ASTM อินเตอร์เนชั่นแนล, เดิมชื่อ American Society for Testing and Materials, เป็นองค์กรมาตรฐานสากลที่พัฒนาและเผยแพร่มาตรฐานทางเทคนิคที่เป็นเอกฉันท์โดยสมัครใจสำหรับวัสดุหลากหลายประเภท, สินค้า, ระบบ, และบริการต่างๆ เดิม ASTM เป็นที่รู้จักในชื่อ American Society of the International Association for Testing and Materials เมื่อก่อตั้งขึ้น 1898 โดยวิศวกรและนักวิทยาศาสตร์การรถไฟเพนซิลวาเนีย. จุดประสงค์คือเพื่อแก้ไขและป้องกันการแตกหักของรางบ่อยครั้งซึ่งสร้างปัญหาให้กับอุตสาหกรรมโดยการพัฒนามาตรฐานที่จะรับรองว่าผลิตภัณฑ์รางคุณภาพสูงขึ้น.
มาตรฐานเหล็กของ ASTM เป็นเครื่องมือในการจำแนกประเภท, กำลังประเมิน, และระบุวัสดุ, เคมี, เครื่องกล, และสมบัติทางโลหะวิทยาของเหล็กชนิดต่างๆ, ซึ่งใช้ในการผลิตชิ้นส่วนเครื่องจักรกลเป็นหลัก, ชิ้นส่วนอุตสาหกรรม, และองค์ประกอบการก่อสร้าง, รวมถึงอุปกรณ์เสริมอื่น ๆ ที่เกี่ยวข้อง.
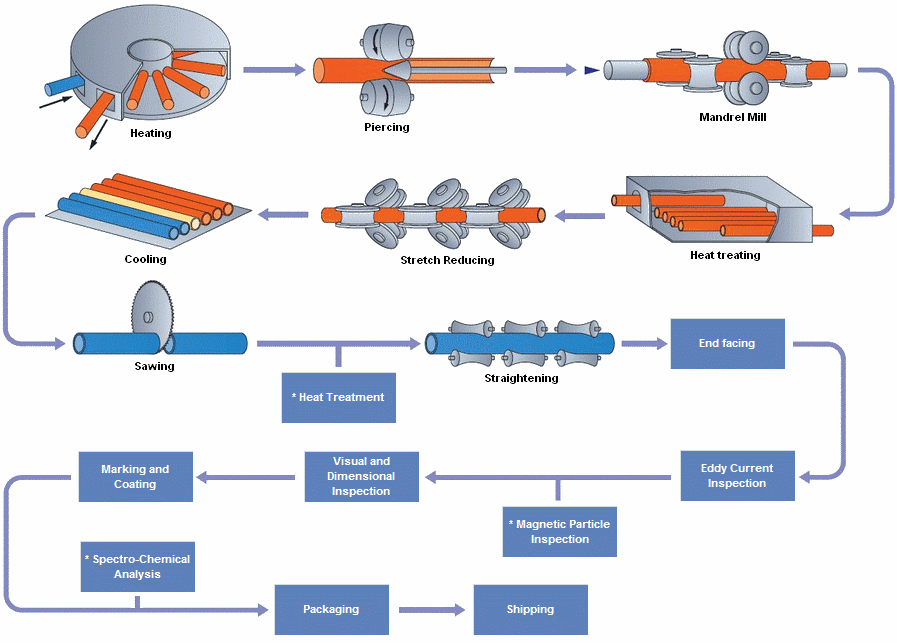
ท่อเป็นส่วนที่เป็นท่อหรือทรงกระบอกกลวง, โดยปกติแต่ไม่จำเป็นต้องมีหน้าตัดเป็นวงกลม, ใช้เพื่อลำเลียงสารที่สามารถไหลได้เป็นหลัก ทั้งของเหลวและก๊าซ (ของเหลว), สารละลาย, ผง, มวลของของแข็งขนาดเล็ก. นอกจากนี้ยังสามารถใช้สำหรับงานโครงสร้างได้อีกด้วย; ท่อกลวงมีความแข็งต่อหน่วยน้ำหนักมากกว่าชิ้นส่วนที่เป็นของแข็ง.
มาตรฐานเหล็กเหล่านี้มีประโยชน์ในการชี้แนะห้องปฏิบัติการและโรงกลั่นโลหะวิทยา, ผู้ผลิตผลิตภัณฑ์, และผู้ใช้เหล็กรายอื่นและตัวเลือกต่างๆ ในขั้นตอนการประมวลผลและการใช้งานที่เหมาะสมเพื่อให้มั่นใจในคุณภาพต่อการใช้งานอย่างปลอดภัย.
คำย่อ. การประยุกต์ใช้ที่สอดคล้องกัน
ข้อกำหนด A53 ASTM A53/A53m-99b สำหรับท่อ, เหล็ก, สีดำและจุ่มร้อน, เคลือบสังกะสี, เชื่อมและไร้รอยต่อ
ข้อกำหนด A74 ASTM A74-98 สำหรับท่อและอุปกรณ์ดินเหล็กหล่อ
ข้อกำหนด A106 ASTM A106-99e1 สำหรับท่อเหล็กคาร์บอนไม่มีรอยต่อสำหรับการให้บริการที่อุณหภูมิสูง
ข้อกำหนด A126 ASTM A126-95e1 สำหรับการหล่อเหล็กสีเทาสำหรับวาล์ว, หน้าแปลน, และอุปกรณ์ท่อ
ข้อกำหนด A134 ASTM A134-96 สำหรับท่อ, เหล็ก, ไฟฟ้าฟิวชั่น (ส่วนโค้ง)-รอย (ขนาด nps 16 และมากกว่า
ข้อกำหนด A135 ASTM A135-97c สำหรับท่อเหล็กเชื่อมต้านทานไฟฟ้า
ข้อกำหนด A139 ASTM A139-96e1 สำหรับฟิวชั่นไฟฟ้า (ส่วนโค้ง)-ท่อเหล็กเชื่อม (nps 4 และมากกว่า)
ข้อกำหนด A182 ASTM A182 / A182m-99 สำหรับหน้าแปลนท่อโลหะผสมเหล็กหลอมหรือรีด, อุปกรณ์ปลอมแปลง, และวาล์วและชิ้นส่วนสำหรับการบริการที่อุณหภูมิสูง
ข้อกำหนด A252 ASTM A252-98 สำหรับเสาเข็มท่อเหล็กเชื่อมและไร้ตะเข็บ
A312 ASTM A312/a312m-00 ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อสเตนเลสออสเทนนิติกแบบไม่มีรอยต่อและแบบเชื่อม
ข้อกำหนด A333 ASTM A333/A333m-99 สำหรับท่อเหล็กไร้รอยต่อและรอยสำหรับบริการที่อุณหภูมิต่ำ
ข้อกำหนด A335 ASTM A335/A335m-99 สำหรับท่อเหล็กโลหะผสมเฟอร์ริติกไร้ตะเข็บสำหรับบริการที่อุณหภูมิสูง
A338 ASTM A338-84(1998) ข้อกำหนดสำหรับหน้าแปลนเหล็กอ่อน, อุปกรณ์ท่อ, และชิ้นส่วนวาล์วสำหรับรางรถไฟ, ทะเล, และบริการงานหนักอื่นๆ ที่อุณหภูมิสูงถึง 650°f (345องศาเซลเซียส)
ข้อกำหนด A358 ASTM A358 / A358m-98 สำหรับท่อเหล็กโลหะผสมออสเทนนิติกโครเมียม - นิกเกิลเชื่อมด้วยไฟฟ้าฟิวชั่นสำหรับการบริการที่อุณหภูมิสูง
ข้อกำหนด A369 ASTM A369/A369m-92 สำหรับท่อหลอมและเจาะเหล็กโลหะผสมคาร์บอนและเฟอร์ริติกสำหรับการให้บริการที่อุณหภูมิสูง
ข้อกำหนด A376 A376/A376m-98 สำหรับท่อเหล็กออสเทนนิติกไร้ตะเข็บสำหรับบริการสถานีกลางที่อุณหภูมิสูง
ดัชนีข้อกำหนด A377 ASTM A377-99 สำหรับท่อแรงดันเหล็กดัด
ข้อกำหนด A409 ASTM A409/A409m-95ae1 สำหรับท่อเหล็กออสเทนนิติกเส้นผ่านศูนย์กลางขนาดใหญ่แบบเชื่อมสำหรับบริการที่มีฤทธิ์กัดกร่อนหรืออุณหภูมิสูง
A426 ASTM A426-92(1997) ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อเหล็กโลหะผสมเฟอร์ริติกหล่อแบบแรงเหวี่ยงสำหรับการบริการที่อุณหภูมิสูง
A451 ASTM A451-93(1997) ข้อกำหนดเฉพาะสำหรับท่อเหล็กออสเทนนิติกหล่อแบบหมุนเหวี่ยงสำหรับงานที่อุณหภูมิสูง
ข้อกำหนด A523 ASTM A523-96 สำหรับท่อเหล็กไร้รอยต่อปลายเรียบและเชื่อมด้วยความต้านทานไฟฟ้าสำหรับวงจรสายเคเบิลชนิดท่อแรงดันสูง
ข้อกำหนด A524 ASTM A524-96 สำหรับท่อเหล็กคาร์บอนไร้ตะเข็บสำหรับอุณหภูมิบรรยากาศและอุณหภูมิต่ำกว่า
ข้อกำหนด A530 ASTM A530/A530m-99 สำหรับข้อกำหนดทั่วไปสำหรับท่อเหล็กคาร์บอนและโลหะผสมเฉพาะ
ข้อกำหนด A648 ASTM A648-95e1 สำหรับลวดเหล็ก, ดึงยากสำหรับท่อคอนกรีตอัดแรง
แนวปฏิบัติ A674 ASTM A674-95 สำหรับการห่อหุ้มโพลีเอทิลีนสำหรับท่อเหล็กดัดสำหรับน้ำหรือของเหลวอื่น ๆ
ข้อกำหนด A691 ASTM A691-98 สำหรับท่อเหล็กคาร์บอนและโลหะผสม, เชื่อมด้วยไฟฟ้าฟิวชั่นสำหรับการให้บริการแรงดันสูงที่อุณหภูมิสูง
A694 ASTM A694/A694m-00 ข้อกำหนดสำหรับการตีขึ้นรูปเหล็กกล้าคาร์บอนและโลหะผสมสำหรับหน้าแปลนท่อ, ฟิตติ้ง, วาล์ว, และอะไหล่สำหรับบริการส่งแรงดันสูง
ข้อกำหนด A716 ASTM A716-99 สำหรับท่อระบายน้ำเหล็กดัด
ข้อกำหนด A733 ASTM A733-99 สำหรับหัวนมท่อเหล็กสแตนเลสออสเทนนิติกแบบเชื่อมและไร้รอยต่อ
ข้อกำหนด A742 ASTM A742/A742m-98 สำหรับเหล็กแผ่น, เคลือบโลหะและเคลือบโพลีเมอร์สำหรับท่อเหล็กลูกฟูก
ข้อกำหนด A746 ASTM A746-99 สำหรับท่อระบายน้ำทิ้งด้วยแรงโน้มถ่วงของเหล็กดัด
ข้อกำหนด A760 ASTM A760/A760m-99 สำหรับท่อเหล็กลูกฟูก, เคลือบโลหะสำหรับท่อระบายน้ำและท่อระบายน้ำ
ข้อกำหนด a761 ASTM A761/A761m-98 สำหรับแผ่นโครงสร้างเหล็กลูกฟูก, เคลือบสังกะสี, สำหรับท่อแบบเกลียวสนาม, ท่อโค้ง, และส่วนโค้ง
ข้อกำหนด A762 ASTM A762/A762m-98 สำหรับท่อเหล็กลูกฟูก, โพลีเมอร์เคลือบล่วงหน้าสำหรับท่อระบายน้ำและท่อระบายน้ำ
ข้อกำหนด A790 ASTM A790/A790m-99 สำหรับท่อสเตนเลสเฟอร์ริติก/ออสเทนนิติกแบบไม่มีรอยต่อและแบบเชื่อม
A796 ASTM A796/A796m-99 แนวปฏิบัติสำหรับการออกแบบโครงสร้างของท่อเหล็กลูกฟูก, ท่อโค้ง, และส่วนโค้งสำหรับท่อระบายน้ำพายุและสุขาภิบาลและงานฝังอื่น ๆ
A798 ASTM A798/A798m-97a แนวปฏิบัติสำหรับการติดตั้งท่อเหล็กลูกฟูกที่ผลิตจากโรงงานสำหรับท่อระบายน้ำทิ้งและการใช้งานอื่น ๆ
A807 ASTM A807/A807m-97 การฝึกปฏิบัติสำหรับการติดตั้งท่อแผ่นโครงสร้างเหล็กลูกฟูกสำหรับท่อระบายน้ำทิ้งและการใช้งานอื่น ๆ
ข้อกำหนด A810 ASTM A810-94 สำหรับการเคลือบสังกะสี (ชุบสังกะสี) ตาข่ายม้วนท่อเหล็ก
ข้อกำหนด A813 ASTM A813/A813m-95e2 สำหรับเดี่ยว- หรือท่อสเตนเลสออสเทนนิติกเชื่อมสองชั้น
A814 ASTM A814/A814m-96 (1998) ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อสเตนเลสออสเทนนิติกเชื่อมงานเย็น
ข้อกำหนด A849 ASTM A849-99 สำหรับการเคลือบภายหลังการใช้งาน, ปู, และบุผิวท่อน้ำทิ้งและท่อระบายน้ำเหล็กลูกฟูก
ข้อกำหนด A861 ASTM A861-94e1 สำหรับท่อเหล็กและข้อต่อซิลิคอนสูง
แนวปฏิบัติ A862 ASTM A862/A862m-98 สำหรับการเคลือบแอสฟัลต์กับท่อระบายน้ำและท่อระบายน้ำเหล็กลูกฟูก
ข้อกำหนด A865 ASTM A865-97 สำหรับข้อต่อแบบเกลียว, เหล็ก, สีดำหรือเคลือบสังกะสี (ชุบสังกะสี) เชื่อมหรือไร้รอยต่อ, เพื่อใช้ในข้อต่อท่อเหล็ก
A872 ASTM A872-91 (1997) ข้อกำหนดเฉพาะสำหรับท่อสเตนเลสเฟอร์ริติก/ออสเทนนิติกหล่อแบบเหวี่ยงเหวี่ยงสำหรับสภาพแวดล้อมที่มีฤทธิ์กัดกร่อน
ข้อกำหนด A885 ASTM A885/A885m-96 สำหรับเหล็กแผ่น, เคลือบคอมโพสิตสังกะสีและเส้นใยอะรามิดสำหรับท่อระบายน้ำเหล็กลูกฟูก, ท่อระบายน้ำ, และท่อระบายใต้
ข้อกำหนด A888 ASTM A888-98e1 สำหรับท่อดินเหล็กหล่อไร้ฮับและอุปกรณ์สำหรับท่อระบายน้ำสุขาภิบาลและพายุ, ของเสีย, และการใช้งานท่อระบายอากาศ
วิธีทดสอบ A926 ASTM A926-97 สำหรับเปรียบเทียบความต้านทานการขัดถูของวัสดุเคลือบสำหรับท่อโลหะลูกฟูก
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ A928 ASTM A928/A928m-98 สำหรับเฟอร์ริติก/ออสเทนนิติก (ดูเพล็กซ์) ท่อเหล็กสแตนเลสเชื่อมไฟฟ้าฟิวชั่นด้วยการเติมโลหะฟิลเลอร์
ข้อกำหนด A929 ASTM A929/A929m-97 สำหรับเหล็กแผ่น, เคลือบโลหะด้วยกรรมวิธีจุ่มร้อนสำหรับท่อเหล็กลูกฟูก
แนวปฏิบัติ A930 ASTM A930-99 สำหรับการวิเคราะห์ต้นทุนวงจรชีวิตของท่อโลหะลูกฟูกที่ใช้สำหรับท่อระบายน้ำ, ท่อระบายน้ำพายุ, และท่อร้อยสายฝังอื่นๆ
ข้อกำหนด A943 ASTM A943/A943m-95e1 สำหรับท่อสเตนเลสออสเทนนิติกไร้ตะเข็บที่ขึ้นรูปด้วยสเปรย์
ข้อกำหนด A949 ASTM A949/A949m-95e1 สำหรับท่อสเตนเลสเฟอร์ริติก/ออสเตนิติกไร้ตะเข็บขึ้นรูปด้วยสเปรย์
ข้อกำหนด A954 ASTM A954-96 สำหรับท่อเหล็กไร้รอยต่อและรอยเชื่อมออสเทนนิติกโครเมียม - นิกเกิล - ซิลิคอน
ข้อกำหนด A972 ASTM A972/A972m-99 สำหรับกองท่อเคลือบอีพ็อกซี่เคลือบฟิวชั่นบอนด์
ข้อกำหนด A978 ASTM A978/A978m-97 สำหรับท่อเหล็กซี่โครงคอมโพสิต, เคลือบล่วงหน้าและโพลีเอทิลีนเรียงรายสำหรับท่อระบายน้ำทิ้งสุขาภิบาลตามแรงโน้มถ่วง, ท่อระบายน้ำพายุ, และการใช้งานพิเศษอื่น ๆ
A984 ASTM A984/A984m-00 ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อเหล็กเส้น, สีดำ, ธรรมดา-end, เชื่อมความต้านทานไฟฟ้า
แนวปฏิบัติ A998 ASTM A998/A998m-98 สำหรับการออกแบบโครงสร้างของการเสริมแรงสำหรับอุปกรณ์ในท่อเหล็กลูกฟูกที่ผลิตจากโรงงานสำหรับท่อระบายน้ำทิ้งและการใช้งานอื่น ๆ
ข้อกำหนด A999 A999/A999m-98 สำหรับข้อกำหนดทั่วไปสำหรับท่อโลหะผสมและสแตนเลส
A1005 ASTM A1005/A1005m-00 ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อเหล็กเส้น, สีดำ, ปลายธรรมดา, ตะเข็บตามยาวและเกลียว, รอยเชื่อมแบบจมอยู่ใต้น้ำคู่
ข้อกำหนด A1006 ASTM A1006/A1006m สำหรับท่อเหล็กเส้น, สีดำ, ปลายธรรมดา, เชื่อมลำแสงเลเซอร์
ท่อเหล็ก
ซุปเปอร์ฮีตเตอร์, หม้อต้มและท่อเบ็ดเตล็ด:
- A178 – A178/A178M-95 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับหม้อต้มเหล็กกล้าคาร์บอนต้านทานไฟฟ้าและหม้อต้มเหล็กคาร์บอน-แมงกานีสและท่อฮีตเตอร์ฮีตเตอร์
- A179 – A179/A179M-90a (1996) e1 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อแลกเปลี่ยนความร้อนและคอนเดนเซอร์เหล็กกล้าคาร์บอนต่ำดึงเย็นแบบไม่มีรอยต่อ
- A192 – A192/A192M-91 (1996) e1 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อหม้อต้มเหล็กกล้าคาร์บอนไร้ตะเข็บสำหรับบริการแรงดันสูง
- A209 – A209/A209M-98 – ข้อมูลจำเพาะสำหรับหม้อไอน้ำโลหะผสมคาร์บอน - โมลิบดีนัม - เหล็กกล้าและท่อฮีตเตอร์ฮีตเตอร์แบบไม่มีรอยต่อ
- A210 – A210/A210M-96 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับหม้อต้มเหล็กกล้าคาร์บอนปานกลางแบบไม่มีรอยต่อและท่อฮีทเตอร์ฮีทเตอร์
- A213 – A213/A213M-99a – ข้อมูลจำเพาะสำหรับหม้อไอน้ำเหล็กโลหะผสมเฟอริติกและออสเทนนิติกไร้รอยต่อ, ซุปเปอร์ฮีตเตอร์, และท่อแลกเปลี่ยนความร้อน
- A249 – A249/A249M-98e1 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับหม้อต้มเหล็กออสเทนนิติกแบบเชื่อม, ซุปเปอร์ฮีตเตอร์, เครื่องแลกเปลี่ยนความร้อน, และท่อคอนเดนเซอร์
- A250 – A250/A250M-95 – ข้อมูลจำเพาะสำหรับหม้อไอน้ำและท่อซุปเปอร์ฮีตเตอร์เชื่อมโลหะผสมเฟอริติกต้านทานไฟฟ้า
- A254 – A254-97 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อเหล็กทองแดงประสาน
- A268 – A268/A268M-96 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อเหล็กกล้าไร้สนิมเฟอริติกและมาร์เทนซิติกแบบไม่มีรอยต่อและแบบเชื่อมสำหรับบริการทั่วไป
- A269 – A269-98 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อเหล็กกล้าไร้สนิมออสเทนนิติกแบบไม่มีรอยต่อและแบบเชื่อมสำหรับบริการทั่วไป
- เอ270 – A270-98ae1 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อสุขาภิบาลสเตนเลสออสเทนนิติกแบบไม่มีรอยต่อและแบบเชื่อม
- A334 – A334/A334M-99 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อคาร์บอนและโลหะผสมเหล็กไร้รอยต่อและแบบเชื่อมสำหรับบริการที่อุณหภูมิต่ำ
- A423 – A423/A423M-95 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อเหล็กโลหะผสมต่ำแบบไม่มีรอยต่อและเชื่อมด้วยไฟฟ้า
- A450 – A450/A450M-96a – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับข้อกำหนดทั่วไปสำหรับคาร์บอน, โลหะผสมเฟอริติก, และท่อเหล็กโลหะผสมออสเทนนิติก
- A608 – A608-91a (1998) – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อโลหะผสมสูงเหล็กหล่อ - โครเมียม - นิกเกิลแบบแรงเหวี่ยงสำหรับการใช้งานแรงดันที่อุณหภูมิสูง
- A618 – A618-99 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อโครงสร้างโลหะผสมต่ำที่มีความแข็งแรงสูงแบบเชื่อมขึ้นรูปร้อนและไร้รอยต่อ
- A632 – A632-98 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อเหล็กกล้าไร้สนิมออสเทนนิติกแบบไม่มีรอยต่อและแบบเชื่อม (เส้นผ่านศูนย์กลางเล็ก) สำหรับบริการทั่วไป
- A688 – A688/A688M-98 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อฮีตเตอร์น้ำป้อนเหล็กกล้าไร้สนิมออสเทนนิติกแบบเชื่อม
- เอ771 – A771/A771M-95 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อสเตนเลสออสเตนนิติกและมาร์เทนซิติกแบบไม่มีรอยต่อสำหรับส่วนประกอบแกนเครื่องปฏิกรณ์ระบายความร้อนด้วยโลหะเหลว
- เอ778 – เอ778-98 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับการเชื่อม, ผลิตภัณฑ์ท่อเหล็กกล้าไร้สนิมออสเทนนิติกที่ไม่มีการอบชุบ
- เอ789 – A789/A789M-00 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อเหล็กกล้าไร้สนิมเฟอริติก / ออสเตนิติกแบบไม่มีรอยต่อและแบบเชื่อมสำหรับบริการทั่วไป
- A803 – A803/A803M-98 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อฮีตเตอร์น้ำป้อนสแตนเลสเฟอริติกแบบเชื่อม
- A822 – A822-90 (1995) e1 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อเหล็กคาร์บอนดึงเย็นแบบไม่มีรอยต่อสำหรับบริการระบบไฮดรอลิก
- A826 – A826/A826M-95 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อท่อเหล็กกล้าไร้สนิมออสเทนนิติกและมาร์เทนซิติกแบบไม่มีรอยต่อสำหรับส่วนประกอบแกนเครื่องปฏิกรณ์ระบายความร้อนด้วยโลหะเหลว
- A847 – A847-99a – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับความแข็งแรงสูงแบบเชื่อมขึ้นรูปเย็นและไร้รอยต่อ, ท่อโครงสร้างโลหะผสมต่ำพร้อมความต้านทานการกัดกร่อนในบรรยากาศที่ดีขึ้น
- A908 – A908-91 (1998) – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อเข็มสแตนเลส
- A953 – A953-96 – ข้อกำหนดสำหรับท่อเหล็กไร้รอยต่อและรอยเชื่อมโลหะผสมโครเมียม - นิกเกิล - ซิลิคอนออสเทนนิติก –