HFI Steel Pipe | High-Frequency Induction Pipe
High-Frequency Induction (HFI) steel pipes are a type of Electric Resistance Welded (ERW) pipe that are produced using high-frequency induction welding. This method is known for its efficiency and effectiveness in creating strong, high-quality welds. Here’s an overview of HFI steel pipes, including their manufacturing process, characteristics, and applications:
HFI (High-Frequency Induction) Steel Pipe
Manufacturing Process
- High-Frequency Induction Welding:
- Induction Coil: The process starts by forming the steel strip into a cylindrical shape using a series of forming rolls.
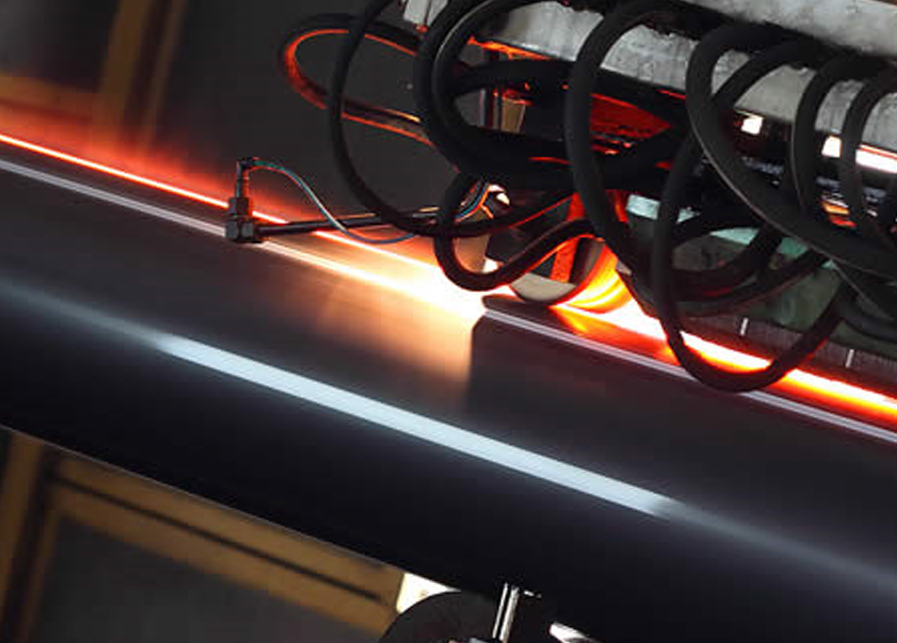
- Induction Heating: The edges of the steel strip are then heated using an induction coil. This coil generates an alternating magnetic field that induces currents (eddy currents) in the steel.
- Welding: The edges are heated to a temperature sufficient for welding without melting the entire material. The heated edges are then pressed together to form a weld under pressure.
- Cooling and Sizing: After welding, the pipe is quickly cooled and passed through sizing rolls to ensure the precise dimensions and roundness of the pipe.
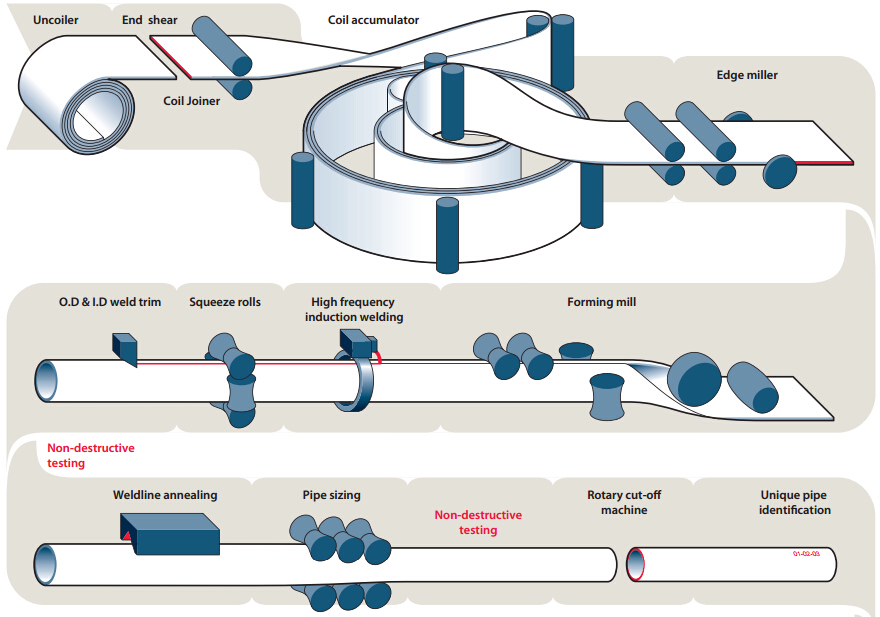
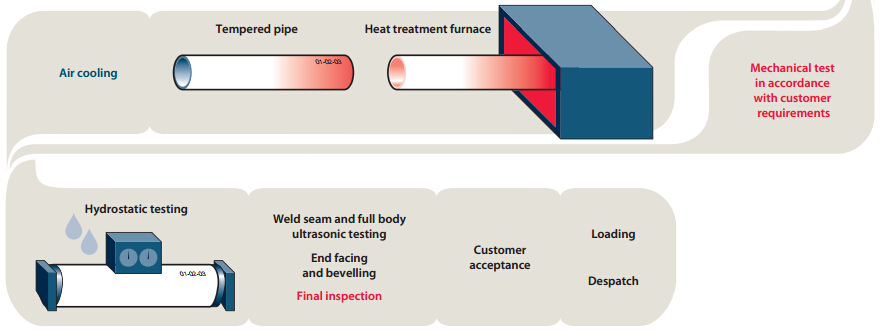
Characteristics
- High-Quality Welds: HFI welding produces strong, reliable welds with good mechanical properties and minimal defects.
- Efficiency: The process is highly efficient and suitable for mass production, providing high throughput.
- Consistent Dimensions: The precise control during manufacturing results in pipes with consistent dimensions and wall thickness.
- Surface Finish: Typically, HFI pipes have a smooth surface finish, which is beneficial for many applications.
Applications
- Oil and Gas Industry: Used for transporting oil, gas, and other fluids under moderate pressure and temperature conditions.
- Construction and Infrastructure: Utilized in structural applications, such as columns and beams, due to their strength and reliability.
- Automotive Industry: Used in the manufacturing of various automotive components.
- Water and Sewage Systems: Suitable for water supply lines and sewage systems due to their durability and corrosion resistance.
- Mechanical and General Engineering: Employed in various mechanical applications requiring pipes with precise dimensions and good mechanical properties.
Advantages of HFI Steel Pipes
- Strength and Durability: HFI pipes offer excellent mechanical properties, making them suitable for demanding applications.
- Cost-Effective: The high efficiency of the HFI welding process makes these pipes relatively cost-effective compared to some other types of welded pipes.
- Quality Control: The process allows for rigorous quality control, ensuring high-quality welds and consistent pipe characteristics.
- Versatility: HFI pipes can be produced in a wide range of sizes and thicknesses, making them versatile for various applications.
Comparison with Other Types of Welded Pipes
| Feature | HFI (High-Frequency Induction) | ERW (Electric Resistance Welded) | EFW (Electric Fusion Welded) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Welding Process | High-frequency induction heating and pressure | Electric resistance heating and pressure | Electric arc or high-frequency induction welding |
| Material Source | Steel coils | Steel coils | Steel plates or coils |
| Strength | High strength, suitable for moderate pressure applications | Moderate strength, suitable for low to medium pressure | Higher strength, suitable for high-pressure applications |
| Cost | Cost-effective due to efficient process | Generally cost-effective | More expensive due to complex process |
| Applications | Oil & gas pipelines, construction, automotive, water systems | Water supply lines, automotive components, low to medium pressure applications | Oil & gas pipelines, structural applications, high-temperature environments |
| Wall Thickness | Consistent wall thickness, can be produced in various sizes | Consistent, typically thinner walls | Can be produced with thicker walls |
| Surface Finish | Smooth surface finish | Generally smooth finish | May have a rougher finish due to welding process |
- Material Preparation:
- Slitting Line: The process begins with cutting a steel strip of the required size on a slitting line.
- Cold Forming: The strip is then fed through a tube mill where it undergoes cold forming using a set of cage rolls and fin passes to form an open pipe.
- High-Frequency Induction Welding:
- Induction Coil: The open pipe passes through a high-frequency inductor, a metal coil with single or multiple windings.
- Induced Current: High-frequency ring current is induced into the pipe, which concentrates at the strip edges converging at the welding point.
- Resistance Heating: The required welding temperature is generated by resistance heating along a narrow zone at the strip edges.
- Pressure Rollers: The heated edges are squeezed together by pressure rollers, resulting in a homogeneous longitudinal weld without any filler metals.
- Flash Removal:
- Inside and Outside Beads: The flash generated on the inside and outside surfaces during welding is removed to the level of the pipe surface using special tools to ensure unobstructed fluid or gas flow.
- Post-Weld Treatment:
- Inductive Annealing: The HFI weld undergoes multi-step inductive annealing to ensure the weld area properties match those of the base material.
- Sizing and Cutting: The continuous pipe string is straightened, size rolled, and cut to length by a flying saw.
- Finishing and Testing:
- Further Processing: Pipes are transferred to finishing sections for processes such as straightening, end chamfering/facing, hydro-testing, non-destructive testing, threading, and galvanizing, based on customer requirements.
Expertise and Applications
TWI Expertise:
- Mechanical Properties and Metallurgical Studies: TWI conducts mechanical properties analysis and metallurgical studies on welds.
- Defect Examination: It examines defects and optimizes HF butt welding of tailored blanks.
- Resource Provision: TWI provides testing facilities for fracture mechanics studies, corrosion and metallurgical test equipment, non-destructive testing, process advice, troubleshooting, and tailored training courses.
Application Areas:
- Industries: HFW welded steel pipes are widely used in oil, natural gas, water, and other liquid transportation and distribution lines, heating, cooling, and ventilation piping, and steel structures for construction and other general purposes.
- Benefits: These pipes are preferred for their precise production tolerances and high-capacity manufacturing methods.
Specifications and Standards
HFI welded steel pipes are produced in compliance with various international standards, including API, ASTM/ASME, DIN, BS, EN, and JIS. Below are the specifications and dimensions for different standards:
API SPEC 5CT
| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Casting | API 5CT | Ø48.3 |
J55, K55, N80, L80 |
| Tubing | API 5CT | Ø48.3 |
J55, K55, N80, L80, H40 |
API SPEC 5L
| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Line Pipes | API 5L | Ø60.3 |
A25, A, B, X42, X46, X52, X56, X60, X65, X70, X80 |













