Preparation:
- Steel surfaces are blasted to remove rust, dirt, and contaminants.
- Surface roughness ensures strong adhesion of the epoxy coating.
- Fusion-Bonded Epoxy Application:
- The epoxy powder is sprayed onto the heated pipe surface.
- The powder melts and fuses, forming a uniform protective layer.
- Curing and Inspection:
- The coating is cured at high temperatures for maximum adhesion.
- Quality tests like holiday detection ensure defect-free coatings.
H2: Properties and Benefits of Epoxy Coatings
- Corrosion Resistance: Prevents rust and chemical degradation.
- Chemical Resistance: Withstands acids, alkalis, and corrosive fluids.
- Abrasion Resistance: Ideal for dredging pipes exposed to sediments.
- Improved Flow Efficiency: Smooth internal lining reduces friction and enhances fluid flow.
- Longevity: Extends the lifespan of steel pipes, reducing maintenance costs.
H2: Applications of Epoxy-Coated Steel Pipes
- Dredging Pipe Systems:
- Used for transporting slurry and sediments in dredging projects.
- Water Supply Systems:
- Ensures clean, corrosion-free water transportation.
- Drainage and Sewer Systems:
- Protects pipes from wastewater chemicals.
- Oil and Gas Pipelines:
- Ideal for buried and submerged pipelines exposed to corrosive soil and fluids.
H2: Comparison of Epoxy Coating with Other Coating Methods
| Coating Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Epoxy Coating | Corrosion-resistant, cost-effective | Limited temperature resistance |
| Polyurethane Coating | Flexible and UV-resistant | Higher cost |
| Galvanized Coating | Affordable for small pipes | Not suitable for aggressive fluids |
| Cement Mortar Lining | Resistant to mechanical damage | Heavy and prone to cracking |
H2: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What Is Fusion-Bonded Epoxy Coating?
FBE is a powder coating applied to steel pipes and fused at high temperatures for corrosion protection.
2. What Applications Require Epoxy-Coated Steel Pipes?
Water supply, dredging, oil and gas pipelines, and drainage systems.
3. How Durable Is Epoxy Coating for Pipelines?
Epoxy coatings can last 20-30 years with proper maintenance.
4. How Is Coating Thickness Tested?
Using magnetic gauges and ultrasonic thickness measurement tools.
5. What Are the Key Standards for Epoxy Coating?
ANSI/AWWA C213, ISO 21809-2, and API RP 5L9.
H2: Inspection and Quality Control
Ensuring the quality of epoxy-coated steel pipes requires rigorous testing and inspection throughout the coating process. The following methods are employed to confirm compliance with international standards:
1. Surface Preparation Inspection
- Objective: Verify cleanliness and roughness of the steel surface before coating.
- Tools Used:
- Visual Inspection for contaminants.
- Surface Profile Gauges to measure roughness.
- ISO 8501 or NACE Standards are used as references.
2. Coating Thickness Measurement
- Objective: Ensure uniform coating thickness to meet design requirements.
- Tools Used:
- Magnetic Thickness Gauges for external coatings.
- Ultrasonic Gauges for internal lining measurements.
- Standards: Compliance with ANSI/AWWA C213 or ISO 21809-2 thickness guidelines.
3. Adhesion Testing
- Objective: Confirm strong bonding between the epoxy and steel substrate.
- Methods Used:
- Pull-Off Test (ASTM D4541): Measures the force needed to detach the coating.
- Cross-Hatch Adhesion Test: Evaluates the coating’s adhesion strength.
4. Holiday Testing (Pin-Hole Detection)
- Objective: Detect defects such as pinholes or voids in the coating.
- Tools Used:
- Holiday Detectors using a low-voltage or high-voltage spark test.
- Standards: Follow NACE RP0188 guidelines for defect detection.
5. Curing Verification
- Objective: Confirm that the epoxy coating has cured completely.
- Techniques: Infrared thermometers or cure test strips to verify heat treatment levels.
Summary Table of Inspection Tests
| Inspection Type | Objective | Tools/Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Preparation | Cleanliness and roughness of steel | ISO 8501, Surface Gauges |
| Coating Thickness | Uniform thickness validation | Magnetic and Ultrasonic Gauges |
| Adhesion Testing | Bond strength verification | Pull-Off Test, Cross-Hatch Test |
| Holiday Testing | Detect coating defects | Holiday Detectors, NACE RP0188 |
| Curing Verification | Proper epoxy curing | Infrared Thermometers |
H2: Maintenance and Repair of Epoxy Coatings
Epoxy-coated steel pipes require periodic maintenance to maximize their service life and efficiency. Maintenance practices include routine inspections, damage detection, and timely repairs.
Routine Inspection
- Conduct visual inspections for signs of corrosion, damage, or defects.
- Use holiday detection periodically to ensure the coating remains intact.
Common Damage and Repair Techniques
| Type of Damage | Cause | Repair Technique |
|---|---|---|
| Pinholes or Voids | Improper application or curing | Reapply liquid epoxy in affected areas. |
| Coating Delamination | Poor adhesion or mechanical damage | Abrasive blasting and re-coating. |
| Abrasion or Wear | Sediment flow in dredging systems | Apply a thicker layer of epoxy. |
Preventive Maintenance Tips
- Avoid excessive mechanical impacts during transportation or installation.
- Use protective sleeves to minimize abrasion in high-wear environments.
- Perform regular pressure and holiday tests to detect early signs of failure.
H2: Cost Factors for Epoxy-Coated Steel Pipes
The cost of epoxy-coated steel pipes depends on several factors, including material selection, coating method, and application environment.
Key Cost Factors
- Material Costs
- Base Pipe Material (e.g., SSAW, LSAW, or seamless pipes).
- Epoxy Coating Materials (Fusion-bonded epoxy powders or liquid epoxy).
- Coating Process
- Fusion-Bonded Epoxy (FBE) costs more due to its thermal curing process.
- Liquid epoxy coatings are generally less expensive for internal linings.
- Surface Preparation
- Blasting and cleaning costs depend on pipeline size and surface conditions.
- Pipe Size and Thickness
- Larger diameters and thicker coatings result in higher costs.
- Labor and Inspection
- Skilled labor for coating application and quality control adds to the overall expense.
Cost Efficiency Over Lifecycle
While the initial cost of epoxy-coated steel pipes may be higher than uncoated alternatives, their durability and low maintenance reduce long-term operating costs significantly.
H2: Environmental Impact of Epoxy-Coated Pipes
Epoxy-coated steel pipes contribute to environmental sustainability by:
- Reducing Pipeline Leaks
- The corrosion-resistant layer prevents leaks that could contaminate water sources and soil.
- Improving Energy Efficiency
- Smooth internal linings reduce friction losses, lowering pumping energy costs.
- Longer Lifespan
- Extends the service life of pipelines, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Compliance with Environmental Standards
- Meets international environmental standards such as ISO 21809-2 and ANSI/AWWA C213.
H2: Buying Guide for Epoxy-Coated Steel Pipes
When purchasing epoxy-coated steel pipes, consider the following factors to ensure quality and performance:
- Choose the Right Standard
- For water supply systems: ANSI/AWWA C213.
- For oil and gas pipelines: ISO 21809-2 or API RP 5L9.
- Select the Proper Pipe Type
- For large-diameter pipelines: Spiral Submerged Arc Welded (SSAW).
- For smaller diameters: ERW or seamless pipes.
- Evaluate Manufacturer Quality
- Ensure compliance with standards and request quality certificates.
- Ask for inspection and testing reports (e.g., adhesion, thickness, holiday testing).
- Check Application Compatibility
- Verify that the coating type suits your pipeline’s operating environment.
- Compare Costs and Lifespan
- Consider lifecycle costs, not just upfront prices.
H2: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What Is Fusion-Bonded Epoxy Coating?
Fusion-Bonded Epoxy (FBE) is a durable powder coating applied to steel pipes to provide corrosion protection.
2. What Applications Require Epoxy-Coated Steel Pipes?
They are used in water supply systems, drainage pipelines, dredging pipes, and oil and gas pipelines.
3. How Durable Is Epoxy Coating for Pipelines?
Epoxy coatings can last 20-30 years with proper maintenance.
4. How Is Coating Thickness Tested?
Thickness is measured using magnetic thickness gauges and ultrasonic tools.
5. What Are the Key Standards for Epoxy Coating?
- ANSI/AWWA C213
- ISO 21809-2
- API RP 5L9
H2: Conclusion
Epoxy-coated steel pipes provide a robust, cost-effective solution for protecting pipelines against corrosion, abrasion, and chemical damage. Their application in water supply systems, drainage pipelines, and oil and gas industries highlights their versatility and reliability. By adhering to international standards such as ANSI/AWWA C213 and ISO 21809-2, epoxy coatings ensure safe and efficient fluid transportation while extending the pipeline’s lifespan.For industries seeking durable and environmentally friendly piping solutions, epoxy-coated steel pipes remain an optimal choice.