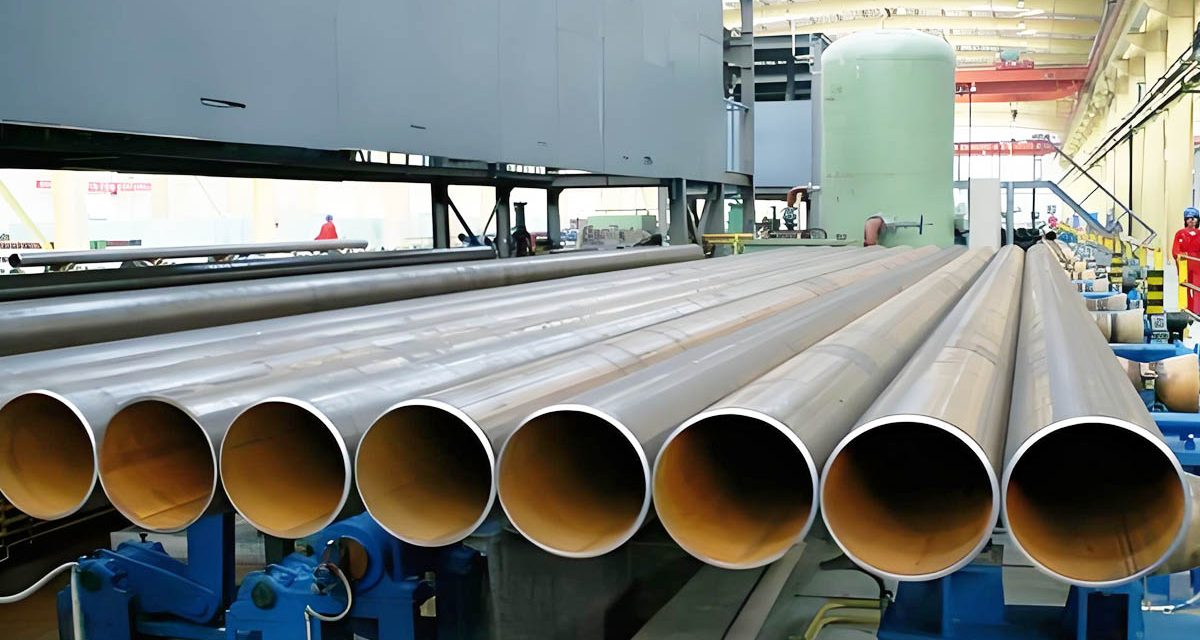
Tuyaux en acier pour restes explosifs des guerres
Tuyaux en acier pour restes explosifs des guerres
Restes explosifs de guerre (Soudé par résistance électrique) tuyaux en acier are a type of steel pipe that are manufactured through a welding process that employs electric resistance. ERW pipes are used in various applications due to their high quality, durabilité, et la rentabilité. Here’s an overview of ERW steel pipes, their manufacturing process, candidatures, et avantages.
Processus de fabrication
- Raw Material:
- The manufacturing process begins with coils of steel, which are cut into strips of appropriate width.
- Formation:
- The steel strips are passed through a series of rollers to form them into a cylindrical shape.
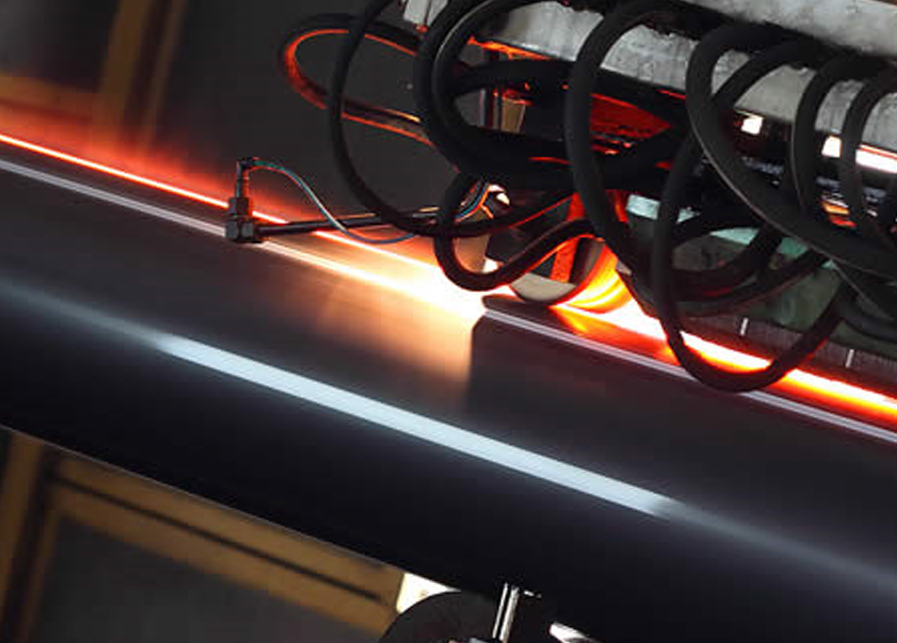
- Soudage:
- The edges of the cylindrical steel strip are heated and pressed together using electric resistance welding, forming a continuous seam. Unlike other welding methods, no filler material is used.
- Finition:
- The welded seam is then annealed (heat-treated) to remove any residual stresses from the welding process.
- The pipe is then cut to the desired length, and further finishing processes like straightening, end-facing, and coating may be applied.
- Contrôle de qualité:
- ERW pipes undergo various quality control tests, including ultrasonic testing, hydrostatic testing, and visual inspection to ensure they meet industry standards and specifications.
Diamètre extérieur
- Gamme: 1/2″ au 28″
Épaisseur de paroi
- Gamme: 1.65 mm à 20 mm (Tous les horaires)
Longueur
- Gamme: 1 m à 12 m ou selon les exigences du client
Normes
- ASTM 5L
- ASTMA53
- ASTMA178
- ASTMA500/501
- ASTMA691
- ASTMA252
- ASTMA672
- DANS 10217
Qualités des matériaux
- API 5L: PSL1/PSL2 Gr.A, Gr.B, X42, X46, X52, X56, X60, X65, X70
- ASTMA53: GR.A, GR.B
- DANS: S275, S275JR, S355JRH, S355J2H
Extrémités de tuyaux
- Extrémité unie
- Extrémité biseautée
- Fileté
Options de traitement de surface
- Nu
- Peint en noir
- Verni
- Galvanisé
- Revêtements anticorrosion (3PE, PP/EP, Revêtement FBE, etc.)
Processus de fabrication
- Étiré à froid
- Laminé à chaud
Tests et assurance qualité
- Analyse des composants chimiques
- Propriétés mécaniques:
- Résistance à la traction ultime
- Limite d'élasticité
- Élongation
- Propriétés techniques:
- Test d'aplatissement
- Essai de flexion
- Essai de dureté
- Essai d'impact
- Inspection des dimensions extérieures
- Essai hydrostatique
- Contrôles non destructifs (CND):
- ET (Test par courants de Foucault)
- RT (Test radiographique)
- Utah (Test par ultrasons)
Spécification
Spécification:
|
INCH
|
DE
(MM)
|
Strandard Wall Thickness
|
|||||||
|
SCH 10WT
(mm)
|
SCH 20WT
(mm)
|
SCH 40WT
(mm)
|
SCH 60WT
(mm)
|
SCH 80WT (mm) |
SCH 100WT (mm) |
SCH 160WT (mm) |
XXS (mm) |
||
|
1/4»
|
13.7
|
|
|
2.24
|
|
3.02
|
|
|
|
|
3/8»
|
17.1
|
|
|
2.31
|
|
3.2
|
|
|
|
|
1/2»
|
21.3
|
2.11
|
|
2.77
|
|
3.73
|
|
4.78
|
7.47
|
|
3/4″
|
26.7
|
2.11
|
|
2.87
|
|
3.91
|
|
5.56
|
7.82
|
|
1″
|
33.4
|
2.77
|
|
3.38
|
|
4.55
|
|
6.35
|
9.09
|
|
1-1/4″
|
42.2
|
2.77
|
|
3.56
|
|
4.85
|
|
6.35
|
9.7
|
|
1-1/2″
|
48.3
|
2.77
|
|
3.68
|
|
5.08
|
|
7.14
|
10.15
|
|
2″
|
60.3
|
2.77
|
|
3.91
|
|
5.54
|
|
8.74
|
11.07
|
|
2-1/2″
|
73
|
3.05
|
|
5.16
|
|
7.01
|
|
9.53
|
14.02
|
|
3″
|
88.9
|
3.05
|
|
5.49
|
|
7.62
|
|
11.13
|
15.24
|
|
3-1/2″
|
101.6
|
3.05
|
|
5.74
|
|
8.08
|
|
|
|
|
4″
|
114.3
|
3.05
|
4.5
|
6.02
|
|
8.56
|
|
13.49
|
17.12
|
|
5″
|
141.3
|
3.4
|
|
6.55
|
|
9.53
|
|
15.88
|
19.05
|
|
6″
|
168.3
|
3.4
|
|
7.11
|
|
10.97
|
|
18.26
|
21.95
|
|
8″
|
219.1
|
3.76
|
6.35
|
8.18
|
10.31
|
12.7
|
15.09
|
23.01
|
22.23
|
|
10″
|
273
|
4.19
|
6.35
|
9.27
|
12.7
|
15.09
|
18.26
|
28.58
|
25.4
|
|
12″
|
323.8
|
4.57
|
6.35
|
10.31
|
14.27
|
17.48
|
21.44
|
33.32
|
25.4
|
|
14″
|
355
|
6.35
|
7.92
|
11.13
|
15.09
|
19.05
|
23.83
|
36.71
|
|
|
16″
|
406
|
6.35
|
7.92
|
12.7
|
16.66
|
21.44
|
26.19
|
40.49
|
|
|
18″
|
457
|
6.35
|
7.92
|
14.27
|
19.05
|
23.83
|
29.36
|
46.24
|
|
|
20″
|
508
|
6.35
|
9.53
|
15.09
|
20.62
|
26.19
|
32.54
|
50.01
|
|
|
22″
|
559
|
6.35
|
9.53
|
|
22.23
|
28.58
|
34.93
|
54.98
|
|
|
24″
|
610
|
6.35
|
9.53
|
17.48
|
24.61
|
30.96
|
38.89
|
59.54
|
|
|
26″
|
660
|
7.92
|
12.7
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28″
|
711
|
7.92
|
12.7
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30″
|
762
|
7.92
|
12.7
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32″
|
813
|
7.92
|
12.7
|
17.48
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34″
|
863
|
7.92
|
12.7
|
17.48
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36″
|
914
|
7.92
|
12.7
|
19.05
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38″
|
965
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40″
|
1016
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
42″
|
1066
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44″
|
1117
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
46″
|
1168
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48″
|
1219
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Standard
Analyse chimique et propriétés mécaniques
| Standard | Classe | Grade | Analyse chimique(%) | Propriétés mécaniques(min)(Mpa) | ||||
| C | Mn | P. | S | Résistance à la traction | Limite d'élasticité | |||
| API 5L | PSL1 | B | 0.26 | 1.20 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 414 | 241 |
| X42 | 0.26 | 1.30 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 414 | 290 | ||
| X46 | 0.26 | 1.40 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 434 | 317 | ||
| X52 | 0.26 | 1.40 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 455 | 359 | ||
| X56 | 0.26 | 1.40 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 490 | 386 | ||
| X60 | 0.26 | 1.40 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 517 | 414 | ||
| X65 | 0.26 | 1.45 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 531 | 448 | ||
| X70 | 0.26 | 1.65 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 565 | 483 | ||
| PSL2 | B | 0.22 | 1.20 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 414 | 241 | |
| X42 | 0.22 | 1.30 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 414 | 290 | ||
| X46 | 0.22 | 1.40 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 434 | 317 | ||
| X52 | 0.22 | 1.40 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 455 | 359 | ||
| X56 | 0.22 | 1.40 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 490 | 386 | ||
| X60 | 0.22 | 1.40 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 517 | 414 | ||
| X65 | 0.22 | 1.45 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 531 | 448 | ||
| X70 | 0.22 | 1.65 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 565 | 483 | ||
| X80 | 0.22 | 1.85 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 621 | 552 | ||
Processus
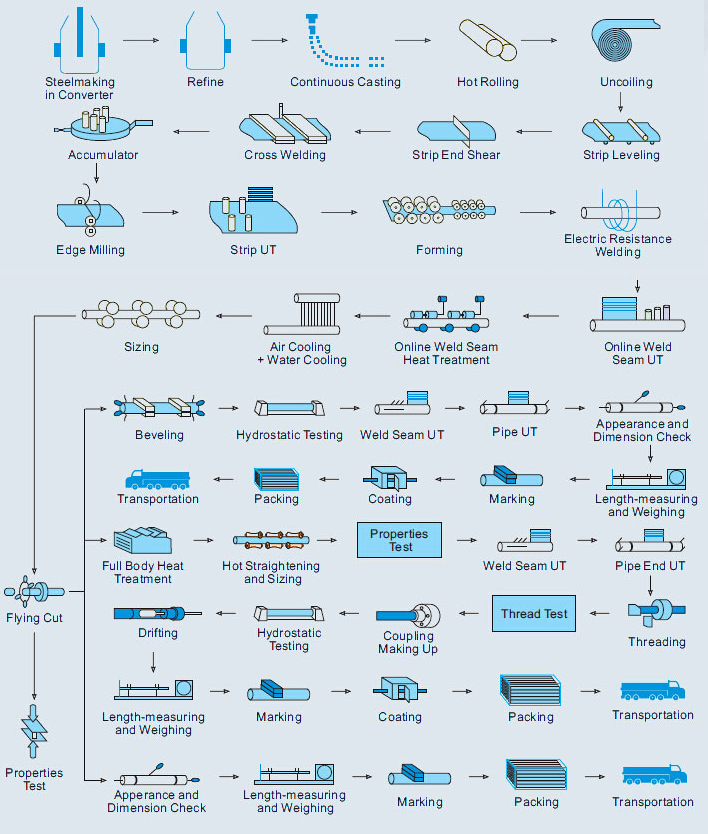
Applications
ERW steel pipes are used in a wide range of applications due to their versatility and cost-efficiency:
- Industrie pétrolière et gazière: Transportation of oil, gaz, et autres fluides.
- Systèmes d'approvisionnement en eau: Pipes for potable water and sewage systems.
- Industrie automobile: Composants structurels, systèmes d'échappement, and other automotive parts.
- Construction: Structural applications in buildings, ponts, et autres projets d'infrastructures.
- Génie Mécanique et Général: Fabrication of mechanical parts and general engineering components.
Avantages
- Rentable: ERW pipes are generally less expensive than seamless pipes.
- High Quality: The manufacturing process ensures a high degree of dimensional accuracy and uniformity.
- Résistance et durabilité: ERW pipes have good mechanical properties and are suitable for high-pressure applications.
- Versatilité: Available in various sizes, épaisseurs, et longueurs, making them suitable for diverse applications.
- Efficacité: The ERW process is efficient, allowing for mass production with consistent quality.
Types of ERW Pipes
- Round ERW Pipes: Commonly used in fluid transportation.
- Square and Rectangular ERW Pipes: Often used in structural applications.
- Galvanized ERW Pipes: Coated with zinc to prevent corrosion, used in outdoor and harsh environments.
Normes et spécifications
ERW steel pipes are manufactured to meet various international standards and specifications, y compris:
- API 5L: Specification for line pipes.
- ASTMA53: Spécification standard pour les tuyaux, acier, noir et trempé à chaud, zingué, soudé et sans soudure.
- ASTMA252: Standard specification for welded and seamless steel pipe piles.
- BS 1387: Spécification pour les tubes et tubulaires en acier vissés et emmanchés et pour les tubes en acier à extrémité lisse adaptés au soudage ou au vissage sur BS 21 filetages de tuyaux.
Conclusion
ERW steel pipes are an essential component in various industries due to their reliability, rentabilité, et polyvalence. Their manufacturing process ensures a high-quality product that meets stringent industry standards, making them a preferred choice for many applications.

















