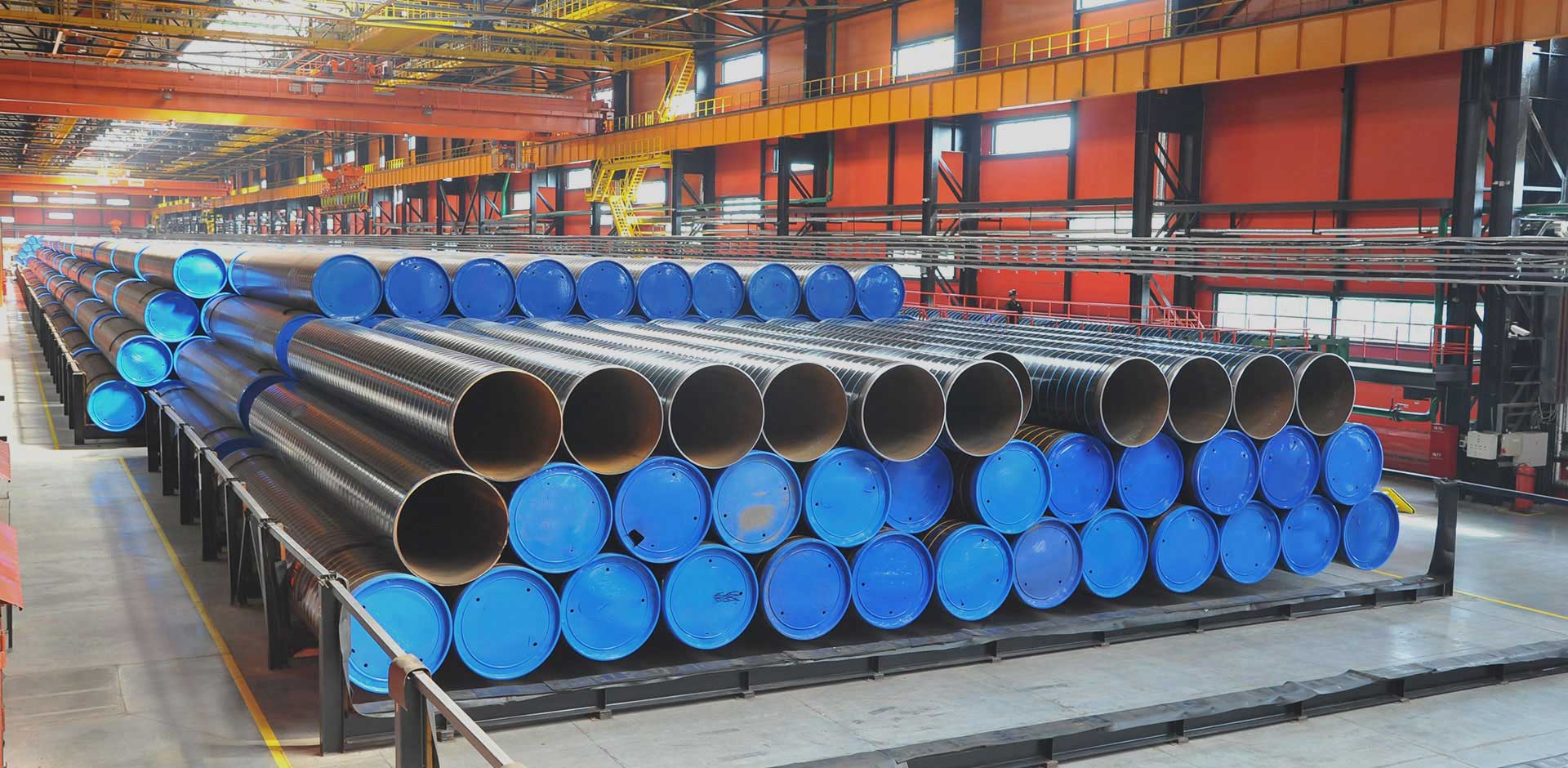
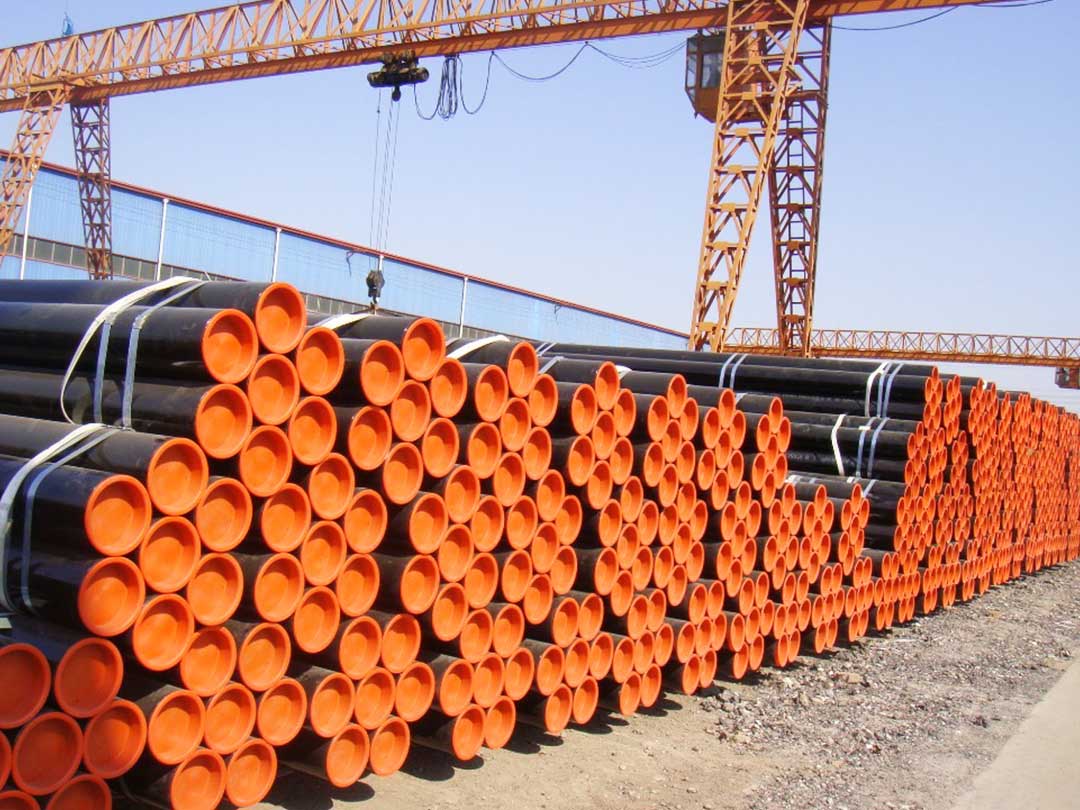
Tuyaux soudés ERW et processus de fabrication

Spécification des tuyaux en acier ERW
Standard: ASTMA53, ASTMA106, API 5L, EN10210, EN10219,ASTM A178, ASTMA500/501, ASTMA691, ASTMA252, ASTMA672, DANS 10217
Nuance d'acier: Catégorie B, X42-X80, S275JR, S275J0H, S275JRH, S355JR, S355J0H, S355JRH
Dimensions
DE: 1/8 pouce à 24 pouce
POIDS: maximum 26,5 mm
Longueur: Longueur fixe ou longueur aléatoire, maximum 12 mètres
| TUYAU ERW de petit diamètre | |||||||
| Diamètre extérieur | Sch 5 | Sch 10 | Sch 40 | ||||
| Pouce | mm | Épaisseur | Kg/mtr | Épaisseur | Kg/mtr | Épaisseur | Kg/mtr |
| 1/2″ | 21.3 | 1.65 | 0.81 | 2.11 | 1.01 | 2.77 | 1.29 |
| 3/4″ | 26.7 | 1.65 | 1.03 | 2.11 | 1.30 | 2.87 | 1.71 |
| 1″ | 33.4 | 1.65 | 1.31 | 2.77 | 2.12 | 3.38 | 2.54 |
| 1 1/4″ | 42.2 | 1.65 | 1.93 | 2.77 | 3.15 | 3.68 | 4.11 |
| 1 1/2″ | 48.3 | 1.65 | 1.93 | 2.77 | 3.15 | 3.68 | 4.11 |
| 2″ | 60.3 | 1.65 | 2.42 | 2.77 | 3.98 | 4.81 | 5.31 |
| 3″ | 88.9 | 2.11 | 4.58 | 3.05 | 6.54 | 5.49 | 11.45 |
| 3 1/2″ | 101.6 | 2.11 | 5.25 | 3.05 | 7.52 | 5.74 | 13.77 |
| 4″ | 114.3 | 2.11 | 5.25 | 3.05 | 7.52 | 5.74 | 13.77 |
| 5″ | 141.3 | 2.77 | 9.50 | 3.40 | 11.74 | 6.55 | 22.10 |
| 6″ | 168.3 | 2.77 | 11.47 | 3.40 | 14.04 | 7.11 | 28.68 |
| 8″ | 219.1 | 2.77 | 14.99 | 3.76 | 20.25 | 8.18 | 43.16 |
| TUYAU ERW de grand diamètre | |||||||||||||||||||
| DE | POIDS | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pouce | mm | 8 5/8″ | 219.1
mm |
10 3/4″ | 273.1
mm |
12 3/4″ | 325.0
mm |
14″ | 355.6
mm |
16″ | 406.4
mm |
18″ | 457.7
mm |
20″ | 508.0
mm |
24″ | 610
mm |
24 4/5″ | 630.0
mm |
| 0.157 | 4.0 | —- | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 0.197 | 5.0 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||
| 0.236 | 6.0 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||
| 0.276 | 7.0 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||
| 0.315 | 8.0 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| 0.354 | 9.0 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| 0.394 | 10.0 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 0.133 | 11.0 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 0.492 | 12.5 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 0.551 | 14.0 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||
| 0.630 | 16.0 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||
| 0.689 | 17.5 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||
| 0.748 | 19.0 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||
| 0.787 | 20.0 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
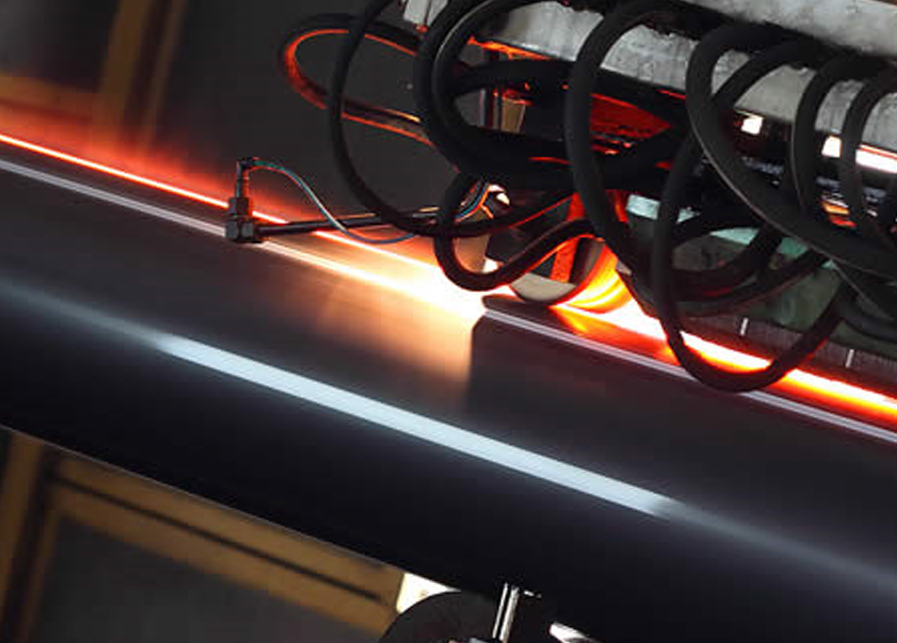
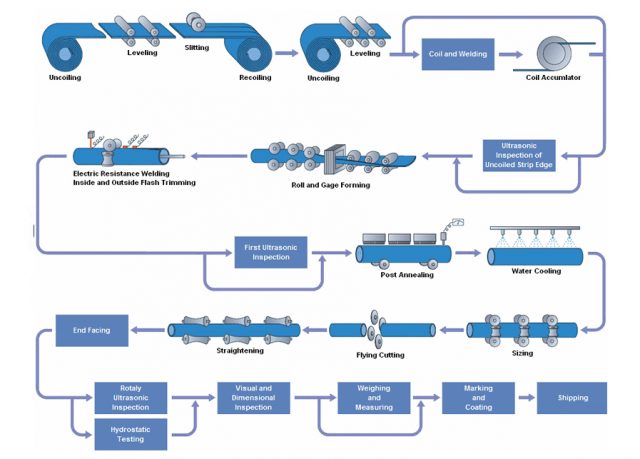
Processus de fabrication de tuyaux soudés
Dans le soudage des restes explosifs des guerres, deux électrodes, généralement en cuivre, sont utilisés pour appliquer une pression et un courant. Les électrodes sont en forme de disque et tournent lorsque le matériau passe entre elles.. Cela permet aux électrodes de rester en contact constant avec le matériau pour réaliser de longues soudures continues..
Un transformateur de soudage fournit de la basse tension, alimentation CA à courant élevé. Le joint du tuyau présente une résistance électrique élevée par rapport au reste du circuit et est chauffé jusqu'à son point de fusion par le courant.. Les surfaces semi-fondues sont pressées ensemble avec une force qui crée une liaison par fusion, résultant en une structure uniformément soudée.
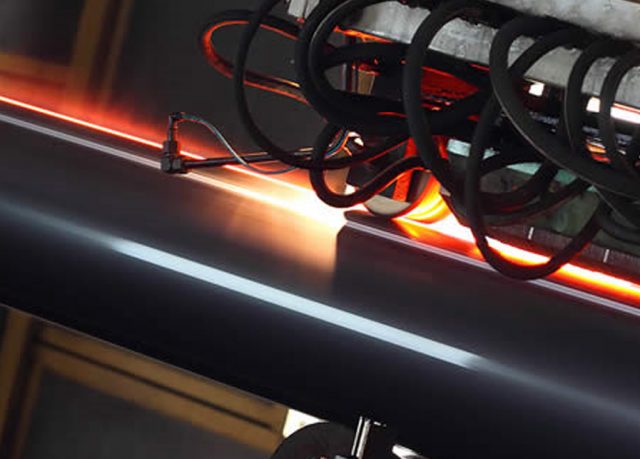

Méthode de traitement thermique des tuyaux en acier au carbone et allié
Les méthodes de traitement thermique des tuyaux en acier au carbone et en acier allié comprennent 4 principalement des types:
Normalisation, Recuit, Trempe et revenu.
Cela améliorera les propriétés mécaniques des matériaux en acier, composition chimique uniforme, et usinabilité. Le traitement thermique des matériaux métalliques en acier peut être divisé en traitement thermique intégral, traitement thermique de surface et traitement thermique chimique. Les tuyaux en acier adoptent généralement le traitement thermique intégral.
La performance du matériau en acier se réfère principalement aux propriétés mécaniques, propriétés physiques, et performances des processus. Le traitement thermique apportera une structure métallurgique différente et des performances correspondantes pour le tuyau en acier, il pourrait donc être mieux appliqué dans différents services industriels ou pétroliers et gaziers.
Il existe deux méthodes pour améliorer les propriétés du matériau en acier. Une méthode consiste à ajuster la composition chimique, méthode d'alliage nommée. L'autre méthode est le traitement thermique. Dans le domaine de la technologie industrielle moderne, le traitement thermique améliore les performances des tuyaux en acier en position dominante.
Fins de traitement thermique
1. Chauffage.
Le matériau en acier pourrait être chauffé en dessous du point critique ou au-dessus du point critique. L'ancienne méthode de chauffage peut stabiliser la structure et éliminer les contraintes résiduelles. Cette dernière méthode peut rendre le matériau austénitisant. L'austénitisation consiste à chauffer l'acier métallique au-dessus de sa température critique suffisamment longtemps, pour qu'il puisse être transformé. Si une trempe suit après l'austénitation, alors le matériau sera durci. La trempe sera assez rapide pour transformer l'austénite en martensite. Une fois atteint la température austénitisante, microstructure appropriée et dureté totale, le matériau du tuyau en acier sera obtenu dans d'autres processus de traitement thermique.
2. Conservation de la chaleur.
Le but de la conservation de la chaleur est d'uniformiser la température de chauffage du matériau en acier, alors il obtiendra une organisation de chauffage raisonnable.
3. Refroidissement
Le processus de refroidissement est le processus clé du traitement thermique, il détermine les propriétés mécaniques des tuyaux en acier après le processus de refroidissement.
Quatre principales méthodes de traitement thermique dans l'industrie des tubes en acier au carbone et alliés Les processus de traitement thermique des tubes en acier comprennent la normalisation, recuit, trempe, trempe et autres processus.
Normalisation
Chauffer le tuyau en acier au-dessus de la température critique, et refroidi à l'air.
En normalisant, la contrainte du matériau en acier pourrait être soulagée, améliore la ductilité et la ténacité pour le processus de travail à froid. Normalisation généralement appliquée aux matériaux des tuyaux en acier au carbone et en acier faiblement allié. Il produira une structure métallique différente, perlite, bolite, un peu de martensite. Ce qui apporte un matériau en acier plus dur et plus résistant, et moins de ductilité que le matériau de recuit complet.
Recuit
Chauffer le matériau au-dessus de sa température critique suffisamment longtemps jusqu'à ce que la microstructure se transforme en austénite. Puis refroidi lentement au four, obtenir une transformation maximale de la ferrite et de la perlite.
Le recuit éliminera les défauts, uniformiser la composition chimique et les grains fins. Ce procédé est généralement appliqué aux produits à haute teneur en carbone, les tuyaux en acier faiblement allié et allié doivent réduire leur dureté et leur résistance, affiner la structure cristalline, améliorer la plasticité, ductilité, ténacité et usinabilité.
Trempe
Chauffer le matériau du tuyau en acier à une température critique jusqu'à ce que la transformation de la microstructure soit terminée, le refroidir à un rythme rapide.
Le but de la trempe est de produire la contrainte thermique et la contrainte tissulaire. It can eliminate and improve through the tempering. The combination of quenching and tempering can make the comprehensive performance improved.
Trempe
Heating the steel material to a precise temperature below the critical point, and often done in the air, vacuum or the inert atmospheres. There are low temperature tempering 205 to 595°F (400 to 1105°F), medium temperature and high temperature tempering (to 700℃ 1300℉).
The purpose of tempering is to increase the toughness of steel and alloy steel pipe. Before tempering, these steel is very hard but too brittle for the most application. After process can improve the plasticity and toughness of steel pipe, reduce or eliminate the residual stress and stabilize the steel pipe’s size. Brings good comprehensive mechanical properties, pour que ça ne change pas en service.
Traitement en solution pour les matériaux de tuyaux en acier à base d'alliage
Chauffer un alliage à une température appropriée, conservez-le à cette température suffisamment longtemps pour qu'un ou plusieurs constituants se transforment en une solution solide, puis le refroidir à un rythme rapide pour maintenir ces constituants en solution.
Il existe plusieurs alliages à base de nickel coulés et corroyés qui peuvent atteindre différentes performances requises par traitement en solution ou par durcissement par vieillissement par précipitation.. Caractéristiques telles que la résistance mécanique à température ambiante et à température élevée, la résistance à la corrosion et la résistance à l'oxydation seront considérablement améliorées par ce traitement thermique. De nombreux alliages à base de nickel développent leurs propriétés souhaitées uniquement grâce au traitement en solution., comme les tuyaux en acier Hastelloy et en alliage de nickel.
Pendant le traitement en solution, le carbure et divers éléments d'alliage sont dissous uniformément dans l'austénite. Un refroidissement rapide rendra les éléments en carbone et en alliage trop tard pour précipiter, et obtenir le processus de traitement thermique d'un seul tissu austénitique. Le traitement en solution peut uniformiser la structure interne et la composition chimique. Il peut également restaurer la résistance à la corrosion des tuyaux en acier Hastelloy et en alliage de nickel..







