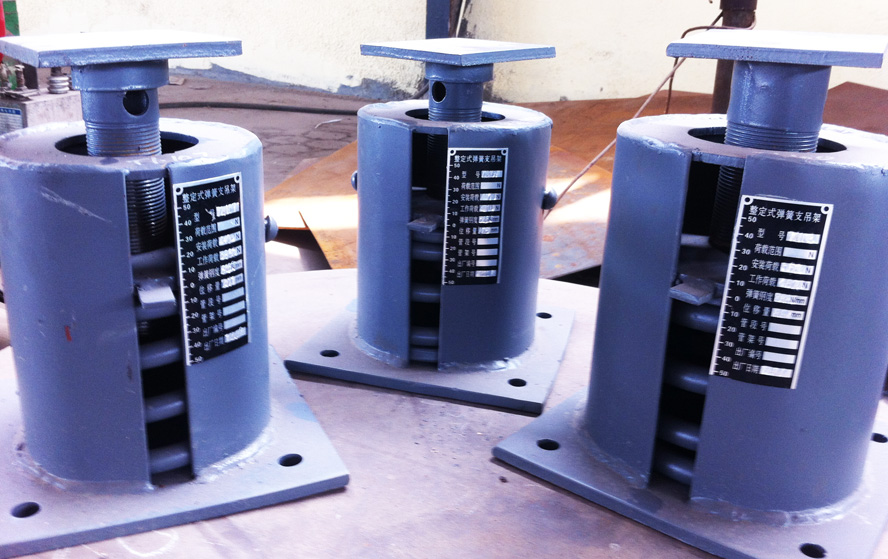
Spring Hanger and Support

Type A- Used where ample head room is available. Specific elevation is desirable.
Type B- Used where headroom is limited. Head attachment is a single lug.
Type C- Used where headroom is limited. Head attachment is side by side lugs
Type D- Used where the spring hanger is mounted on top of a pair of back to back channels. Provides for adjustment of the load from above the supporting channels
Type E- Used where the spring hanger is mounted on top of a pair of back to back channels. Provides for adjustment of the load from below the supporting channels.
Type F-Used where the spring hanger must be placed under the piping to provide support from the floor or a structural member. Typically supplied with a load flange but can also be supplied with a roller.
Type G-Used were head room is insufficient to accommodate the spring hangerand the necessary associated hardware. Also used where an interference exits directly above the piping system being supported is not centered between the spring hangers, each hanger will then carry its proportional load
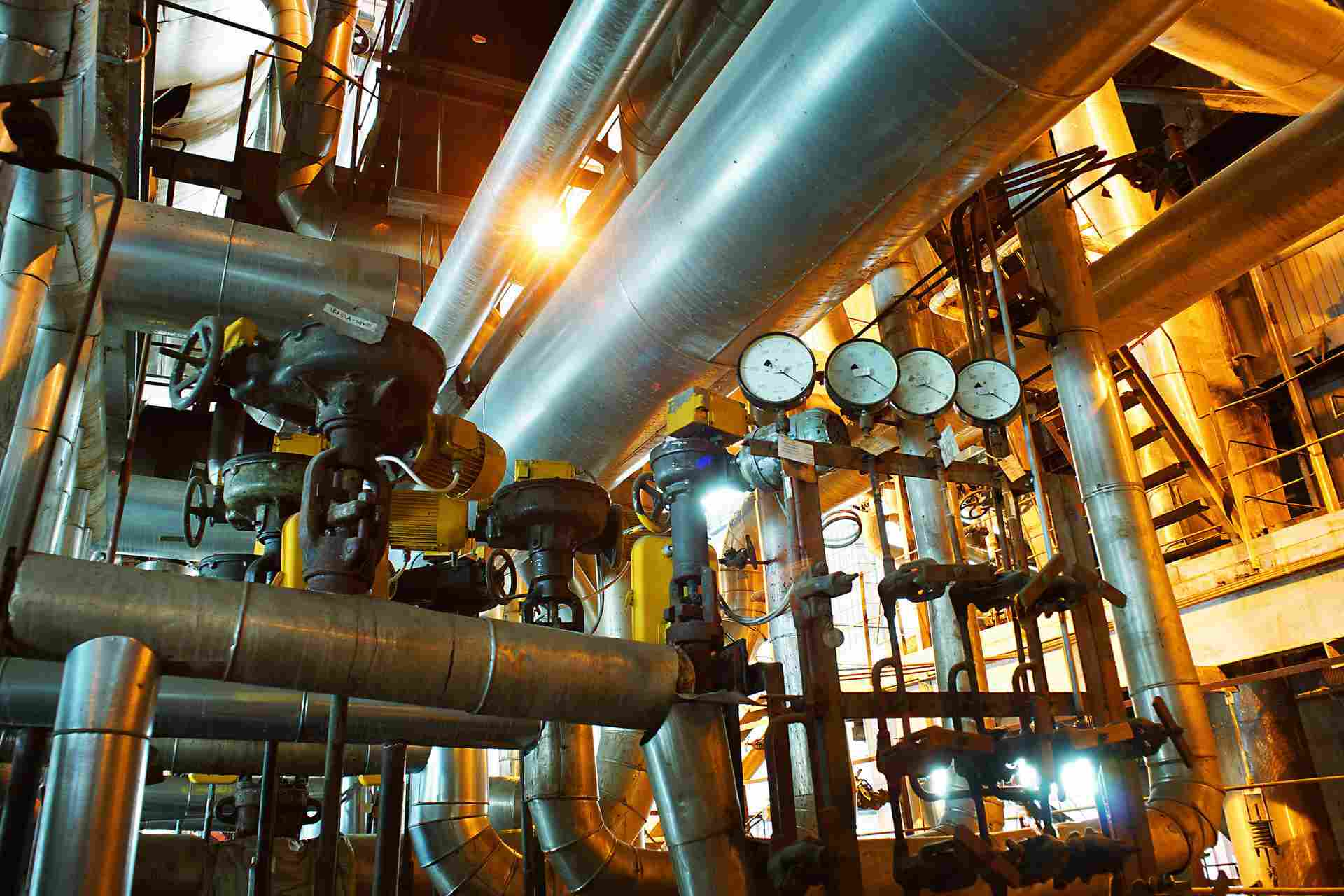
When pipe moves vertically and when loads on attached equipment are required to remain constant as the pipe moves, then a spring hanger should be considered. Spring hangers are used to provide support to a pipe at a support location at the time the pipe is installed. Pipe movement is generally caused by thermal expansion or contraction of the piping system but it can also result from the movement of the equipment to which the pipe is connected. The underlying objective for using a spring hanger is to minimize the change of load applied by the piping on the connected equipment.




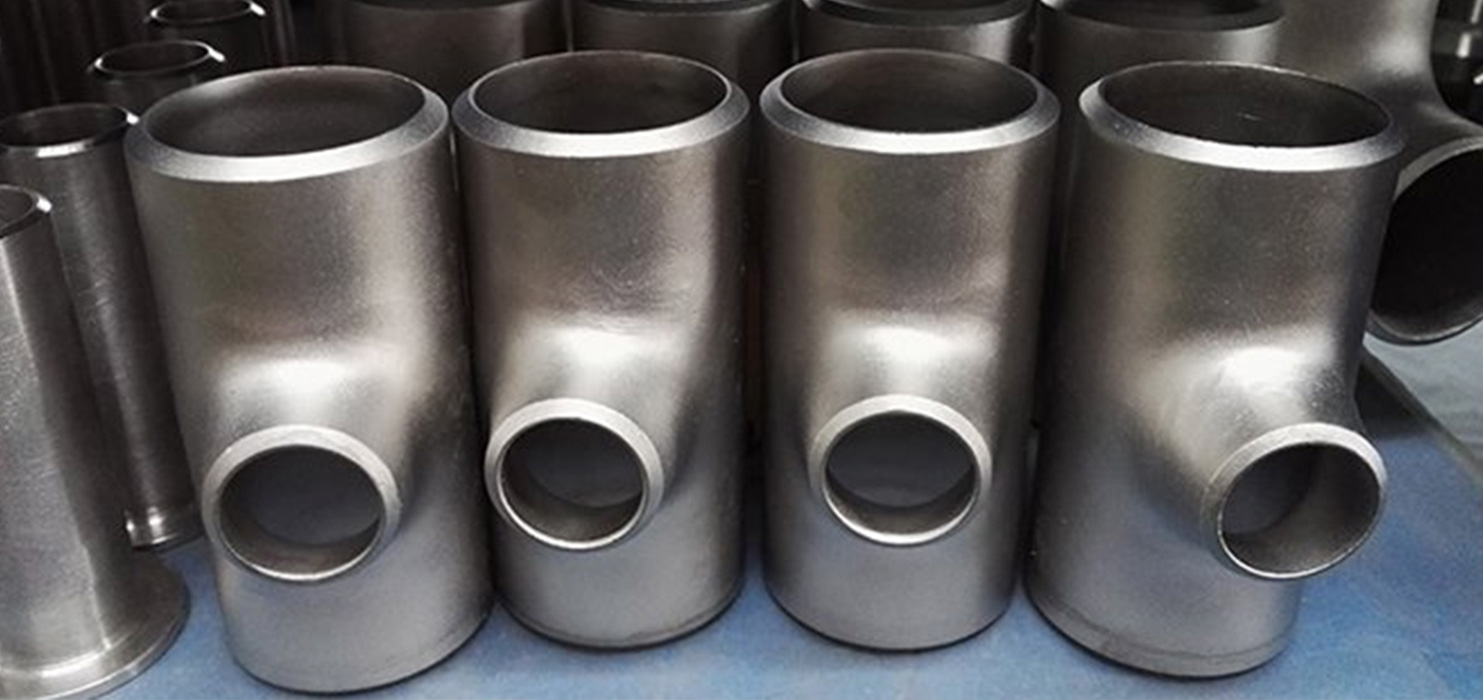
ERW BLACK Pipes. Electric Resistance Welded (ERW) Pipes are manufactured from Hot Rolled Coils / Slits. All the incoming coils are verified based on the test certificate received from steel mill for their chemistry and mechanical properties. ERW pipe is cold-formed into a cylindrical shape, not hot-formed.
Seamless pipe is manufactured by extruding the metal to the desired length; therefore ERW pipe have a welded joint in its cross-section, while seamless pipe does not have any joint in its cross-section through-out its length. In Seamless pipe, there are no welding or joints and is manufactured from solid round billets.
The 3 elements of pipe dimension Dimension Standards of carbon and stainless steel pipe (ASME B36.10M & B36.19M) Pipe Size Schedule (Schedule 40 & 80 steel pipe means) Means of Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) and Nominal Diameter (DN) Steel Pipe Dimension Chart (Size chart) Pipe Weight Class Schedule (WGT)
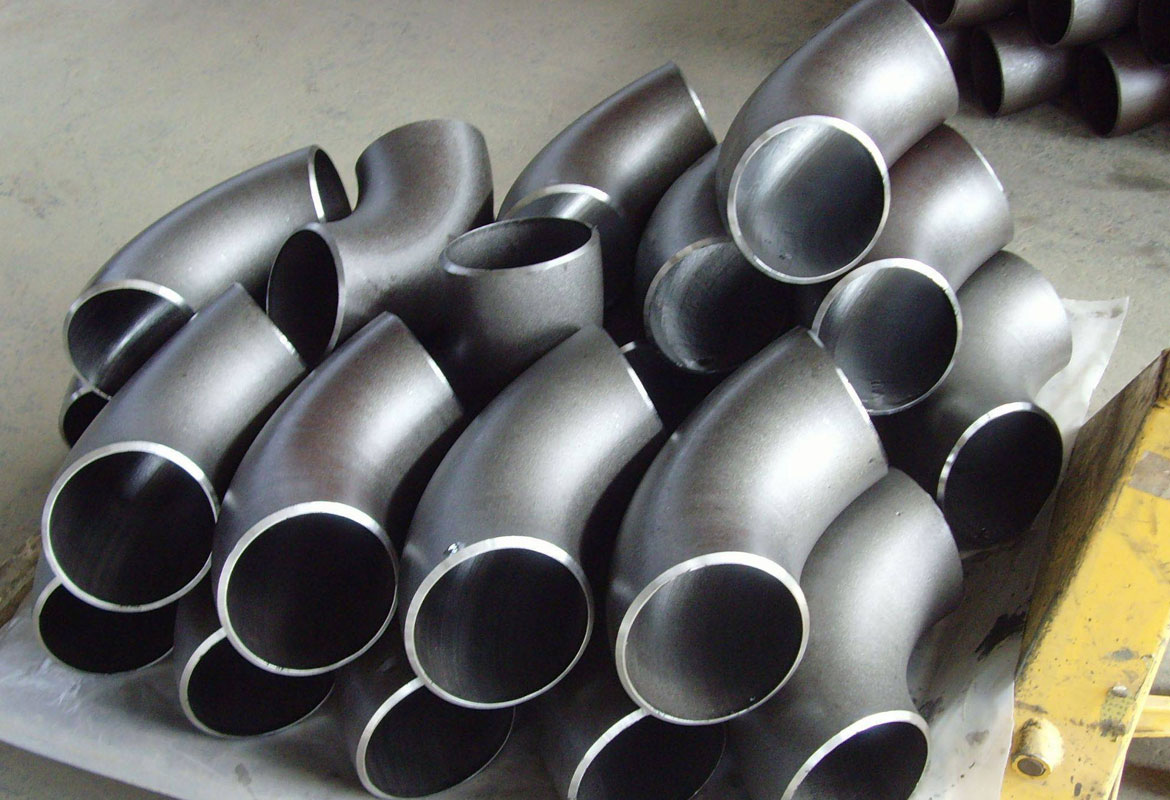
Pipe fittings are used in plumbing systems to connect straight sections of pipe or tubes, to accommodate different sizes or shapes, and for other purposes such as regulating (or measuring) fluid flow. These fittings are used in plumbing systems to control the transfer of water, gas or liquid waste within pipes or plumbing systems in domestic or commercial environments. Fittings (especially uncommon types) require money, time, materials and tools to install and are an important part of plumbing and plumbing systems. Common pipe fittings mainly include: flange, elbows, couplings, unions, spools, reducers, bushings, tees, diverter tees, crosses, caps, plugs, barbs and valves. Although valves are technically fittings, they are usually discussed separately.
Pipe fitting bodies are usually made of the same base material as the pipe or tubing they are connected to: copper, steel, PVC, CPVC or ABS. Any material permitted by plumbing, health or building codes (as applicable) may be used, but it must be compatible with the other materials in the system, the fluid being conveyed, and the temperature and pressure inside (and outside) the system. Brass or bronze fittings over copper Common in plumbing and plumbing systems. Fire resistance, shock resistance, mechanical strength, anti-theft and other factors also affect the choice of material for pipe fittings.
Material Stainless Steel ASME / ASTM SA / A403 SA / A 774 WP-S, WP-W, WP-WX, 304, 304L, 316, 316L, 304/304L, 316/316L, DIN 1.4301, DIN1.4306, DIN 1.4401, DIN 1.4404 Dimension ANSI B16.9, ANSI B16.28, MSS-SP-43 Type A, MSS-SP-43 Type B, JIS B2312, JIS B2313 Thickness Schedule 5S, 10S, 20S, S10, S20, S30, STD, 40S, S40, S60, XS, 80S, S80, S100, S120, S140, S160, XXS and etc.







