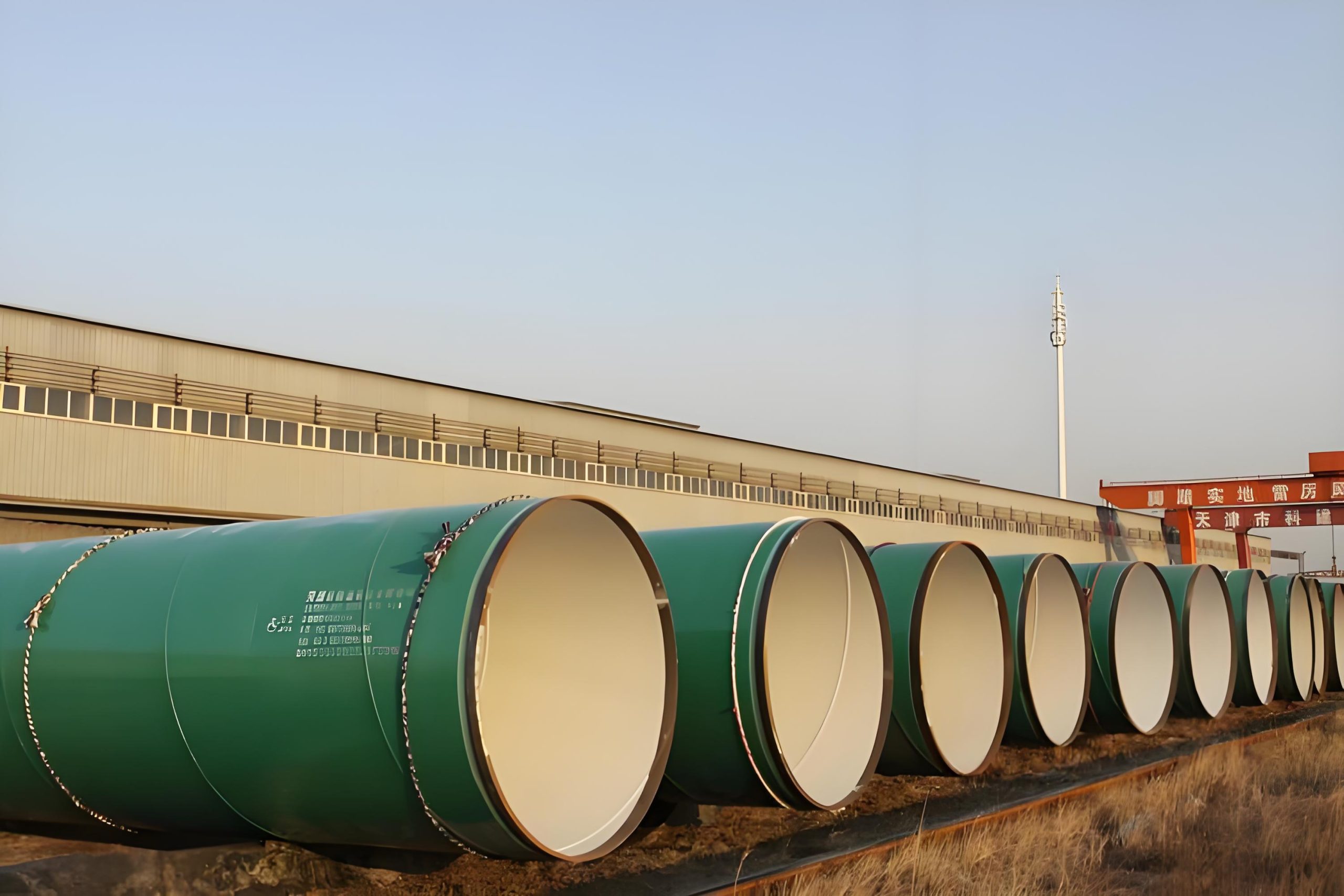
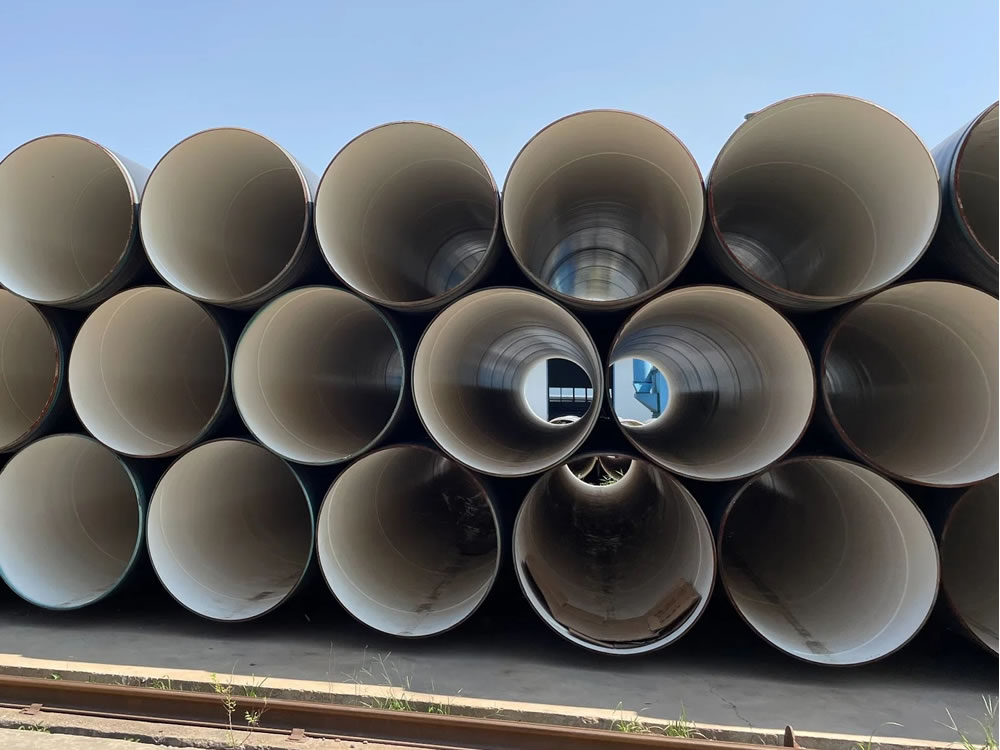
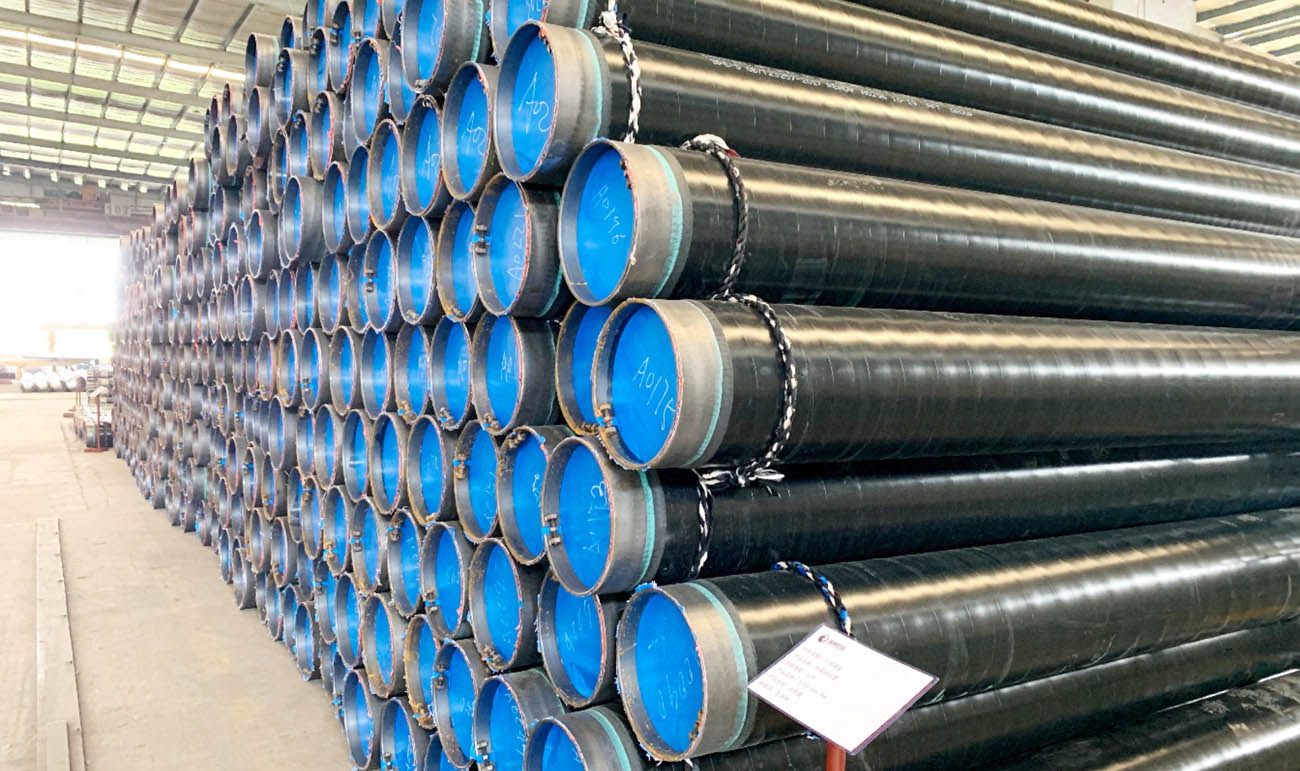
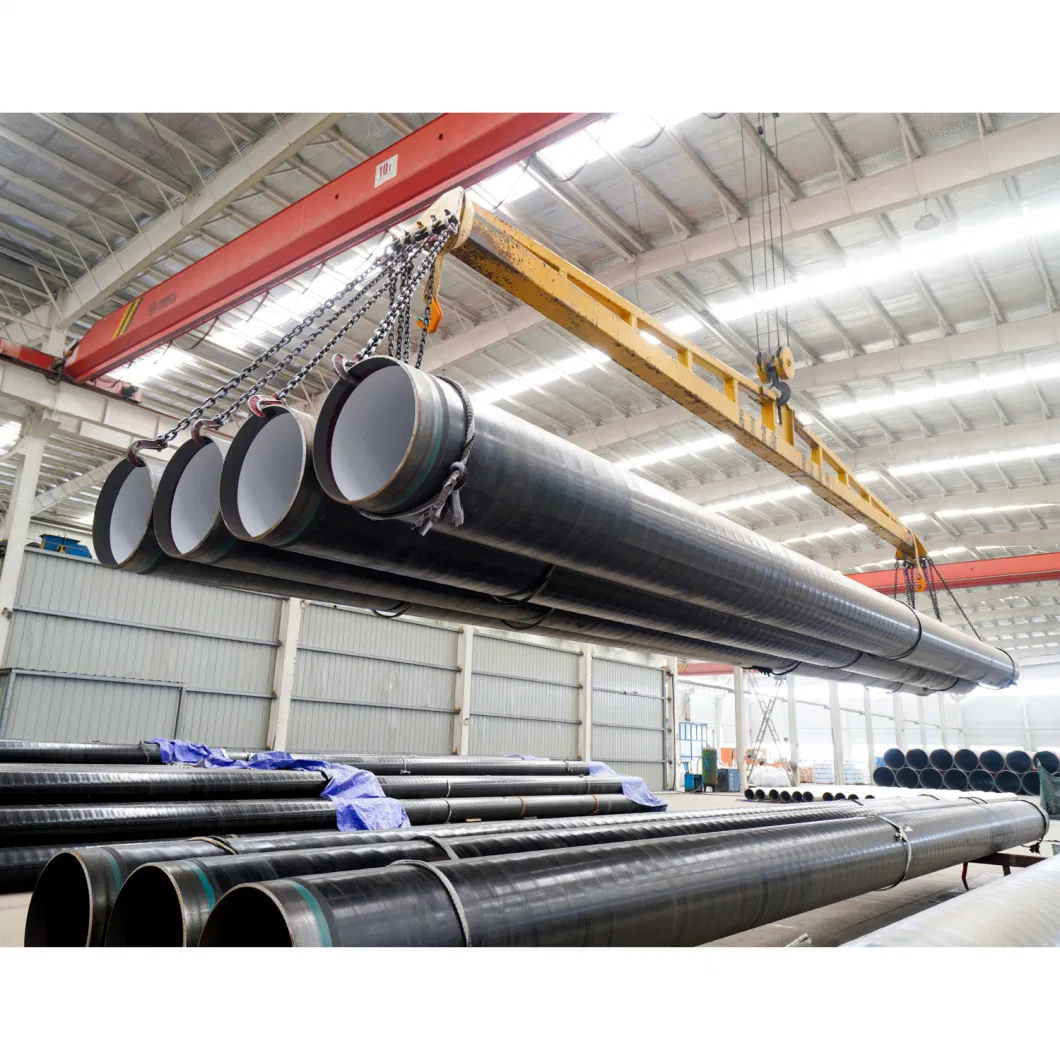
Epoxy Internal Coating Steel Pipes

Epoxy Internal Coating for Steel Pipes
Epoxy internal coating is a widely used method to protect the interior surfaces of steel pipes from corrosion, abrasion, and chemical attacks. Epoxy coatings are known for their excellent adhesion, chemical resistance, and durability, making them ideal for various industrial applications, including oil and gas, water treatment, and chemical processing.
Benefits of Epoxy Internal Coating
- Corrosion Resistance:
- Epoxy coatings provide a robust barrier against corrosive substances, significantly reducing the risk of internal corrosion and extending the service life of steel pipes.
- Chemical Resistance:
- Epoxy coatings are highly resistant to a variety of chemicals, making them suitable for pipelines transporting aggressive substances.
- Improved Flow Efficiency:
- The smooth, frictionless surface created by the epoxy coating enhances fluid flow, reducing energy consumption and improving overall system efficiency.
- Durability:
- Epoxy coatings offer excellent wear resistance, protecting the pipe interior from abrasion and mechanical damage.
- Reduced Contamination:
- Prevents the leaching of metal ions from the steel into the transported fluid, which is crucial in applications like potable water supply.
epoxy internal coating steel pipe
Internal coating systems for steel pipes using epoxy-based liquid paints, including Novolac, accompanying market trends.
The principal uses of these coatings
1. To improve the flow of liquids by reducing the roughness of the pipes’ inner surfaces, in the case of Flow Coating.
2. To provide anticorrosive protection, in cases in which bicomponent epoxy coatings, 100% solid epoxys and Novolac coatings are applied.
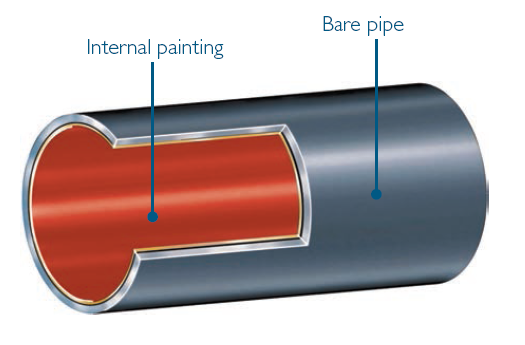
The internal surface of the pipe is cleaned previously. After cleaning, the epoxy paint is applied to the pipe’s inner surface through an airless guns system, forming a uniform layer that cures in the open air.
The typical thickness for the internal coating system varies between 60 and 100μm for gas transportation pipelines and between 200 and 500μm for pipes designed to conduct water or other liquids.

Capacity
Nominal diameter: 4″~48″ (Outer diameter: 114.3mm~1219.2mm)
Length: 8m~13m
Types of Epoxy Coatings
- Fusion-Bonded Epoxy (FBE):
- Applications: Commonly used in the oil and gas industry for pipeline protection.
- Features: Applied as a powder that fuses to the pipe surface when heated, creating a strong, durable coating.
- Liquid Epoxy:
- Applications: Suitable for water, wastewater, and industrial applications.
- Features: Applied as a liquid and cures to form a hard, protective layer. Can be applied in multiple coats for increased protection.
Application Process
- Surface Preparation:
- Cleaning: The pipe interior is cleaned to remove rust, scale, oil, and other contaminants. Methods include abrasive blasting, chemical cleaning, or a combination of both.
- Inspection: The cleaned surface is inspected to ensure it is free of contaminants and properly prepared for coating.
- Coating Application:
- Method: The epoxy is applied using spray, brush, or roller, depending on the specific requirements. For FBE, the pipe is heated, and the epoxy powder is sprayed onto the surface, where it melts and fuses to form a continuous coating.
- Multiple Coats: In some cases, multiple coats of epoxy are applied to achieve the desired thickness and protection level.
- Curing:
- Process: The coated pipe is allowed to cure. For liquid epoxy, this may involve air drying or oven curing. For FBE, the coating cures as it cools after application.
- Time: The curing time depends on the type of epoxy and the environmental conditions.
- Inspection and Testing:
- Visual Inspection: Ensures the coating is uniform and free of defects such as bubbles, pinholes, or cracks.
- Thickness Measurement: Verifies the coating thickness meets the specified requirements.
- Adhesion Testing: Ensures the coating has properly bonded to the steel surface.
- Holiday Testing: Detects any discontinuities or defects in the coating that could allow corrosion.
Standards and Specifications
- NACE SP0394: Standard for the application of internal coatings on steel pipelines for corrosion control.
- AWWA C210: Standard for liquid-epoxy coatings on the interior and exterior surfaces of steel water pipelines.
- API RP 5L2: Recommended practice for internal coating of line pipe for non-corrosive gas transmission service.
- ISO 15741: Paints and varnishes – Friction-reduction coatings for the interior surfaces of pipelines used for oil and gas transportation.
Conclusion
Epoxy internal coatings provide a highly effective means of protecting steel pipes from corrosion, chemical attack, and abrasion. By enhancing the durability and efficiency of pipelines, epoxy coatings help to extend the service life of the piping system and reduce maintenance costs. Adhering to industry standards and following proper application procedures ensures the optimal performance of the epoxy coating in various industrial applications.