Technologie
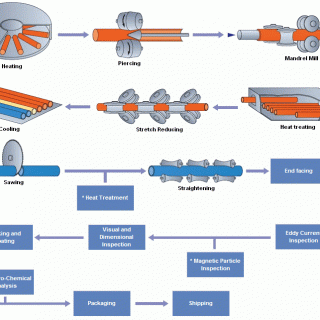
Tuyaux en acier en acier à paroi épaisse à parois épaisses, produit à travers des processus avancés comme le piercing chaud et le traitement thermique, Offrez une force et une fiabilité exceptionnelles. Grades internationaux de EN (par ex., 34CrMo4) et ASTM (par ex., A519 4140) Parallèlement aux normes GB répond aux besoins divers, des cylindres hydrauliques aux infrastructures énergétiques, Assurer les performances sous haute pression et stress.
For high-pressure hydraulic cylinders, seamless steel pipes such as ST52 (E355), SAE 4140 (42CrMo), 37Mn, and 34CrMo4 are widely used, adhering to standards like DIN 2391, ASTMA519, and GB 18248. These grades offer the necessary strength, dureté, and precision to ensure safety and performance under extreme pressures. Selection depends on specific pressure requirements, conditions environnementales, and manufacturing processes like honing or heat treatment.
The welding of UNS N08825 pipelines demands a holistic approach integrating material science, process engineering, and stringent quality control. By optimizing TIG/MIG/SMAW parameters, mitigating defects through pre/post-weld treatments, and adhering to international standards, industries can leverage the alloy’s full potential in corrosive and high-temperature environments. Continuous advancements in welding technologies promise enhanced efficiency and reliability for future applications.
Welding Inconel 625 and P22 requires meticulous control of thermal gradients, filler selection, and post-weld treatments to address metallurgical incompatibilities. Industry standards and advanced processes (par ex., Embrouille, soudage au laser) enhance joint reliability in critical applications. Continuous innovation in welding technology will further optimize these dissimilar joints for extreme environments.
Par la pratique de soudage de plus que 400 PORTS DYNE dans la section Gasification du dispositif de synthèse chimique de l'ammoniac chimique Liuguo, Il est montré que le processus de soudage ci-dessus peut assurer complètement la qualité du soudage. À en juger par le résultat du taux de passage de 96%, c'est suffisant. Prouver ce.
Pour résumer, La technologie de traitement de surface du nickel 200 comprend des méthodes telles que le décapage, Surfaces de recuit et de polissage lumineux. Ces technologies présentent leurs avantages uniques et leur place à l'amélioration des différents scénarios d'application.
Le choix entre Inconel® X-750 (NOUS N07750) et alliage de nickel 600 dépend en grande partie des exigences spécifiques de l'application: Choisissez Inconel X-750 pour la stress élevé, Applications à haute température où la résistance mécanique, résistance à la fatigue, et la résistance au fluage est critique (par ex., aérospatial, nucléaire, et turbines à gaz). Choisissez l'alliage nickel 600 Pour une résistance à la corrosion polyvalente dans les applications à usage général ou lorsque la fabrication et la rentabilité sont plus importantes (par ex., traitement chimique, marin, et échangeurs de chaleur).
L'Hastelloy C-276 se distingue comme l'un des alliages les plus polyvalents et les plus résistants à la corrosion disponibles aujourd'hui. Ses propriétés uniques le rendent indispensable dans les industries où la performance et la fiabilité sont primordiales. De la résistance aux acides agressifs dans les usines chimiques à la résistance aux conditions difficiles des environnements marins, L'Hastelloy C-276 a prouvé sa valeur à maintes reprises. Bien que son coût élevé et les défis de fabrication puissent poser des limites, les avantages qu'il offre dépassent de loin ces inconvénients pour les applications critiques. Alors que les industries mondiales continuent de repousser les limites de l'innovation, L'Hastelloy C-276 restera un matériau de base pour les environnements exigeants, assurer la sécurité, efficacité, et durabilité pour les années à venir.
L'analyse CFD du débit d'eau à l'intérieur des tuyaux coudés soudés bout à bout révèle que le tuyau coudé à bord normal surpasse le tuyau coudé à bord vif en termes d'efficacité d'écoulement., consommation d'énergie, et l'intégrité structurelle. Les principales conclusions comprennent:
Lors du choix entre des tuyaux sans soudure et soudés en alliage à haute teneur en nickel, prendre en compte des facteurs tels que les exigences de pression, résistance à la corrosion, coût, et la disponibilité des tailles pour vous assurer que vous choisissez le bon type de tuyau pour votre projet. Pour plus d’informations ou une assistance dans la sélection du bon tuyau, consultez un spécialiste des matériaux ou un fournisseur qui peut vous guider tout au long du processus de prise de décision..
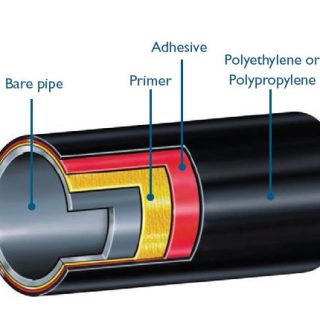
Les revêtements 3LPP et 3PE offrent une excellente protection aux canalisations en acier, mais ils sont conçus pour différentes conditions de fonctionnement. 3Revêtements LPP, avec leur résistance aux hautes températures et leur résistance mécanique supérieure, sont idéaux pour les canalisations situées dans des environnements difficiles ou celles transportant des fluides chauds. D'autre part, 3Revêtements PE, avec leur rentabilité et leur bonne flexibilité, sont mieux adaptés aux canalisations situées dans des environnements modérés où la température et les contraintes mécaniques sont plus faibles.
Les joints soudés dans les tuyaux en acier allié ASTM A335 P5 sont sensibles à diverses formes de corrosion, en particulier dans les environnements difficiles. Le processus de soudage, zone affectée par la chaleur, et le traitement thermique après soudage jouent tous un rôle essentiel dans la détermination du comportement à la corrosion du matériau.. En employant des techniques de soudage appropriées,
En suivant ces directives, les opérateurs peuvent gérer efficacement l’intégrité des canalisations corrodées, garantir un fonctionnement continu et sûr dans des environnements difficiles.
Le marché des tubes de cuvelage est prêt pour la croissance et la transformation à mesure qu'il s'adapte à l'évolution des demandes de l'industrie et aux progrès technologiques.. Même si des défis tels que la volatilité des prix des matières premières et les perturbations de la chaîne d’approvisionnement persistent, la résilience et la capacité d’innovation du marché offrent d’importantes opportunités de croissance. À mesure que nous approchons 2025, l’accent mis sur la durabilité, technologies intelligentes, et les matériaux avancés façonneront l'avenir du marché des tubes de tubage, assurer sa pertinence et sa contribution continues au paysage énergétique mondial.
La technologie de connexion pour les tuyaux de tubage est un élément essentiel de la construction de puits, assurer l’exploitation sûre et efficace des puits de pétrole et de gaz. Des connexions filetées et soudées traditionnelles aux technologies mécaniques et intelligentes avancées, l'industrie continue d'innover pour répondre aux exigences d'environnements de plus en plus difficiles. En sélectionnant la technologie de connexion appropriée et en adhérant aux meilleures pratiques, les opérateurs peuvent optimiser les performances des puits, améliorer la sécurité, et prolonger la durée de vie de leurs puits.
Les phases de forage, enveloppe, et les tubes font partie intégrante du développement réussi d’un puits de pétrole ou de gaz. Chaque phase nécessite une planification minutieuse, exécution précise, et le respect des normes de sécurité et environnementales. En comprenant et en gérant efficacement ces phases, les opérateurs peuvent optimiser la production, minimiser les risques, et assurer la longévité du puits. À mesure que la technologie progresse, de nouvelles techniques et de nouveaux matériaux continuent d'améliorer l'efficacité et la sécurité de ces opérations, contribuer à l’évolution continue de l’industrie pétrolière et gazière.
Les dommages causés aux tuyaux de tubage de puits posent des défis importants pour l'intégrité et l'efficacité des puits. Comprendre les causes des dommages et utiliser des technologies de réparation appropriées sont essentiels pour maintenir des opérations sûres et efficaces.. De la corrosion et des contraintes mécaniques à l'activité sismique et à l'usure abrasive, divers facteurs peuvent contribuer aux dommages au boîtier. En utilisant une combinaison de méthodes de réparation traditionnelles et de technologies avancées, les opérateurs peuvent résoudre efficacement ces problèmes et prolonger la durée de vie de leurs puits. En plus, la mise en œuvre de mesures préventives et de meilleures pratiques peut contribuer à minimiser le risque de dommages et à assurer le succès continu des opérations sur les puits. Alors que la technologie continue d’évoluer, de nouvelles solutions et de nouveaux matériaux amélioreront encore la capacité de prévenir et de réparer les dommages causés aux tuyaux de tubage de puits, contribuer à la durabilité et à la sécurité de l’industrie pétrolière et gazière.
En résumé, tandis que le revêtement et le revêtement sont essentiels à la protection des pipelines, ils servent des objectifs distincts et sont appliqués dans différents contextes. Le revêtement se concentre sur la protection externe, protéger les tuyaux des facteurs environnementaux, tandis que la doublure assure la protection interne, protéger les tuyaux des substances qu’ils transportent. Les deux processus offrent des avantages significatifs, y compris la résistance à la corrosion, efficacité de flux améliorée, et durée de vie prolongée. Alors que la technologie continue de progresser, l’efficacité et la durabilité des méthodes de revêtement et de revêtement devraient s’améliorer, assurer la fiabilité et la sécurité continues des systèmes de pipelines dans diverses industries.
La conception de la pression d'application pour les pipelines chimiques est influencée par une combinaison de propriétés chimiques, exigences de débit, perte de friction, sélection des matériaux, et les conditions environnementales. En considérant attentivement ces facteurs, les ingénieurs peuvent assurer le transport sûr et efficace des substances chimiques, minimiser les risques et maintenir l’intégrité du pipeline.
L'autre raison principale pour laquelle la galvanisation à chaud offre une meilleure protection contre la corrosion est que le revêtement est appliqué pendant le processus de fabrication avant l'installation de l'acier.. Cela signifie que toutes les zones coupées ou endommagées lors de l'installation auront toujours un revêtement protecteur.. Autres méthodes de galvanisation, comme la pré-galvanisation, enduire l'acier avant qu'il ne soit coupé et fabriqué. Cela laisse toutes les zones coupées ou endommagées lors de l'installation vulnérables à la rouille et à la corrosion..
Les spécifications internationales ASTM pour les tubes en acier énumèrent les exigences standard pour les tubes de chaudières et de surchauffeurs., tubes de service général, tubes en acier en service de raffinerie, tubes d'échangeur de chaleur et de condenseur, tubes mécaniques et structurels.
Type A- Utilisé là où un espace libre suffisant est disponible. Une élévation spécifique est souhaitable. Tapez B- Utilisé là où la marge est limitée. La fixation de la tête est une seule patte. Tapez C- Utilisé là où la marge est limitée. La fixation de la tête se fait avec des pattes côte à côte
Le tuyau en acier au carbone est très résistant aux chocs et aux vibrations, ce qui le rend idéal pour le transport de l'eau., huile & gaz et autres fluides sous les chaussées. Dimensions Size: 1/8″ à 48″ / DN6 to DN1200 Thickness: Sch 20, MST, 40, XS, 80, 120, 160, XXS Type: Seamless or welded pipe Surface: Apprêt, Huile antirouille, FBE, 2PE, 3LPE Coated Material: ASTMA106B, A53, API 5L B, X42, X46, X52, X56, X60, X65, X70 Service: Coupe, Biseautage, Enfilage, Rainurage, Revêtement, Galvanisation
Les tuyaux sans soudure sont fabriqués selon un procédé de perçage, où une billette solide est chauffée et percée pour former un tube creux. Tubes soudés, d'autre part, sont formés en joignant deux bords de plaques d'acier ou de bobines à l'aide de diverses techniques de soudage.
Le 3 elements of pipe dimension Dimension Standards of carbon and stainless steel pipe (ASME B36.10M & B36.19M) Tableau des tailles de tuyaux (Calendrier 40 & 80 tuyau en acier signifie) Moyens de taille nominale du tuyau (NPS) et diamètre nominal (DN) Tableau des dimensions des tuyaux en acier (Tableau des tailles) Calendrier des classes de poids des tuyaux (WGT)
Le tuyau sans soudure est fabriqué en extrudant le métal à la longueur souhaitée; par conséquent, les tuyaux ERW ont un joint soudé dans leur section transversale, tandis que le tuyau sans soudure n'a aucun joint dans sa section transversale sur toute sa longueur. Dans un tuyau sans soudure, il n'y a pas de soudure ni de joints et est fabriqué à partir de billettes rondes solides.
Tuyaux ERW NOIR. Soudé par résistance électrique (Restes explosifs de guerre) Les tuyaux sont fabriqués à partir de bobines laminées à chaud / Fentes. Toutes les bobines entrantes sont vérifiées sur la base du certificat de test reçu de l'aciérie pour leurs propriétés chimiques et mécaniques.. Le tuyau ERW est formé à froid pour lui donner une forme cylindrique, non formé à chaud.