Multifunctional ms erw black round tube
ERW BLACK Pipes. Electric Resistance Welded (ERW) Pipes are manufactured from Hot Rolled Coils / Slits. All the incoming coils are verified based on the test certificate received from steel mill for their chemistry and mechanical properties. ERW pipe is cold-formed into a cylindrical shape, not hot-formed.
ERW black round steel pipe
Seamless pipe is manufactured by extruding the metal to the desired length; therefore ERW pipe have a welded joint in its cross-section, while seamless pipe does not have any joint in its cross-section through-out its length. In Seamless pipe, there are no welding or joints and is manufactured from solid round billets.
Dimensions and weights of seamless Pipe according to standards
The 3 elements of pipe dimension Dimension Standards of carbon and stainless steel pipe (ASME B36.10M & B36.19M) Pipe Size Schedule (Schedule 40 & 80 steel pipe means) Means of Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) and Nominal Diameter (DN) Steel Pipe Dimension Chart (Size chart) Pipe Weight Class Schedule (WGT)
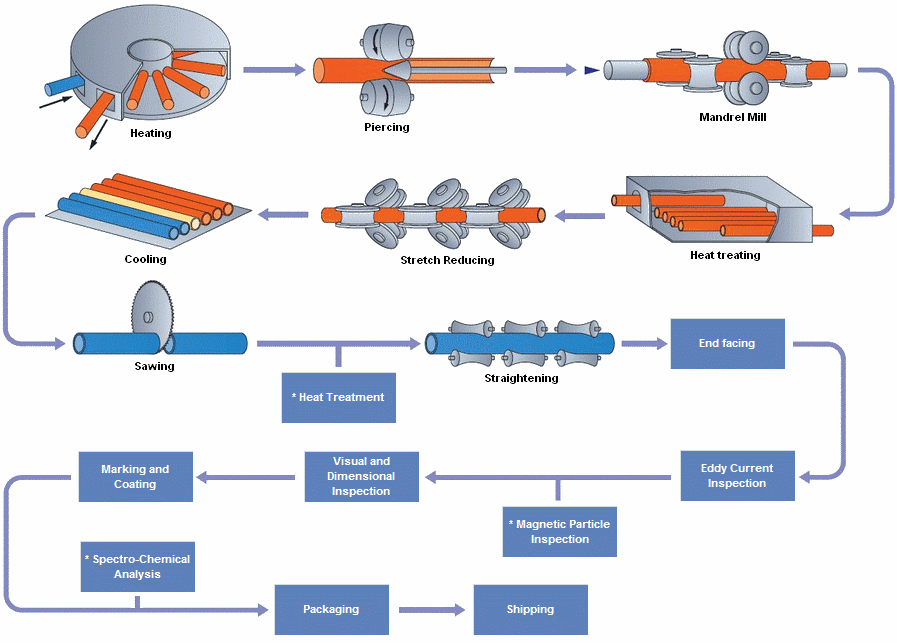
Steel Pipe and Manufacturing Processes
Seamless pipes are manufactured using a piercing process, where a solid billet is heated and pierced to form a hollow tube. Welded pipes, on the other hand, are formed by joining two edges of steel plates or coils using various welding techniques.
UL List Steel Pipe
Carbon steel pipe is highly resistant to shock and vibration which making it ideal to transport water, oil & gas and other fluids under roadways. Dimensions Size: 1/8″ to 48″ / DN6 to DN1200 Thickness: Sch 20, STD, 40, XS, 80, 120, 160, XXS Type: Seamless or welded pipe Surface: Primer, Anti rust oil, FBE, 2PE, 3LPE Coated Material: ASTM A106B, A53, API 5L B, X42, X46, X52, X56, X60, X65, X70 Service: Cutting, Beveling, Threading, Grooving, Coating, Galvanizing
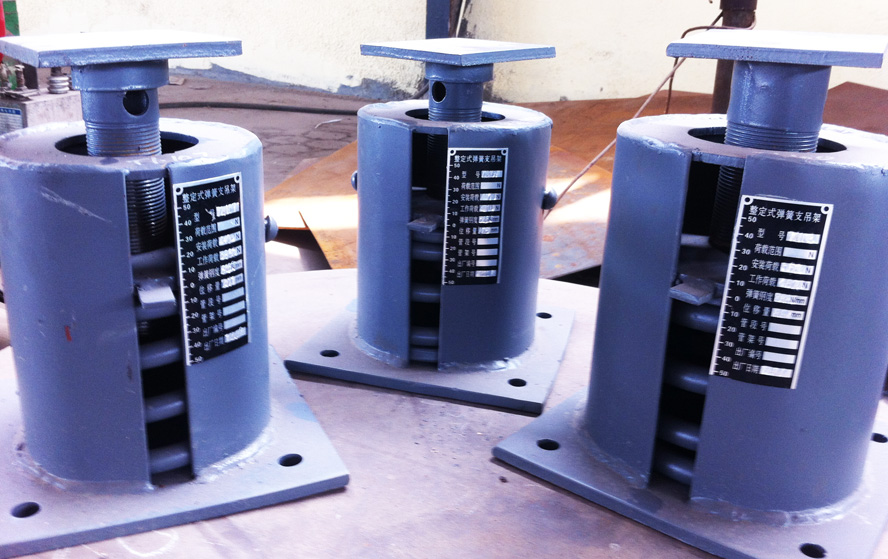
Spring Hanger and Support
Type A- Used where ample head room is available. Specific elevation is desirable. Type B- Used where headroom is limited. Head attachment is a single lug. Type C- Used where headroom is limited. Head attachment is side by side lugs