No entanto, 904L continua a ser a escolha indispensável para ambientes químicos complexos onde a água do mar é misturada com ácidos redutores, ou para sistemas estagnados onde seu conteúdo de cobre pode ajudar na resistência a tipos específicos de biocorrosão. Além disso, se a aplicação exigir extensa conformação a frio ou envolver condições criogênicas, a natureza austenítica pura do 904L fornece um nível de confiabilidade que a estrutura duplex não pode garantir.
Tecnologia
O barulho 2391 Tubo sem costura grau St45, fornecido na condição NBK, representa o auge da engenharia de tubos de aço de precisão. Sua excelência é um resultado calculado do controle metalúrgico avançado, plasticidade severa no trabalho a frio, e processamento térmico meticuloso. A sua superioridade funcional é validada pela sua comprovada capacidade de:
O método de formação JCOE oferece um equilíbrio superior de desempenho mecânico, Controle de estresse residual, e integridade da solda em comparação com a flexão de UoE e três rolos. Enquanto Uoe permanece preferível para o alto volume, Tubos de parede fina, JCOE é indispensável para parede pesada, Aplicações de alta resistência. Os avanços futuros devem se concentrar na otimização da força da imprensa acionada pela IA e nas técnicas de formação híbrida para aumentar ainda mais a eficiência.
Para ASME B31.3, A pressão do projeto deve ser a pressão máxima que o sistema deve experimentar em condições normais ou perturbadas, incluindo qualquer configuração de alívio de pressão ou válvula de segurança, com consideração para práticas de design conservador.
Resumo: O efeito da temperatura de temperamento após a queima de 920 ℃ Na microestrutura e propriedades mecânicas de um aço de revestimento de óleo profundo do poço, foi estudado com a ajuda do microscópio óptico (Se), Microscópio eletrônico de varredura (Quem), máquina de teste de tração e outros equipamentos. Os resultados mostram que o aço de teste é temperado em 500-600 ℃ Para obter troostita temperada, que tem alta força, Plasticidade e resistência. A faixa de flutuação do produto da plástico-força é 20.5-22.1 GPA ·%, e a faixa de flutuação de energia de absorção de impacto é 94.6-100.3 J.. Quando a temperatura de temperamento é 550 ℃, O aço de teste de invólucro de petróleo profundo tem as melhores propriedades mecânicas abrangentes. Neste momento, A força de tração é 978 MPa, a força de escoamento é 935 MPa, O produto de plástico de força é 22.1 GPA ·%, e a energia de absorção de impacto é 100.3 J.. Palavras -chave: Aço da carcaça de óleo; temperatura de temering; microestrutura; propriedades mecânicas
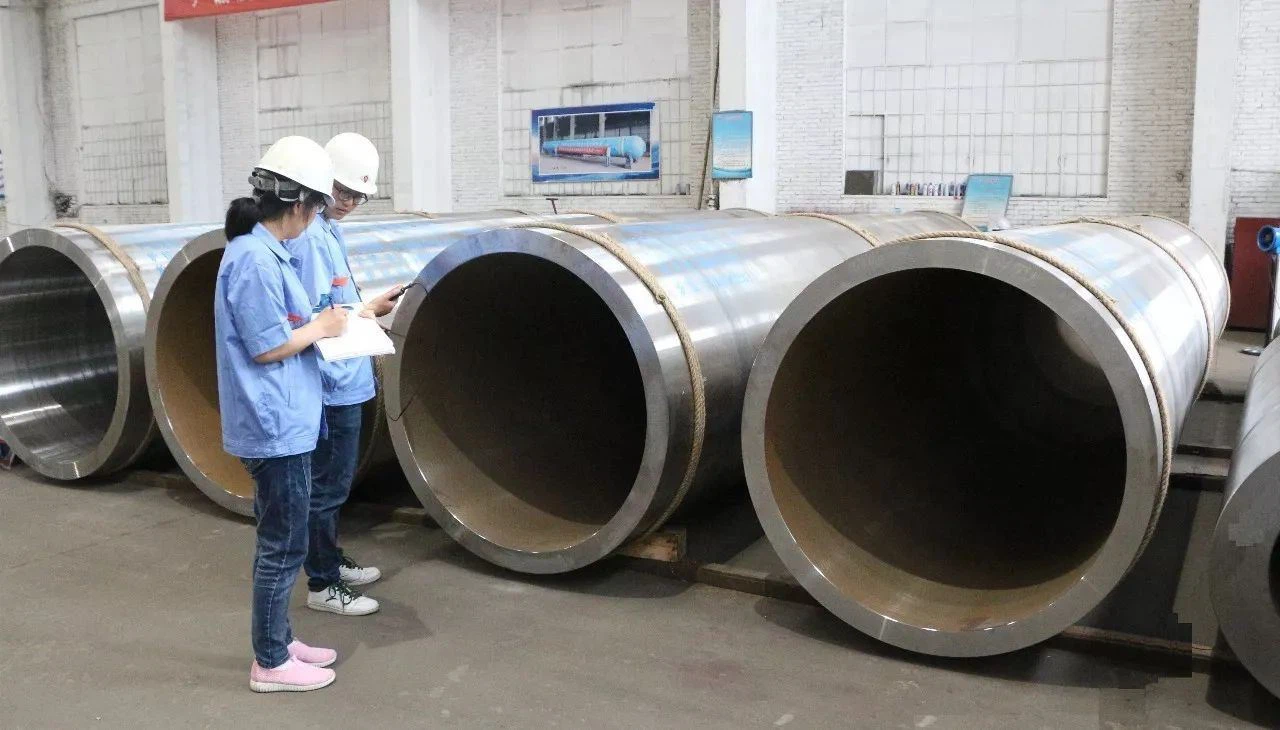
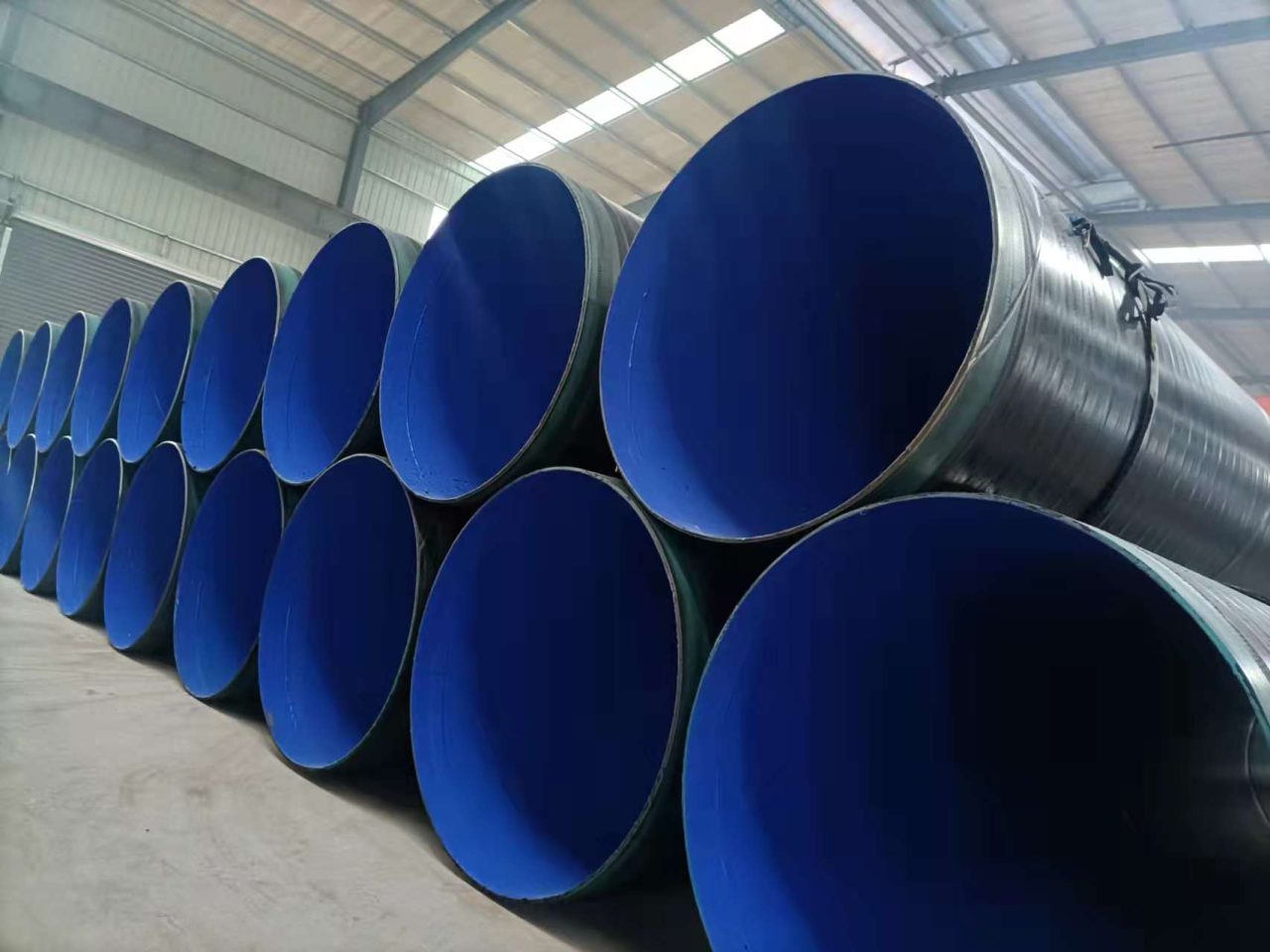
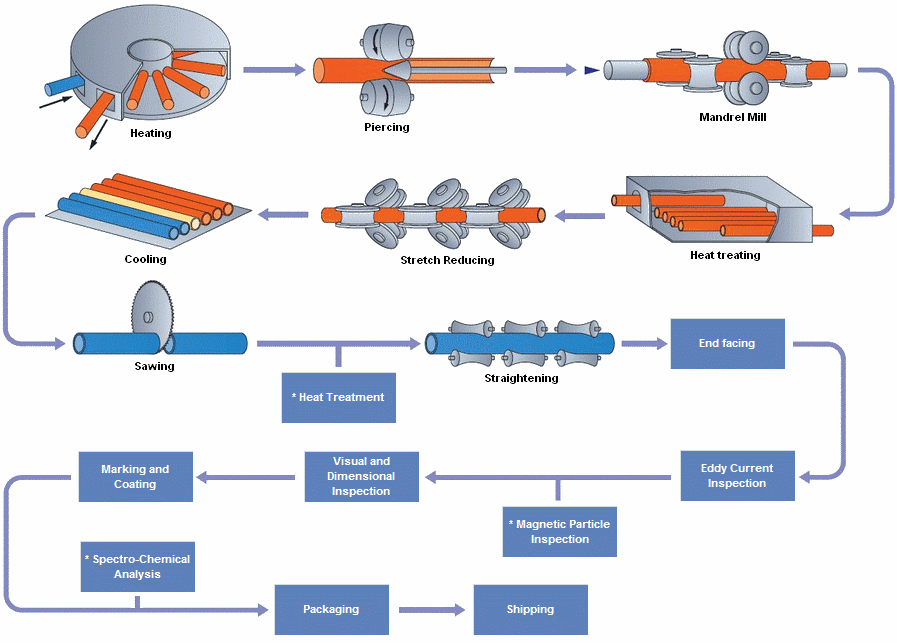
Tubos de aço sem paredes grossas de grande diâmetro, produzido através de processos avançados como piercing quente e tratamento térmico, oferecer força e confiabilidade excepcionais. Notas internacionais de EN (por exemplo, 34CrMo4) e ASTM (por exemplo, A519 4140) juntamente com os padrões GB atendem às diversas necessidades, De cilindros hidráulicos à infraestrutura energética, garantir o desempenho sob alta pressão e estresse.
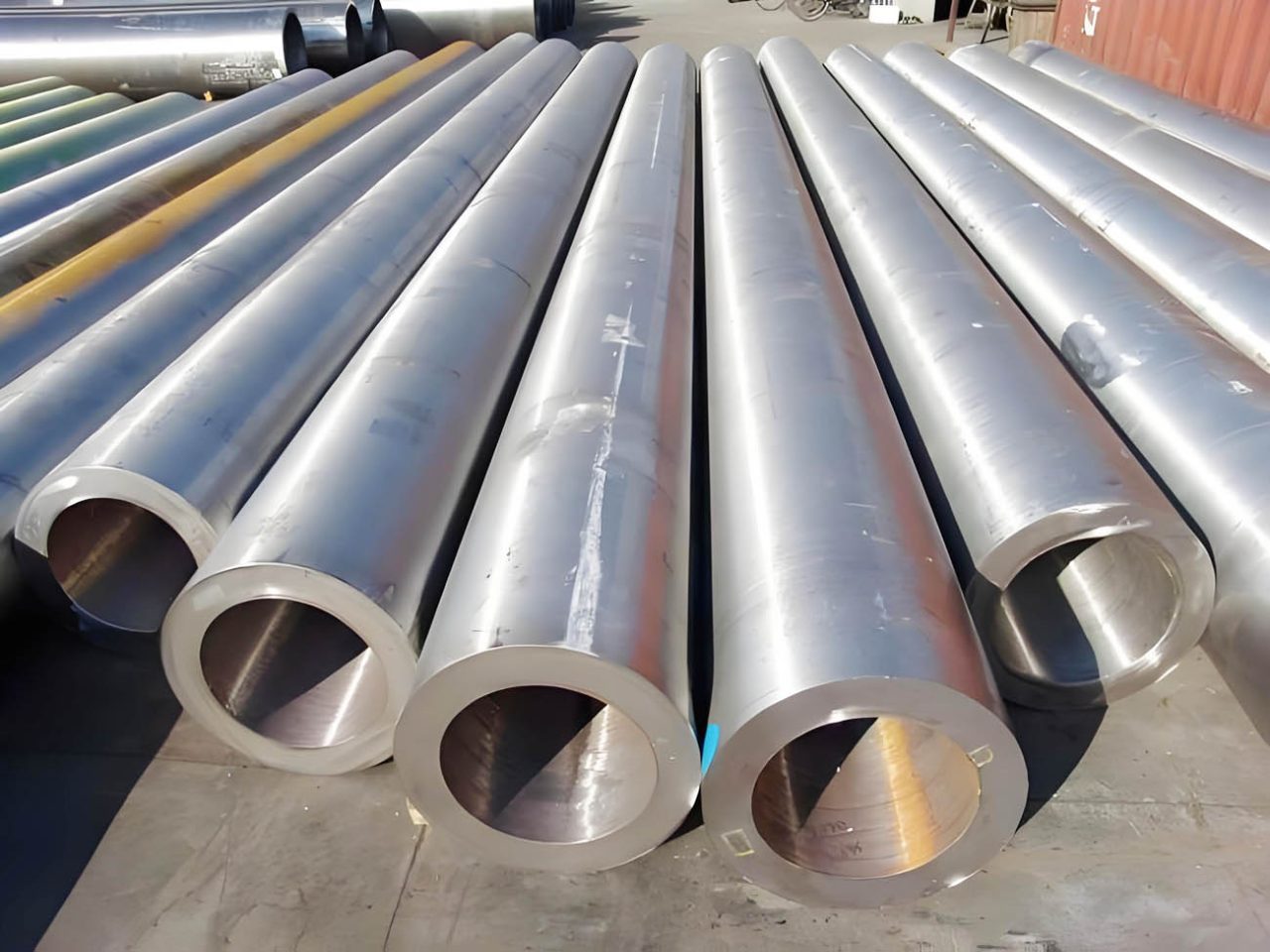
Para cilindros hidráulicos de alta pressão, tubos de aço sem costura, como ST52 (E355), SAE 4140 (42CrMo), 37Mn, e 34crmo4 são amplamente utilizados, aderindo a padrões como DIN 2391, ASTM A519, e GB 18248. Essas notas oferecem a força necessária, resistência, e precisão para garantir a segurança e o desempenho sob pressões extremas. A seleção depende de requisitos de pressão específicos, condições ambientais, e processos de fabricação como aprimoramento ou tratamento térmico.
A soldagem de pipelines uns N08825 exige uma abordagem holística que integra ciência do material, engenharia de processos, e controle rigoroso de qualidade. Otimizando os parâmetros TIG/MIG/SMAW, Mitigação de defeitos através de tratamentos pré/pós-soldado, e aderir aos padrões internacionais, As indústrias podem alavancar todo o potencial da liga em ambientes corrosivos e de alta temperatura. Avanços contínuos nas tecnologias de soldagem prometem eficiência e confiabilidade aprimoradas para aplicativos futuros.
Soldagem Inconel 625 e p22 requer controle meticuloso de gradientes térmicos, Seleção de enchimento, e tratamentos pós-solda para lidar com as incompatibilidades metalúrgicas. Padrões da indústria e processos avançados (por exemplo, EMB, soldagem a laser) Aumente a confiabilidade conjunta em aplicações críticas. Continuous innovation in welding technology will further optimize these dissimilar joints for extreme environments.
Através da prática de soldagem de mais de 400 Portas Dyne na seção de gaseificação do dispositivo de síntese de amônia química Liuguo, É mostrado que o processo de soldagem acima pode garantir completamente a qualidade da soldagem. A julgar pelo resultado da taxa de aprovação de 96%, é suficiente. Provar isso.
Resumindo, Nickel 200's surface treatment technology includes methods such as pickling, Superfícies brilhantes de recozimento e polimento. Essas tecnologias têm suas vantagens e espaço exclusivos para melhorias em diferentes cenários de aplicação.
A escolha entre Inconel® X-750 (EUA N07750) e liga de níquel 600 depende em grande parte dos requisitos específicos do aplicativo: Escolha Inconel X-750 para o estresse alto, aplicações de alta temperatura onde força mecânica, Resistência à fadiga, e a resistência da fluência é crítica (por exemplo, aeroespacial, nuclear, e turbinas a gás). Escolha liga de níquel 600 Para resistência à corrosão versátil em aplicações de uso geral ou onde a fabricação e a eficiência de custo são mais importantes (por exemplo, processamento químico, marinho, e trocadores de calor).
Hastelloy C-276 se destaca como uma das ligas mais versáteis e resistentes à corrosão disponíveis hoje. Suas propriedades únicas o tornam indispensável nas indústrias onde o desempenho e a confiabilidade são fundamentais. De resistir a ácidos agressivos em plantas químicas até as condições adversas dos ambientes marinhos, Hastelloy C-276 provou seu valor várias vezes. Embora seus desafios de alto custo e fabricação possam representar limitações, Os benefícios que ele oferecem em muito essas desvantagens para aplicações críticas. Como as indústrias globais continuam a ultrapassar os limites da inovação, Hastelloy C-276 continuará sendo um material da pedra angular para ambientes exigentes, garantindo a segurança, eficiência, e durabilidade nos próximos anos.
A análise do CFD do fluxo de água dentro dos tubos de cotovelo de Buttweld revela que o tubo de cotovelo de gado normal supera o tubo de cotovelo de arestas afiadas em termos de eficiência de fluxo, consumo de energia, e integridade estrutural. As principais descobertas incluem:
Ao selecionar entre tubos de liga níquel alta e soldada e soldados, Considere fatores como requisitos de pressão, resistência à corrosão, custo, e disponibilidade de tamanho para garantir que você escolha o tipo certo de tubo para o seu projeto. Para obter mais informações ou assistência na seleção do tubo certo, Consulte um especialista em materiais ou fornecedor que possa ajudar a guiá-lo no processo de tomada de decisão.
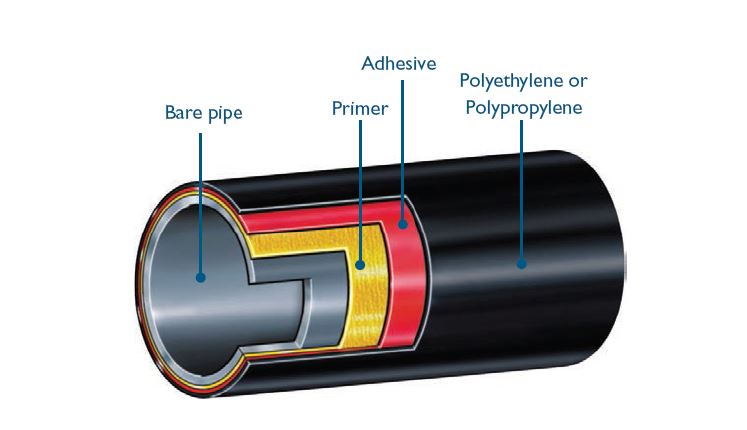
Os revestimentos 3LPP e 3PE oferecem excelente proteção para tubulações de aço, Mas eles são projetados para diferentes condições operacionais. 3Revestimentos LPP, com sua resistência de alta temperatura e força mecânica superior, são ideais para oleodutos em ambientes agressivos ou para aqueles que transportam fluidos quentes. Por outro lado, 3Revestimentos PE, com sua relação custo-benefício e boa flexibilidade, são mais adequados para oleodutos em ambientes moderados, onde a temperatura e a tensão mecânica são mais baixos.
Juntas soldadas em tubos de liga de aço ASTM A335 P5 são suscetíveis a diversas formas de corrosão, especialmente em ambientes agressivos. O processo de soldagem, zona afetada pelo calor, e o tratamento térmico pós-soldagem desempenham papéis críticos na determinação do comportamento de corrosão do material. Ao empregar técnicas de soldagem adequadas,
Seguindo estas diretrizes, Os operadores podem efetivamente gerenciar a integridade dos tubos corroídos, garantir uma operação segura contínua em ambientes desafiadores.
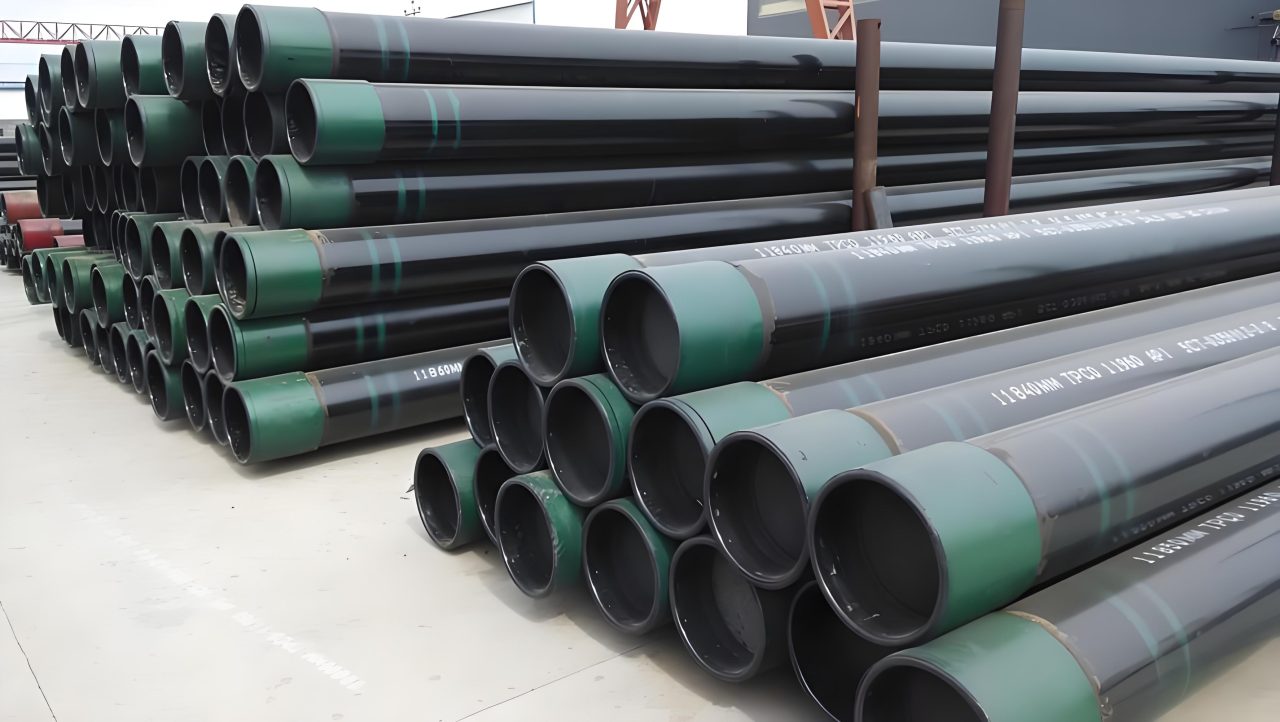
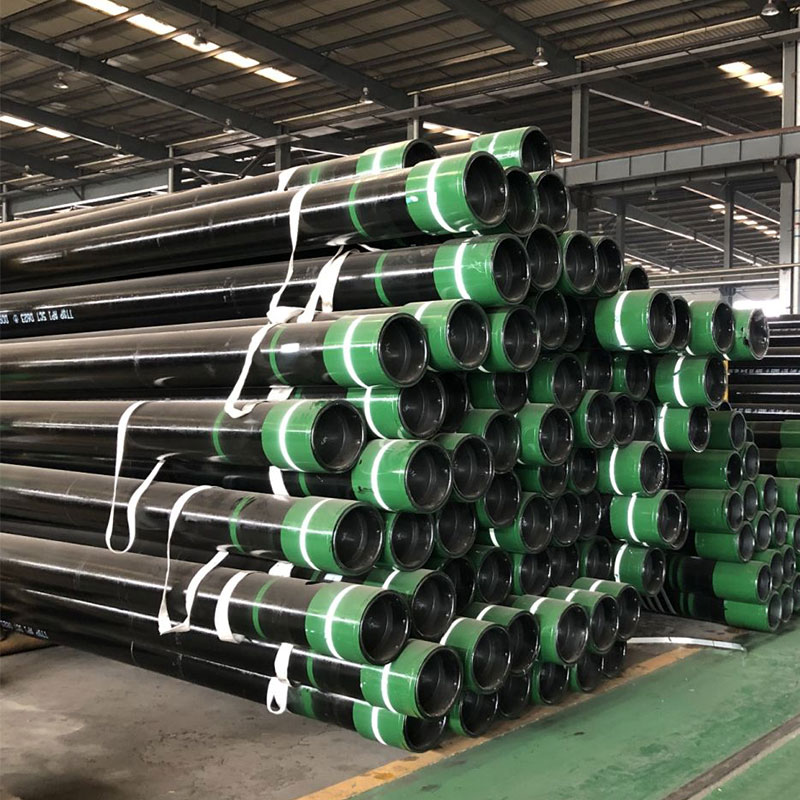
O mercado de tubos de carcaça está pronto para o crescimento e a transformação, à medida que se adapta à evolução das demandas da indústria e dos avanços tecnológicos. Enquanto desafios como a volatilidade dos preços da matéria -prima e as interrupções da cadeia de suprimentos persistem, the market's resilience and innovation capacity offer significant opportunities for growth. Quando nos aproximamos 2025, o foco na sustentabilidade, Tecnologias inteligentes, e materiais avançados moldarão o futuro do mercado de tubos de carcaça, Garantir sua relevância e contribuição contínuas para o cenário global de energia.
A tecnologia de conexão para tubos de invólucro é um componente crítico da construção de poços, garantindo a operação segura e eficiente de poços de petróleo e gás. Desde conexões tradicionais de rosqueamento e soldado até tecnologias mecânicas e inteligentes avançadas, A indústria continua inovando para atender às demandas de ambientes cada vez mais desafiadores. Selecionando a tecnologia de conexão apropriada e aderência às melhores práticas, Os operadores podem otimizar o desempenho do poço, Aumente a segurança, e prolongar a vida útil de seus poços.
As fases da perfuração, invólucro, e a tubulação é parte integrante do desenvolvimento bem -sucedido de um poço de petróleo ou gás. Cada fase requer planejamento cuidadoso, execução precisa, e adesão aos padrões de segurança e ambiental. Ao entender e gerenciar efetivamente essas fases, Os operadores podem otimizar a produção, minimizar riscos, e garantir a longevidade do poço. À medida que a tecnologia avança, Novas técnicas e materiais continuam a aumentar a eficiência e a segurança dessas operações, contribuindo para a evolução contínua da indústria de petróleo e gás.
Dano de tubo de poço coloca os desafios significativos à integridade e eficiência dos poços. Compreender as causas de danos e empregar tecnologias de reparo apropriadas são essenciais para manter operações seguras e eficazes. De corrosão e estresse mecânico à atividade sísmica e desgaste abrasivo, Vários fatores podem contribuir para os danos causados pelo invólucro. Utilizando uma combinação de métodos de reparo tradicionais e tecnologias avançadas, Os operadores podem abordar efetivamente essas questões e prolongar a vida útil de seus poços. Adicionalmente, A implementação de medidas preventivas e práticas recomendadas pode ajudar a minimizar o risco de danos e garantir o sucesso contínuo de operações de poço. À medida que a tecnologia continua a evoluir, Novas soluções e materiais aumentarão ainda mais a capacidade de prevenir e reparar danos causados pelo tubo de carcaça do poço, contribuindo para a sustentabilidade e segurança da indústria de petróleo e gás.
Resumindo, Enquanto o revestimento e o forro são essenciais para proteger pipelines, Eles servem a propósitos distintos e são aplicados em diferentes contextos. O revestimento se concentra na proteção externa, proteger tubos de fatores ambientais, Enquanto o revestimento aborda a proteção interna, proteger os tubos das substâncias que eles carregam. Ambos os processos oferecem benefícios significativos, incluindo resistência à corrosão, Eficiência de fluxo aprimorada, e vida útil prolongada. À medida que a tecnologia continua a avançar, Espera -se que a eficácia e a sustentabilidade dos métodos de revestimento e revestimento melhorem, garantindo a confiabilidade e a segurança contínuas dos sistemas de pipeline em vários setores.
O projeto da pressão de aplicação para tubulações químicas é influenciado por uma combinação de propriedades químicas, Requisitos de vazão, perda por atrito, seleção de materiais, e condições ambientais. Ao considerar cuidadosamente esses fatores, engenheiros podem garantir o transporte seguro e eficiente de substâncias químicas, minimizando riscos e mantendo a integridade do pipeline.
A outra razão principal pela qual a galvanização por imersão a quente fornece melhor proteção contra corrosão é que o revestimento é aplicado durante o processo de fabricação, antes da instalação do aço.. Isso significa que quaisquer áreas cortadas ou danificadas durante a instalação ainda terão uma camada protetora. Outros métodos de galvanização, como pré-galvanização, revestir o aço antes de ser cortado e fabricado. Isso deixa quaisquer áreas cortadas ou danificadas durante a instalação vulneráveis à ferrugem e corrosão.
As especificações ASTM International para tubos de aço listam requisitos padrão para tubos de caldeiras e superaquecedores, tubos de serviço geral, tubos de aço em serviço de refinaria, tubos do trocador de calor e do condensador, tubulação mecânica e estrutural.
Tipo A- Usado onde há amplo espaço para a cabeça disponível. Elevação específica é desejável. Tipo B- Usado onde o headroom é limitado. O acessório da cabeça é um único terminal. Tipo C- Usado onde o headroom é limitado. O acessório da cabeça é com alças lado a lado
O tubo de aço carbono é altamente resistente a choques e vibrações, o que o torna ideal para transportar água, óleo & gás e outros fluidos sob estradas. Dimensions Size: 1/8″a 48″ / DN6 to DN1200 Thickness: Sch 20, DST, 40, XS, 80, 120, 160, XXS Type: Seamless or welded pipe Surface: Cartilha, Óleo antiferrugem, FBE, 2Educação Física, 3LPE Coated Material: ASTM A106B, A53, API 5L B, X42, X46, X52, X56, X60, X65, X70 Service: Corte, Chanfrar, Rosqueamento, Ranhura, Revestimento, Galvanização
Tubos sem costura são fabricados usando um processo de perfuração, onde um tarugo sólido é aquecido e perfurado para formar um tubo oco. Tubos soldados, por outro lado, são formados pela união de duas bordas de placas ou bobinas de aço usando várias técnicas de soldagem.
O 3 elements of pipe dimension Dimension Standards of carbon and stainless steel pipe (ASME B36.10M & B36.19M) Cronograma de tamanho de tubo (Agendar 40 & 80 tubo de aço significa) Meios de tamanho nominal do tubo (NPS) e diâmetro nominal (DN) Tabela de dimensões de tubos de aço (Tabela de tamanhos) Cronograma de Classe de Peso do Tubo (WGT)